Abstract
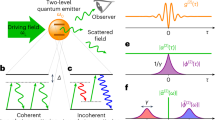
Emission from a resonantly excited quantum emitter is a fascinating research topic within the field of quantum optics and is a useful source for different types of quantum light fields. The resonance spectrum consists of a single spectral line that develops into a triplet above saturation of the quantum emitter1,2,3. The three closely spaced photon channels from the resonance fluorescence have different photon statistical signatures4. We present a detailed photon statistics analysis of the resonance fluorescence emission triplet from a solid-state-based artificial atom, that is, a semiconductor quantum dot. The photon correlation measurements demonstrate both ‘single’ and ‘cascaded’ photon emission from the Mollow triplet sidebands5. The bright and narrow sideband emission (5.9 × 106 photons per second into the first lens) can be conveniently frequency-tuned by laser detuning over 15 times its linewidth (Δv ≈ 1.0 GHz). These unique properties make the Mollow triplet sideband emission a valuable light source for quantum light spectroscopy and quantum information applications, for example.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mollow, B. R. Power spectrum of light scattered by two-level systems. Phys. Rev. 188, 1969–1975 (1969).
Flagg, E. B. et al. Resonantly driven coherent oscillations in a solid-state quantum emitter. Nature Phys. 5, 203–207 (2009).
Vamivakas, A. N., Zhong, Y., Yong, C-Y. & Atatüre, M. Spin-resolved quantum-dot resonance fluorescence. Nature Phys. 5, 198–202 (2009).
Nienhuis, G. Spectral correlations in resonance fluorescence. Phys. Rev. A 47, 510–518 (1993).
Schrama, A., Nienhuis, G., Dijkerman, H. A., Steijsiger, C. & Heideman, H. G. Intensity correlations between the components of the resonance fluorescence triplet. Phys. Rev. A 45, 8045–8055 (1992).
Aspect, A., Roger, G., Reynaud, S., Dalibard, J. & Cohen-Tannoudji, C. Time Correlations between the two sidebands of the resonance fluorescence triplet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 617–620 (1980).
Thompson, J. K., Simon, J., Huanquian, L. & Vuletić, V. A high-brightness source of narrowband, identical-photon pairs. Science 313, 74–77 (2006).
Michler, P. et al. A quantum dot single-photon turnstile device. Science 290, 2282–2285 (2000).
Stevenson, R. M. et al. A semiconductor source of triggered entangled photon pairs. Nature 439, 179–182 (2006).
Akopian, N. et al. Entangled photon pairs from semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 130501 (2006).
Moreau, E. et al. Quantum cascade of photons in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 183601 (2001).
Kiraz, A., Atatüre, M. & Imamoğlu, A. Quantum-dot single-photon sources: Prospects for applications in linear optics quantum-information processing. Phys. Rev. A 69, 032305 (2004).
Kamada H, et al. Exciton Rabi oscillation in a single quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 246401 (2001).
Zrenner, A. et al. Coherent properties of a two-level system based on a quantum-dot photodiode. Nature 418, 612–614 (2002).
Xu, X. et al. Coherent optical spectroscopy of a strongly driven quantum dot. Science 317, 929–932 (2007).
Jundt, G., Robledo, L., Högele, A., Fält, S. & Imamoğlu, A. Observation of dressed excitonic states in a single quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 177401 (2008).
Muller, A. et al. Resonance fluorescence from a coherently driven semiconductor quantum dot in a cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 187402 (2007).
Ates, S. et al. Post-selected indistinguishable photons from the resonance fluorescence of a single quantum dot in a microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 167402 (2009).
Muller, A., Fang, W., Lawall, J. & Solomon, G. S. Creating polarization-entangled photon pairs from a semiconductor quantum dot using the optical Stark effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 217402 (2009).
Ulrich, S. M. et al. Dephasing of Mollow triplet sideband emission of a resonantly driven quantum dot in a microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 247403 (2011).
Roy, C. & Hughes, S. Phonon-dressed Mollow triplet in the regime of cavity-QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 247402 (2011).
Cohen-Tannoudji, C., Dupont-Roc, J. & Grynberg, G. Atom–Photon Interactions (Wiley-VCH, 2004).
Aichele, T., Reinaudi, G. & Benson, O. Seperating cascaded photons from a single quantum dot: demonstration of multiplexed quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. B 70, 235329 (2004).
Claudon, J. et al. A highly efficient single-photon source based on a quantum dot in a photonic nanowire. Nature Photon. 4, 174–177 (2010).
Santori, C., Pelton, M., Salamo, G., Dale, Y. & Yamamoto, Y. Triggered single photons from a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1502–1505 (2001).
Bayer, M. et al. Fine structure of neutral and charged excitons in self-assembled In(Ga)As/(Al)GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 65, 195315 (2002).
Akopian, N., Wang, L., Rastelli, A., Schmidt O. G. & Zwiller, V. Hybrid semiconductor–atomic interface: slowing down single photons from a quantum dot. Nature Photon 5, 230–233 (2011).
Gisin, N. & Thew, R. Quantum communication. Nature Photon. 1, 165–171 (2007).
Freedhoff, H. & Quang, T. Ultrasharp lines in the absorption and fluorescence spectra of an atom in a cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 474–477 (1994).
Quang, T. & Freedhoff, H. Atomic population inversion and enhancement of resonance fluorescence in a cavity. Phys. Rev. A 47, 2285–2292 (1993).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge D. Richter and W-M. Schulz for providing high-quality samples and M. Wiesner for help in sample processing. We also appreciate a fruitful discussion with S. Hughes. The authors acknowledge financial support from the Deutsche Forschungs-gemeinschaft (research group 730). A.U. acknowledges funding from the International Max Planck Research School for Advanced Materials. S.W. acknowledges financial support from the Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.R. and M.J. designed the sample structure. A.U., S.W., S.M.U. and P.M. conceived the experiments. A.U., S.W. and S.M.U. performed the experiments and analysed the data. A.U., S.W., S.M.U. and P.M. wrote the manuscript, with input from the other authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 397 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulhaq, A., Weiler, S., Ulrich, S. et al. Cascaded single-photon emission from the Mollow triplet sidebands of a quantum dot. Nature Photon 6, 238–242 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.23
This article is cited by
-
Entanglement in Resonance Fluorescence
npj Nanophotonics (2024)
-
Dynamic resonance fluorescence in solid-state cavity quantum electrodynamics
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
On the simultaneous scattering of two photons by a single two-level atom
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Ultra-low loss quantum photonic circuits integrated with single quantum emitters
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Optically driving the radiative Auger transition
Nature Communications (2021)