Abstract
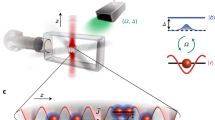
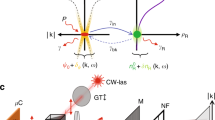
Microcavity polaritons are composite half-light half-matter quasiparticles, which have recently been demonstrated to exhibit rich physical properties, such as non-equilibrium condensation, parametric scattering and superfluidity. At the same time, polaritons have important advantages over photons for information processing, because their excitonic component leads to weaker diffraction and stronger interparticle interactions, implying, respectively, tighter localization and lower powers for nonlinear functionality. Here, we present the first experimental observations of bright polariton solitons in a strongly coupled semiconductor microcavity. The polariton solitons are shown to be micrometre-scale localized non-diffracting wave packets with a corresponding broad spectrum in momentum space. Unlike the solitons known in Bose condensed atomic gases, they are non-equilibrium and rely on a balance between losses and external pumping. Microcavity polariton solitons are excited on picosecond timescales, and thus have further benefits for information processing over light-only solitons in semiconductor cavity lasers, which have nanosecond response times.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 November 2011
The title of this Article originally published online was incorrect. This error has been corrected for all versions of the Article.
References
Mollenauer, L. F., Stolen, R. H. & Gordon, J. P. Experimental observation of picosecond pulse narrowing and solitons in optical fibers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1095–1098 (1980).
Kivshar, Y. & Agrawal, G. Optical Solitons: From Fibres to Photonic Crystals (Academic Press, 2001).
Skryabin, D. V. & Gorbach, A. V. Colloquium: looking at a soliton through the prism of optical supercontinuum. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1287–1299 (2010).
Aitchison, J. S. et al. Spatial optical solitons in planar glass waveguides. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8, 1290–1297 (1991).
Askaryan, G. A. Effects of the gradient of a strong electromagnetic beam on electrons and atoms. Sov. Phys. JETP 15, 1088–1090 (1962).
Khaykovich, L. et al. Formation of a matter-wave bright soliton. Science 296, 1290–1293 (2002).
Strecker, K. E., Partridge, G. B., Truscott, A. G. & Hulet, R. G. Formation and propagation of matter-wave soliton trains. Nature 417, 150–153 (2002).
Eiermann, B. et al. Bright Bose–Einstein gap solitons of atoms with repulsive interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 230401 (2004).
Fleischer, J. W., Segev, M., Efremidis, N. K. & Christodoulides, D. N. Observation of two-dimensional discrete solitons in optically induced nonlinear photonic lattices. Nature 422, 147–150 (2003).
Kavokin, A., Baumberg, J. J., Malpuech, G. & Laussy, F. P. Microcavities, Semiconductor Science and Technology (Oxford Univ. Press, 2007).
Gibbs, H. M., Khitrova, G. & Koch, S. W. Exciton–polariton light–semiconductor coupling effects. Nature Photon. 5, 275–282 (2011).
Kasprzak, J. et al. Bose–Einstein condensation of exciton polaritons. Nature Phys. 443, 409–414 (2006).
Balili, R., Hartwell, V., Snoke, D., Pfeiffer, L. & West, K. Bose–Einstein condensation of microcavity polaritons in a trap. Science 316, 1007–1010 (2007).
Lagoudakis, K. G. et al. Quantized vortices in an exciton–polariton condensate. Nature Phys. 4, 706–710 (2008).
Lagoudakis, K. G. et al. Observation of half-quantum vortices in an exciton–polariton condensate. Science 326, 974–976 (2009).
Amo, A. et al. Superfluidity of polaritons in semiconductor microcavities. Nature Phys. 5, 805–810 (2009).
Gippius, N. A., Tikhodeev, S. G., Kulakovskii, V. D., Krizhanovskii, D. N. & Tartakovskii, A. I. Nonlinear dynamics of polariton scattering in semiconductor microcavity: bistability vs stimulated scattering. Europhys. Lett. 67, 997–1003 (2004).
Amo, A. et al. Exciton–polariton spin switches. Nature Photon. 4, 361–366 (2010).
Sarkar, D. et al. Polarization bistability and resultant spin rings in semiconductor microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 216402 (2010).
Paraiso, T. K., Wouters, M., Leger, Y., Morier-Genoud, F. & Deveaud-Pledran, B. Multi-stability of a coherent spin ensemble in a semiconductor microcavity. Nature Mater. 9, 655–660 (2010).
Savvidis, P. G. et al. Angle-resonant stimulated polariton amplifier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1547–1550 (2000).
Akhmediev, N. & Ankiewicz-Kik, A. (eds) Dissipative Solitons (Springer, 2005).
Ackemann, T., Firth, W. J. & Oppo, G.-L. in Advances in Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 57 (eds Arimondo, E., Berman, P. R. & Lin, C. C.) Ch. 6, 323–421 (Academic Press, 2009).
Rosanov, N. N., Fedorov, S. V., Khadzi, P. I. & Belousov, I. V. Dissipative solitons of the Bose–Einstein condensate of excitons. JETP Lett. 85, 426–428 (2007).
Egorov, O. A., Skryabin, D. V., Yulin, A. V. & Lederer, F. Bright cavity polariton solitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 153904 (2009).
Egorov, O. A., Gorbach, A. V., Lederer, F. & Skryabin, D. V. Two-dimensional localization of exciton polaritons in microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 073903 (2010).
Fleischhauer, M. & Lukin, M. D. Dark-state polaritons in electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5094–5097 (2000).
Saffman, M. & Skryabin, D. in Spatial Solitons (eds Trillo, S. & Torruellas, W.) (Springer, 2001).
Skryabin, D. V. Energy of the soliton internal modes and broken symmetries in nonlinear optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19, 529–536 (2002).
Carusotto, I. & Ciuti, C. Probing microcavity polariton superfluidity through resonant Rayleigh scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 166401 (2004).
Krizhanovskii, D. N. et al. Self-organization of multiple polariton–polariton scattering in semiconductor microcavities. Phys. Rev. B 77, 115336 (2008).
Amo, A. et al. Collective fluid dynamics of a polariton condensate in a semiconductor microcavity. Nature 457, 291–296 (2009).
Krizhanovskii, D. N. et al. Rotation of the plane of polarization of light in a semiconductor microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 73, 073303 (2006).
Barland, S. et al. Cavity solitons as pixels in semiconductor microcavities. Nature 419, 699–702 (2002).
Pedaci, F. et al. All-optical delay line using semiconductor cavity solitons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 011101 (2008).
Liew, T. C. H., Kavokin, A. V. & Shelykh, I. A. Optical circuits based on polariton neurons in semiconductor microcavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 016402 (2008).
Christmann, G. et al. Room temperature polariton lasing in a GaN–AlGaN multiple quantum well microcavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 051102 (2008).
Tsintzos, S. I. et al. Room temperature GaAs exciton–polariton light emitting diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 071109 (2009).
Amo, A. et al. Polariton superfluids reveal quantum hydrodynamic solitons. Science 332, 1167–1170 (2011).
Liew, T. C. H., Kavokin, A. V. & Shelykh, I. A. Excitation of vortices in semiconductor microcavities. Phys. Rev. B 75, 241301 (2007).
Acknowledgements
The Sheffield group thanks EPSRC (EP/G001642, EP/H023259, EP/E051448), the FP7 ITN Clermont 4 and the Royal Society for support of this work, and A. Amo for a helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors prepared the manuscript and analysed the experimental and numerical data. M.S. and D.N.K. conducted the experimental measurements. A.V.G., R.H. and D.V.S. conducted the theoretical and numerical work. D.V.S. proposed the concept. K.B. and R.H. fabricated the microcavity.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 323 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sich, M., Krizhanovskii, D., Skolnick, M. et al. Observation of bright polariton solitons in a semiconductor microcavity. Nature Photon 6, 50–55 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.267
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.267
This article is cited by
-
Ultrafast imaging of polariton propagation and interactions
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Halide perovskites enable polaritonic XY spin Hamiltonian at room temperature
Nature Materials (2022)
-
Polariton condensates for classical and quantum computing
Nature Reviews Physics (2022)
-
Room-temperature polariton quantum fluids in halide perovskites
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Ultrafast-nonlinear ultraviolet pulse modulation in an AlInGaN polariton waveguide operating up to room temperature
Nature Communications (2021)