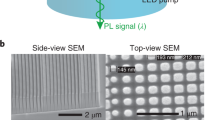
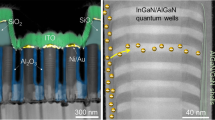
Abstract
Single-crystalline GaN-based light-emitting diodes (s-LEDs) on crystalline sapphire wafers can provide point-like light sources with high conversion efficiency and long working lifetimes. Recently, s-LEDs on silicon wafers have been developed in efforts to overcome the size limitations of the sapphire substrate. However, to create larger, cheaper and efficient flat light sources, the fabrication of high-performance s-LEDs on amorphous glass substrates would be required, which remains a scientific challenge. Here, we report the fabrication of nearly single-crystalline GaN on amorphous glass substrates, in the form of pyramid arrays. This is achieved by high-temperature, predominant GaN growth on a site-confined nucleation layer with preferential polycrystalline morphology through local hetero-epitaxy. InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum wells formed on the GaN pyramid arrays exhibit a high internal quantum efficiency of 52%. LED arrays fabricated using these GaN pyramid arrays demonstrate reliable and stable area-type electroluminescent emission with a luminance of 600 cd m−2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakamura, S., Iwasa, N., Senoh, M. & Mukai, T. Hole compensation mechanism of p-type GaN films. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 31, 1258–1266 (1992).
Nakamura, S., Mukai, T. & Senoh, M. Candela-class high-brightness InGaN/AlGaN double-heterostructure blue-light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 64, 1687–1689 (1994).
Gardner, N. F. et al. Blue-emitting InGaN–GaN double-heterostructure light-emitting diodes reaching maximum quantum efficiency above 200 A/cm2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 243506 (2007).
Wierer, J. J., David, A. & Megens, M. M. III-nitride photonic-crystal light-emitting diodes with high extraction efficiency. Nature Photon. 3, 163–169 (2009).
Shchekin, O. B. et al. High performance thin-film flip-chip InGaN–GaN light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 071109 (2006).
Narukawa, Y. et al. Improvement of luminous efficiency in white light emitting diodes by reducing a forward-bias voltage, Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 46, L963–L965 (2007).
Kim, J. H. & Holloway, P. H. Room-temperature photoluminescence and electroluminescence properties of sputter-grown gallium nitride doped with europium. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 4787–4790 (2004).
Asahi, H. et al. Very strong photoluminescence emission from GaN grown on amorphous silica substrate by gas source MBE. J. Cryst. Growth 201/202, 371–375 (1999).
Bour, D. P. et al. Polycrystalline nitride semiconductor light-emitting diodes fabricated on quartz substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2182–2184 (2000).
Roussel, P. Markets and technology needs for UHB-LEDs. Proc. SPIE 6797, 679703 (2007).
Wildeson, I. H. et al. III-nitride nanopyramid light emitting diodes grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 044303 (2010).
Lin, H. W., Lu, Y. J., Chen, H. Y., Lee, H. M. & Gwo, S. InGaN/GaN nanorod array white light-emitting diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 073101 (2010).
Chen, L. Y., Huang, Y. Y., Chang, C. S. & Huang, J. J. High output power density and low leakage current of InGaN/GaN nanorod light emitting diode with mechanical polishing process. International Conference on Compound Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology (2010), Portland, USA, 251–256 (CS Mantech, 2010).
Kuykendall, T., Ulrich, P., Aloni, S. & Yang, P. Complete composition tunability of InGaN nanowires using a combinatorial approach. Nature Mater. 6, 951–956 (2007).
Lee, C. H. et al. GaN/In1−xGaxN/GaN/ZnO nanoarchitecture light emitting diode microarrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 213101 (2009).
Consonni, V., Knelangen, M., Geelhaar, L., Trampert, A. & Riechert, H. Nucleation mechanisms of epitaxial GaN nanowires: origin of their self-induced formation and initial radius. Phys. Rev. B 81, 085310 (2010).
Consonni, V. et al. Nucleation mechanisms of self-induced GaN nanowires grown on an amorphous interlayer. Phys. Rev. B 83, 035310 (2011).
Kitamura, S., Hiramatsu, K. & Sawaki, N. Fabrication of GaN hexagonal pyramids on dot-patterned GaN/sapphire substrates via selective metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 34, L1184–L1186 (1995).
Sekiguchi, H., Kishino, K. & Kikuchi, A. Ti-mask selective-area growth of GaN by rf-plasma-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy for fabricating regularly arranged InGaN/GaN nanocolumns. Appl. Phys. Exp. 1, 124002 (2008).
Hersee, S. D., Sun, X. & Wang, X. The controlled growth of GaN nanowires. Nano Lett. 6, 1808–1811 (2006).
Tal-Gutelmacher, E., Gemma, R., Pundt, A. & Kirchheim, R. Hydrogen behavior in nanocrystalline titanium thin films. Acta Materialia. 58, 3042–3049 (2010).
Matysina, Z. A. The relative surface energy of hexagonal close-packed crystals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 60, 70–78 (1999).
Da Silva, J. L. F., Stampfl, C. & Scheffler, M. Converged properties of clean metal surfaces by all-electron first-principles calculations. Surf. Sci. 600, 703–715 (2006).
Nakamura, S. In situ monitoring of GaN growth using interference effects. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 30, 1620–1627 (1991).
Liu, C. et al. Variations in mechanisms of selective area growth of GaN on nanopatterned substrates by MOVPE. Phys. Status Solidi C 7, 32–35 (2010).
Tanaka, S., Kawaguchi, Y., Sawaki, N., Hibino, M. & Hiramatsu, K. Defect structure in selective area growth GaN pyramid on (111) Si substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2701–2703 (2000).
Chang, C. I., Lai, Y. L., Liu, C. P. & Wang, R. C. The influence of mask area ratio on GaN regrowth by epitaxial lateral overgrowth. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 420–424 (2008).
Guo, W., Zhang, M., Banerjee, A. & Bhattacharya, P. Catalyst-free InGaN/GaN nanowire light emitting diodes grown on (001) silicon by molecular beam epitaxy. Nano Lett. 10, 3355–3359 (2010).
Miller, D. A. B. et al. Band-edge electroabsorption in quantum well structures: the quantum-confined Stark effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 2173–2176 (1984).
Chichibu, S. F. et al. Origin of defect-insensitive emission probability in In-containing (Al,In,Ga)N alloy semiconductors. Nature Mater. 5, 810–816 (2006).
Miyake, H., Nakao, K. & Hiramatsu, K. Blue emission from InGaN/GaN hexagonal pyramid structures. Superlatt. Microstruct. 41, 341–346 (2007).
Wächter, C. et al. High wavelength tunability of InGaN quantum wells grown on semipolar GaN pyramid facets. Phys. Status Solidi B 248, 605–610 (2011).
Schubert, E. F. Light-Emitting Diodes (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2006).
Wunderer, T. et al. Three-dimensional GaN for semipolar light emitters. Phys. Status Solidi B 248, 549–560 (2011).
Sugiura, L. Dislocation motion in GaN light-emitting devices and its effect on device lifetime. J. Appl. Phys. 81, 1633–1638 (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank K.Y. Park (Sysnex Inc.) and J.M. Zuo (University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign) for fruitful discussions, H.Y. Ahn, E.H. Cho, K.H. Kim, H.K. Kim, J.W. Yoo, J.H. Lee, Y.K. Cha, Y.T. Ryu, J.S. Cho, K.W. Park, S.H. Song, M.J. Shin and S.M. Kim (Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology) and H.B. Yoo (Seoul National University) for technical support. J.M.K. thanks Y.J. Park and C.S. Sone (Samsung LED) for their valuable comments on the manuscript. M.K. acknowledges support from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF no. 2010-0017-609).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.H.C. designed and carried out experiments, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. A.Z. developed the device design and process flow. S.I.K. and C.W.B. optimized the pre-orienting and nucleation layers. M.H.Y. conduced TEM analysis. S.S.P. guided the experimental investigations. H.S. prepared submicrometre hole-patterned templates. U.J.K., H.B.S. and J.S.L. performed the optical measurements, including cathodoluminescence, photoluminescence and electroluminescence. M.K. and J.M.K. guided the theoretical investigations and edited the manuscript. K.K. designed the project. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1783 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Zoulkarneev, A., Kim, S. et al. Nearly single-crystalline GaN light-emitting diodes on amorphous glass substrates. Nature Photon 5, 763–769 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.253
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2011.253
This article is cited by
-
Electrically driven mid-submicrometre pixelation of InGaN micro-light-emitting diode displays for augmented-reality glasses
Nature Photonics (2021)
-
Direct Growth of Single Crystalline GaN Nanowires on Indium Tin Oxide-Coated Silica
Nanoscale Research Letters (2019)
-
Direct Growth of III-Nitride Nanowire-Based Yellow Light-Emitting Diode on Amorphous Quartz Using Thin Ti Interlayer
Nanoscale Research Letters (2018)
-
Latent Order in High-Angle Grain Boundary of GaN
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
A Rapid Method for Deposition of Sn-Doped GaN Thin Films on Glass and Polyethylene Terephthalate Substrates
Journal of Electronic Materials (2018)