Abstract
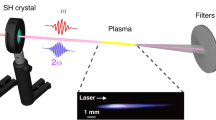
Frequency mixing an ultrafast-pulse laser's fundamental and second-harmonic fields in semiconductors1,2, atomic gases3,4, and on metal surfaces5 generates a directional electrical current for which the magnitude and polarity depend upon the relative phase between these two fields1,2,3,4,5. As this current occurs on the timescale of the duration of the laser pulse, in the case of ultrafast lasers (<100 fs), this process can generate electromagnetic radiation at terahertz frequencies. Although such terahertz generation has been observed in semiconductors6 and air7,8,9,10,11,12,13, the terahertz generation mechanism is not well understood and the terahertz yield has not been optimized. Here, we demonstrate a coherent control scheme to optimize terahertz generation in gases, yielding a new source of high-energy (>5 µJ), super-broadband terahertz radiation (∼75 THz) as well as an enhanced accompanying third harmonic. We also present a unifying explanation for such extremely broad electromagnetic radiation generation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haché, A. et al. Observation of coherently controlled photocurrent in unbiased, bulk GaAs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 306–309 (1997).
Dupont, E., Corkum, P. B., Liu, H. C., Buchanan, M. & Wasilewski, Z. R. Phase-controlled currents in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3596–3599 (1995).
Yin, Y.-Y., Chan, C., Elliott, D. S. & Smith, A. V. Asymmetric photoelectron angular distribution from interfering photoionization processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2353–2356 (1992).
Schumacher, D. W., Weihe, F., Muller, H. G. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Phase dependence of intense field ionization: a study using two colours. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1344–1347 (1994).
Güdde, J., Rohleder, M., Meier, T., Koch, S. W. & Höfer, U. Time-resolved investigation of coherently controlled electric currents at a metal surface. Science 318, 1287–1291 (2007).
Côte, D., Fraser, J. M., DeCamp, M., Bucksbaum, P. H. & van Driel, H. M. THz emission from coherently controlled photocurrents in GaAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3959–3961 (1999).
Cook, D. J. & Hochstrasser, R. M. Intense terahertz pulses by four-wave rectification in air. Opt. Lett. 25, 1210–1212 (2000).
Kress, M., Löffler, T., Eden, S., Thomson, M. & Rokos, H. G. Terahertz-pulse generation by photoionization of air with laser pulses composed of both fundamental and second-harmonic waves. Opt. Lett. 29, 1120–1122 (2004).
Bartel, T., Gaal, P., Reimann, K., Woerner, M. & Elsaesser, T. Generation of single-cycle THz transients with high electric-field amplitudes. Opt. Lett. 30, 2805–2807 (2005).
Xie, X., Dai, J. & Zhang, X.-C. Coherent control of THz wave generation in ambient air. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 075005 (2006).
Dai, J., Xie, X. & Zhang, X.-C. Detection of broadband terahertz waves with a laser-induced plasma in gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 103903 (2006).
Kim, K. Y., Glownia, J. H., Taylor, A. J. & Rodriguez, G. Terahertz emission from ultrafast ionizing air in symmetry-broken laser fields. Opt. Express 15, 4577–4584 (2007).
Kreβ, M. et al. Determination of the carrier-envelope phase of few-cycle laser pulses with terahertz-emission spectroscopy. Nature Phys. 2, 327–331 (2006).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong-field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Kulander, K. C., Schafer, K. J. & Krause, J. L. Super Intense Laser-Atom Physics (eds Piraux, B., L'Huillier, A. & Rzazewski, K.) 95–110 (Plenum, New York, 1993).
Augst, S., Strickland, D., Meyerhofer, D. D., Chin, S. L. & Eberly, J. H. Tunnelling ionization of noble gases in a high-intensity laser field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 2212–2215 (1989).
Guo, C., Li, M., Nibarger, J. P. & Gibson, G. N. Single and double ionization of diatomic molecules in strong laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 58, R4271–R4274 (1998).
Lide, D. R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th edn, Vol. 10, 178 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2003).
D'Amico, C. et al. Conical forward THz emission from femtosecond-laser-beam filamentation in air. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 235002 (2007).
Lovberg, R. H. Plasma Diagnostic Techniques (eds Huddlestone, R. H. & Leonhard, S. L.) 69–112 (Academic, New York, 1965).
Edlén, B. The refractive index of air. Metrologia 2, 71–80 (1966).
Keldysh, L. V. Ionization in the field of a strong electromagnetic wave. Soc. Phys. JETP 20, 1307–1314 (1965).
Rodriguez, G., Siders, C. W., Guo, C. & Taylor, A. J. Coherent ultrafast MI-FROG spectroscopy of optical field ionization in molecular H2, N2 and O2 . IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 7, 579–591 (2001).
Landau, L. D. & Lifshitz, E. M. Quantum Mechanics (Pergamon, Oxford, 1977).
Ammosov, M. V., Delone, N. B. & Krainov, V. P. Tunnelling ionization of complex atoms and of atomic ions in an alternating electromagnetic field. Sov. Phys. JETP 64, 1191–1194 (1986).
Schlessinger, L. & Wright, J. Inverse-bremsstrahlung absorption rate in an intense laser field. Phys. Rev. A 20, 1934–1945 (1979).
Ditmire, T. Simulations of heating and electron energy distribution in optical field ionized plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 54, 6735–6740 (1996).
Constant, E. et al. Optimizing high harmonic generation in absorbing gases: model and experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1668–1671 (1999).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported through the Los Alamos National Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program for Los Alamos National Security, LLC, under the auspices of the Department of Energy, contract no. DE-AC52-06NA25396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.J.T. and J.H.G. provided management oversight to this project, while K.Y.K. and G.R. planned and executed the work. K.Y.K. designed the experiment and carried out the measurements. K.Y.K. and G.R. analysed the data and performed the simulations. All authors contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K., Taylor, A., Glownia, J. et al. Coherent control of terahertz supercontinuum generation in ultrafast laser–gas interactions. Nature Photon 2, 605–609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2008.153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2008.153
This article is cited by
-
Magnetic field enhanced strong THz generation by the array of AR-CNTs
Journal of Optics (2024)
-
Multi-millijoule terahertz emission from laser-wakefield-accelerated electrons
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Widely tunable electron bunch trains for the generation of high-power narrowband 1–10 THz radiation
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Ultrafast terahertz emission from emerging symmetry-broken materials
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Terahertz Radiation from Two-Color Laser-Induced Gas Plasma Filament Under a Wide Range of Pressure
Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (2023)