Abstract
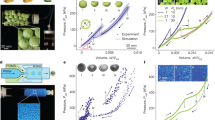
A random laser is a system formed by a random assembly of elastic scatterers dispersed into an optical gain medium1. The multiple light scattering replaces the standard optical cavity of traditional lasers and the interplay between gain and scattering determines the lasing properties. All random lasers studied to date have consisted of irregularly shaped or polydisperse scatterers, with a certain average scattering strength that was constant over the frequency window of the laser2,3,4. In this letter we consider the case where the scattering is resonant. We demonstrate that randomly assembled monodisperse spheres can sustain scattering resonances over the gain frequency window, and that the lasing wavelength can therefore be controlled by means of the diameter and refractive index of the spheres. The system is therefore a random laser with an a priori designed lasing peak within the gain curve.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noginov, M. A. Solid-State Random Lasers (Springer, Berlin, 2005).
Letokhov, V. S. Generation of light by a scattering medium with negative resonance absorption. Sov. Phys. JETP 26, 835–840 (1968).
Lawandy, N. M., Balachandran, R. M., Gomes, A. S. L. & Sauvain, E. Laser action in strongly scattering media. Nature 368, 436–438 (1994).
Cao, H., et al. Ultraviolet lasing in resonators formed by scattering in semiconductor polycrystalline films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 3656–3658 (1998).
Markushev, V. M., Zolin, V. F. & Briskina, C. M. Powder laser. Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk. 45, 847–850 (1986).
Bahoura, M., Morris, K. J. & Noginov, M. A. Threshold and slope efficiency of Nd0.5La0.5Al3(BO3)4 ceramic random laser: effect of the pumped spot size. Opt. Commun. 201, 405–411 (2002).
Klein, S., Cregut, O., Gindre, D., Boeglin, A. & Dorkenoo, K. D. Random laser action in organic film during the photopolymerization process. Opt. Express 3, 5387–5392 (2005).
Polson, R. C. & Vardeny, Z. V. Random lasing in human tissues. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1289–1291 (2004).
Wiersma, D. S. & Lagendijk, A. Light diffusion with gain and random lasers. Phys. Rev. E 54, 4256–4265 (1996).
Cao, H. et al. Photon statistics of random lasers with resonant feedback. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4524–4527 (2001).
Florescu, L. & John, S. Photon statistics and coherence in light emission from a random laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 013602 (2004).
Soukoulis, C. M., Xunya Jiang, Xu, J. Y. & Cao, H. Dynamic response and relaxation oscillations in random lasers. Phys. Rev. B 65, 041103 (2002).
van der Molen, K. L., Mosk, A. P. & Lagendijk, A. Relaxation oscillation in long-pulsed random lasers. arXiv:physics/0703045v1 (2007).
Popov, O., Zilbershtein, A. & Davidov, D. Random lasing from dye-gold nanoparticles in polymer films: Enhanced gain at the surface-plasmon-resonance wavelength. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 191116 (2006).
Shkunov, M. N. et al. Tunable gap-state lasing in switchable directions for opal photonic crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 12, 21–26 (2002);
Scharrer, M. et al. Ultraviolet lasing in high-order bands of three-dimensional ZnO photonic crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 201103 (2006).
Shkunov, M. N. et al. Photonic versus random lasing in opal single crystals. Synth. Met. 116, 485–491 (2001).
Teh, L. K., Wong, C. C., Yang H. Y., Lau, S. P. & Yu, S. F. Lasing in electrodeposited ZnO inverse opal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 161116 (2007).
Mishchenko, M. I., Travis, L. D. & Lacis, A. A. Scattering, Absorption, and Emission of Light by Small Particles (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002).
Garcia, P. D., Sapienza, R., Blanco, A. & Lopez, C. Photonic glass: a novel random material for light. Adv. Mater. 19, 2597–2602 (2007).
Jiang, P., Bertone, J. F., Hwang, K. S. & Colvin, V. L. Single-crystal colloidal multilayers of controlled thickness. Chem. Mater. 11, 2132–2140 (1999).
Sapienza, R., et al. Observation of resonant behavior in the energy velocity of diffused light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 233902 (2007).
Garcia, N., Genack, A. Z. & Lisyansky, A. A. Measurement of the transport mean free path of diffusing photons. Phys. Rev. B 46, 14475–14479 (1992).
Durian, D. J. Influence of boundary reflection and refraction on diffusive photon transport. Phys. Rev. E 50, 857–866 (1994).
Siegman, A. E. Lasers (Stanford University, University Science Books, Oxford, 1986).
van Soest, G. & Lagendijk, A. Beta factor in a random laser. Phys. Rev. E 65, 047601 (2002).
van der Molen, K. L., Mosk, A. P. & Lagendijk, A. Intrinsic intensity fluctuations in random lasers. Phys. Rev. A 74, 053808 (2006).
Goodwin, J. W., Hearn, J., Ho, C. C. & Ottewill, R. H. Studies on the preparation and characterisation of monodisperse polystyrene laticee. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 252, 464–471 (1974).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank J.J. Saenz, R. Righini and M. Colocci for useful discussions. The work was financially supported by the European Commission (EC) (LENS) under contract number RII3-CT-2003-506350, by the European Union (EU) through the Network of Excellence IST-2-511616-NOE (PHOREMOST), CICyT NAN2004-08843-C05, MAT2006-09062, the Spanish MEC Consolider-QOIT CSD2006-0019 and the Comunidad de Madrid S-0505/ESP-0200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottardo, S., Sapienza, R., García, P. et al. Resonance-driven random lasing. Nature Photon 2, 429–432 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2008.102
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2008.102
This article is cited by
-
Structural design of random lasers with specified emission bands
Optical Review (2024)
-
Self-organized lasers from reconfigurable colloidal assemblies
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Controlling random lasing action
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Determining random lasing action
Nature Reviews Physics (2019)
-
Random lasing from structurally-modulated silk fibroin nanofibers
Scientific Reports (2017)