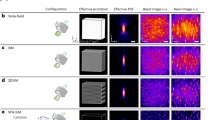
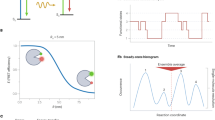
Abstract
Fluorescent particles are routinely used to probe biological processes1. The quantum properties of single spins within fluorescent particles have been explored in the field of nanoscale magnetometry2,3,4,5,6,7,8, but not yet in biological environments. Here, we demonstrate optically detected magnetic resonance of individual fluorescent nanodiamond nitrogen-vacancy centres inside living human HeLa cells, and measure their location, orientation, spin levels and spin coherence times with nanoscale precision. Quantum coherence was measured through Rabi and spin-echo sequences over long (>10 h) periods, and orientation was tracked with effective 1° angular precision over acquisition times of 89 ms. The quantum spin levels served as fingerprints, allowing individual centres with identical fluorescence to be identified and tracked simultaneously. Furthermore, monitoring decoherence rates in response to changes in the local environment may provide new information about intracellular processes. The experiments reported here demonstrate the viability of controlled single spin probes for nanomagnetometry in biological systems, opening up a host of new possibilities for quantum-based imaging in the life sciences.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos, P. The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nature Biotechnol. 22, 47–52 (2004).
Maze, J. R. et al. Nanoscale magnetic sensing with an individual electronic spin in diamond. Nature 455, 644–648 (2008).
Balasubramanian, G. et al. Nanoscale imaging magnetometry with diamond spins under ambient conditions. Nature 455, 648–651 (2008).
Chernobrod, B. M. & Berman, G. P. Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 014903 (2005).
Taylor, J. M. et al. High-sensitivity diamond magnetometer with nanoscale resolution. Nature Phys. 4, 810–816 (2008).
Degen, C. L. Scanning magnetic field microscope with a diamond single-spin sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 243111 (2008).
Cole, J. H. & Hollenberg, L. C. L. Scanning quantum decoherence microscopy. Nanotechology 20, 495401 (2009).
Hall, L. T., Cole, J. H., Hill, C. D. & Hollenberg, L. C. L. Sensing of fluctuating nanoscale magnetic fields using nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 220802 (2009).
Forkey, J. N., Quinlan, M. E., Alexander Shaw, M., Corrie, J. E. T. & Goldman, Y. E. Three-dimensional structural dynamics of myosin V by single-molecule fluorescence polarization. Nature 422, 399–404 (2003).
Sieber, J. J. et al. Anatomy and dynamics of a supramolecular membrane protein cluster. Science 317, 1072–1076 (2007).
Miyawaki, A. et al. Fluorescent indicators for Ca2+ based on green fluorescent proteins and calmodulin. Nature 388, 882–887 (1997).
Hall, L. T. et al. Monitoring ion-channel function in real time through quantum decoherence. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 18777–18782 (2010).
Funk, R. H. W., Monsees, T. & Özkucur, N. Electromagnetic effects—from cell biology to medicine. Prog. Histochem. Cyto. 43, 177–264 (2009).
Gruber, A. et al. Scanning confocal optical microscopy and magnetic resonance on single defect centers. Science 276, 2012–2014 (1997).
Balasubramanian, G. et al. Ultralong spin coherence time in isotopically engineered diamond. Nature Mater. 8, 383–387 (2009).
Schrand, A. M. et al. Are diamond nanoparticles cytotoxic? J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 2–7 (2007).
Chao, J. I. et al. Nanometer-sized diamond particle as a probe for biolabeling. Biophys. J. 93, 2199–2208 (2007).
Maurer, P. C. et al. Far-field optical imaging and manipulation of individual spins with nanoscale resolution. Nature Phys. 6, 912–918 (2010).
Steinert, S. et al. High sensitivity magnetic imaging using an array of spins in diamond. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81, 043705 (2010).
Hall, L. T., Hill, C. D., Cole, J. H. & Hollenberg, L. C. L. Ultrasensitive diamond magnetometry using optimal dynamic decoupling. Phys. Rev. B 82, 045208 (2010).
de Lange, G. et al. Single-spin magnetometry with multipulse sensing sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 080802 (2011).
Chang, Y. R. et al. Mass production and dynamic imaging of fluorescent nanodiamonds. Nature Nanotech. 3, 284–288 (2008).
Neugart, F. et al. Dynamics of diamond nanoparticles in solution and cells. Nano. Lett. 7, 3588–3591 (2007).
Fu, C. C. et al. Characterization and application of single fluorescent nanodiamonds as cellular biomarkers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 727–732 (2007).
Faklaris, O. et al. Photoluminescent diamond nanoparticles for cell labeling: study of the uptake mechanism in mammalian cells. ACS Nano 3, 3955–3962 (2009).
Bradac, C. et al. Observation and control of blinking nitrogen-vacancy centres in discrete nanodiamonds. Nature Nanotech. 5, 345–349 (2010).
Hossain, F. M., Doherty, M. W., Wilson, H. F. & Hollenberg, L. C. L. Ab initio electronic and optical properties of the N-V center in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 226403 (2008).
Zimmermann, T., Rietdorf, J. & Pepperkok, R. Spectral imaging and its applications in live cell microscopy. FEBS Lett. 546, 87–92 (2003).
Hanson, R., Dobrovitski, V. V., Feiguin, A. E., Gywat, O. & Awschalom, D. D. Coherent dynamics of a single spin interacting with an adjustable spin bath. Science 320, 352–355 (2008).
Cai, J. & Jones, D. P. Superoxide in apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 11401–11404 (1998).
Epstein, R. J., Mendoza, F. M., Kato, Y. K. & Awschalom, D. D. Anisotropic interactions of a single spin and dark-spin spectroscopy in diamond. Nature Phys. 1, 94–98 (2005).
Wittrup, A. et al. Magnetic nanoparticle-based isolation of endocytic vesicles reveals a role of the heat shock protein GRP75 in macromolecular delivery. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 13342–13347 (2010).
Chung, I., Shimizu, K. T. & Bawendi, M. G. Room temperature measurements of the 3D orientation of single CdSe quantum dots using polarization microscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 405–408 (2003).
Rosenberg, S. A., Quinlan, M. E., Forkey, J. N. & Goldman, Y. E. Rotational motions of macromolecules by single-molecule fluorescence microscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 38, 583–593 (2005).
Kukura, P. et al. High-speed nanoscopic tracking of the position and orientation of a single virus. Nature Meth. 6, 923–927 (2009).
Engel, G. S. et al. Evidence for wavelike energy transfer through quantum coherence in photosynthetic systems. Nature 446, 782–786,(2007).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank F. Jelezko and A. Johnston for helpful discussions and advice, and S. Szilagyi for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Australian Research Council under the Centre of Excellence scheme (CE110001027), the Discovery Project scheme (DP0770715 and DP0877360), the Federation Fellowship Scheme (FF0776078) and the Baden-Wuerttemberg Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.P.M., A.S., D.S. and R.E.S. designed and constructed the confocal/ESR system, performed the measurements and carried out the data analysis. Y.Y. and F.C. planned and conducted the cellular uptake experiments, and analysed the data. D.M., L.T.H. and L.C.L.H. carried out the theoretical analyses. L.C.L.H., J.W., F.C., P.M. and S.P. conceived and directed the project. L.C.L.H. wrote the paper with contributions from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 859 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGuinness, L., Yan, Y., Stacey, A. et al. Quantum measurement and orientation tracking of fluorescent nanodiamonds inside living cells. Nature Nanotech 6, 358–363 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.64
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.64
This article is cited by
-
Neuronal growth on high-aspect-ratio diamond nanopillar arrays for biosensing applications
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Quantum sensors for biomedical applications
Nature Reviews Physics (2023)
-
Noisy intermediate-scale quantum computers
Frontiers of Physics (2023)
-
Decoupling nuclear spins via interaction-induced freezing in nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Toxicity and biodistribution of nanodiamond coupled with calcein
Journal of Materials Science (2023)