Abstract
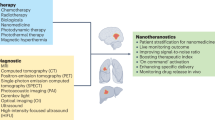
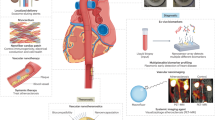
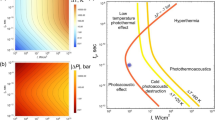
The use of carbon nanotubes in medicine is now at the crossroads between a proof-of-principle concept and an established preclinical candidate for a variety of therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Progress towards clinical trials will depend on the outcomes of efficacy and toxicology studies, which will provide the necessary risk-to-benefit assessments for carbon-nanotube-based materials. Here we focus on carbon nanotubes that have been studied in preclinical animal models, and draw attention to the promises, facts and challenges of these materials as they transition from research to the clinical phase. We address common questions regarding the use of carbon nanotubes in disease imaging and therapy, and highlight the opportunities and challenges ahead.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prato, M., Kostarelos, K. & Bianco, A. Functionalized carbon nanotubes in drug design and discovery. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 60–68 (2008).
Boczkowski, J. & Lanone, S. Potential uses of carbon nanotubes in the medical field: how worried should patients be? Nanomedicine 2, 407–410 (2007).
Itkis, M. E. et al. Comparison of analytical techniques for purity evaluation of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 3439–3448 (2005).
Iijima, S. & Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 363, 603–605 (1993).
Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56–58 (1991).
Jorio, A., Dresselhaus, G. & Dresselhaus, M. S. Carbon Nanotubes: Advanced Topics in the Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications (Springer-Verlag, 2008).
Tasis, D., Tagmatarchis, N., Bianco, A. & Prato, M. Chemistry of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 106, 1105–1136 (2006).
Liu, Z. et al. In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nature Nanotech. 2, 47–52 (2007).
Ali-Boucetta, H. et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotube-doxorubicin supramolecular complexes for cancer therapeutics. Chem. Commun. 12, 459–461 (2008).
Gannon, C. J. et al. Carbon nanotube-enhanced thermal destruction of cancer cells in a noninvasive radiofrequency field. Cancer 110, 2654–2665 (2007).
Zheng, M. et al. DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes. Nature Mater. 2, 338–342 (2003).
Kostarelos, K. et al. Cellular uptake of functionalized carbon nanotubes is independent of functional group and cell type. Nature Nanotech. 2, 108–113 (2007).
Podesta, J. P. et al. Antitumor activity and prolonged survival by carbon nanotube-mediated therapeutic siRNA silencing in a human lung xenograft model. Small 5, 1176–1185 (2009).
Liu, Z., Tabakman, S., Welsher, K. & Dai, H. Carbon nanotubes in biology and medicine: In vitro and in vivo detection, imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2, 85–120 (2009).
De la Zerda, A. et al. Carbon nanotubes as photoacoustic molecular imaging agents in living mice. Nature Nanotech. 3, 557–562 (2008).
Liu, Z. et al. Drug delivery with carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 68, 6652–6660 (2008).
Lacerda, L. et al. Dynamic imaging of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube systemic circulation and urinary excretion. Adv. Mater. 20, 225–230 (2008).
McDevitt, M. R. et al. PET imaging of soluble yttrium-86-labeled carbon nanotubes in mice. PLoS ONE 2, e907 (2007).
Singh, R. et al. Tissue biodistribution and blood clearance rates of intravenously administered carbon nanotube radiotracers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 3357–3362 (2006).
Yandar, N. et al. Immunological profile of a Plasmodium vivax AMA-1 N-terminus peptide-carbon nanotube conjugate in an infected Plasmodium berghei mouse model. Vaccine 26, 5864–5873 (2008).
Pantarotto, D. et al. Immunization with peptide-functionalized carbon nanotubes enhances virus-specific neutralizing antibody responses. Chem. Biol. 10, 961–966 (2003).
McDevitt, M. R. et al. Tumor targeting with antibody-functionalized, radiolabeled carbon nanotubes. J. Nucl. Med. 48, 1180–1189 (2007).
Deng, X. et al. Translocation and fate of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in vivo. Carbon 45, 1419–1424 (2007).
Wang, H. et al. Biodistribution of carbon single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4, 1019–1024 (2004).
Meng, J. et al. Carbon nanotubes conjugated to tumor lysate protein enhance the efficacy of an antitumor immunotherapy. Small 4, 1364–1370 (2008).
Zhang, Z. et al. Delivery of telomerase reverse transcriptase small interfering RNA in complex with positively charged single-walled carbon nanotubes suppresses tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 4933–4939 (2006).
Bhirde, A. A. et al. Targeted killing of cancer cells in vivo and in vitro with EGF-directed carbon nanotube-based drug delivery. ACS Nano 3, 307–316 (2009).
Ryman-Rasmussen, J. P. et al. Inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes potentiate airway fibrosis in murine allergic asthma. Am. J. Resp. Cell Mol. 40, 349–358 (2009).
Shvedova, A. A. et al. Inhalation vs. aspiration of single-walled carbon nanotubes in C57BL/6 mice: inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and mutagenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung C. 295, 552–565 (2008).
Chou, C. C. et al. Single-walled carbon nanotubes can induce pulmonary injury in mouse model. Nano Lett. 8, 437–445 (2008).
Mitchell, L. A. et al. Pulmonary and systemic immune response to inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Toxicol. Sci. 100, 203–214 (2007).
Takagi, A. et al. Induction of mesothelioma in p53± mouse by intraperitoneal application of multi-wall carbon nanotube. J. Toxicol. Sci. 33, 105–116 (2008).
Poland, C. A. et al. Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nature Nanotech. 3, 423–428 (2008).
Cherukuri, P. et al. Mammalian pharmacokinetics of carbon nanotubes using intrinsic near-infrared fluorescence. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 18882–18886 (2006).
Yang, S. T. et al. Biodistribution of pristine single-walled carbon nanotubes in vivo. J. Phys. Chem. 111, 17761–17764 (2007).
Schipper, M. L. et al. A pilot toxicology study of single-walled carbon nanotubes in a small sample of mice. Nature Nanotech. 3, 216–221 (2008).
Liu, Z. et al. Circulation and long-term fate of functionalized, biocompatible single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice probed by Raman spectroscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 1410–1415 (2008).
Yang, S. T. et al. Long-term accumulation and low toxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes in intravenously exposed mice. Toxicol. Lett. 181, 182–189 (2008).
Kostarelos, K. The long and short of carbon nanotube toxicity. Nature Biotechnol. 26, 774–776 (2008).
Lacerda, L. et al. Carbon-nanotube shape and individualization critical for renal excretion. Small 4, 1130–1132 (2008).
Lacerda, L. et al. Tissue histology and physiology following intravenous administration of different types of functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Nanomedicine 3, 149–161 (2008).
Keefer, E. W. et al. Carbon nanotube coating improves neuronal recordings. Nature Nanotech. 3, 434–439 (2008).
Sitharaman, B. et al. In vivo biocompatibility of ultra-short single-walled carbon nanotube/biodegradable polymer nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. Bone 43, 362–370 (2008).
Khang, D., Park, G. E. & Webster, T. J. Enhanced chondrocyte densities on carbon nanotube composites: the combined role of nanosurface roughness and electrical stimulation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 86, 253–260 (2008).
Heller, D. A. et al. Multimodal optical sensing and analyte specificity using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotech. 4, 114–120 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the University of Trieste, INSTM, Italian Ministry of Education MUR (cofin Prot. 2006034372 and Firb RBIN04HC3S), Regione Friuli Venezia-Giulia, CNRS and the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (grant ANR-05-JCJC-0031-01). Partial support is also acknowledged from the European Union FP7 ANTICARB (HEALTH-2007-201587) research programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostarelos, K., Bianco, A. & Prato, M. Promises, facts and challenges for carbon nanotubes in imaging and therapeutics. Nature Nanotech 4, 627–633 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.241
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.241
This article is cited by
-
Pristine/folate-functionalized graphene oxide as two intrinsically radioiodinated nano-theranostics: self/dual in vivo targeting comparative study
Cancer Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Unveiling the Bio-corona Fingerprinting of Potential Anticancer Carbon Nanotubes Coupled with d-Amino Acid Oxidase
Molecular Biotechnology (2022)
-
Hybrid material of structural DNA with inorganic compound: synthesis, applications, and perspective
Nano Convergence (2020)