Abstract
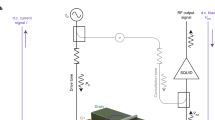
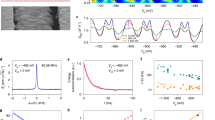
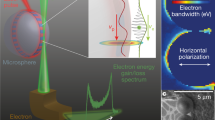
The single-electron transistor is the fastest and most sensitive electrometer available today1,2. Single-electron pumps and turnstiles are also being explored as part of the global effort to redefine the ampere in terms of the fundamental physical constants3,4,5,6. However, the possibility of electrons tunnelling coherently through these devices, a phenomenon known as co-tunnelling7, imposes a fundamental limit on device performance. It has been predicted8 that it should be possible to completely suppress co-tunnelling in mechanical versions of the single-electron transistor9, which would allow mechanical devices to outperform conventional single-electron transistors in many applications. However, the mechanical devices developed so far are fundamentally limited by unwanted interactions with the electrical mechanisms that are used to excite the devices10,11,12. Here we show that it is possible to overcome this problem by using ultrasonic waves rather than electrical currents as the excitation mechanism, which we demonstrate at low temperatures. This is a significant step towards the development of high-performance devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoelkopf, R. J., Wahlgren, P., Kozhevnikov, A. A., Delsing, P. & Prober, D. E. The radio-frequency single-electron transistor (RF-SET): A fast and ultrasensitive electrometer. Science 280, 1238–1242 (1998).
Devoret, M. H. & Schoelkopf, R. J. Amplifying quantum signals with the single-electron transistor. Nature 406, 1039–1046 (2000).
Keller, M. W., Martinis, J. M., Zimmermann, N. M. & Steinbach, A. H. Accuracy of electron counting using 7-junction electron pump. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 1804–1806 (1996).
Ono, Y., Zimmermann, N. M., Yamazaki, K. & Takahashi, Y. Turnstile operation using a silicon dual-gate single-electron transitor. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 42, L1109–L1111 (2003).
Geerligs, L. J. et al. Frequency-locked turnstile device for single electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 2691–2694 (1990).
Fonseca, L. R. C., Korotkov, A. N. & Likharev, K. K. A numerical study of the accuracy of single-electron current standards. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 9155–9165 (1996).
De Franceschi, S. et al. Electron cotunnelling in a semiconductor quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 878–881 (2001).
Weiss, C. & Zwerger, W. Accuracy of a mechanical single-electron shuttle. Europhys. Lett. 47, 97–103 (1999).
Gorelik, L. Y. et al. Shuttle mechanism for charge transfer in coulomb blockade nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4526–4529 (1998).
Erbe, A., Blick, R. H., Tilke, A., Kriele, A. & Kotthaus, J. P. A mechanically flexible tunneling contact operating at radio frequencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 3751–3753 (1998).
Erbe, A., Weiss, C., Zwerger, W. & Blick, R. H. Nanomechanical resonator shuttling single electrons at radio frequencies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 096106 (2001).
Scheible, D. V. & Blick., R. H. Silicon nanopillars for mechanical single-electron transport. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4632–4634 (2004).
Verbridge, S. S., Parpia, J. M., Reichenbach, R. B., Bellan, L. M. & Craighead, H. G. High quality factor resonance at room temperature with nanostrings under high tensile stress. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 124304 (2006).
Jänchen, G. et al. Mechanical properties of high-aspect-ratio atomic-force microscope tips. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 4623–4625 (2002).
Shaw, S. W. The dynamics of a harmonically excited system having rigid amplitude constraints. J. Appl. Mech. 52, 453–464 (1985).
Isacsson, A. Dynamics of a three-terminal mechanically flexible tunnelling contact. Phys. Rev. B 64, 035326 (2001).
Devoret, M. H. & Grabert, H. in Single Charge Tunneling (eds Grabert, H. & Devoret, M. H.) (Plenum, New York, 1992).
Sze, S. M. in Physics of Semiconductor Devices (ed. Sze, S. M.) (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1981).
Azuma, Y. et al. One by one single-electron transport in nanomechanical Coulomb blockade shuttle. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 053120 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge financial support of the German Excellence Initiative via the Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM) and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ko 416/18-1). We thank K. Karrai for helpful discussion and S. Manus for expert technical help. D.R.K. thankfully acknowledges support by the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.R.K. conceived and designed the experiment, analysed the data and wrote the paper. E.M.W. and J.P.K. co-wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koenig, D., Weig, E. & Kotthaus, J. Ultrasonically driven nanomechanical single-electron shuttle. Nature Nanotech 3, 482–485 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.178
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.178