Abstract
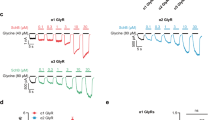
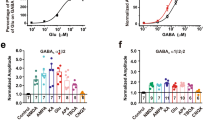
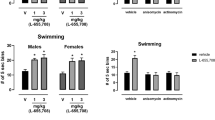
Developments in the molecular biology and pharmacology of GLUK5, a subtype of the kainate class of ionotropic glutamate receptors, have enabled insights into the roles of this subunit in synaptic transmission and plasticity. However, little is known about the possible functions of GLUK5-containing kainate receptors in pathological conditions. We report here that, in hippocampal slices, selective antagonists of GLUK5-containing kainate receptors prevented development of epileptiform activity—evoked by the muscarinic agonist, pilocarpine—and inhibited the activity when it was pre-established. In conscious rats, these GLUK5 antagonists prevented and interrupted limbic seizures induced by intra-hippocampal pilocarpine perfusion, and attenuated accompanying rises in extracellular L-glutamate and GABA. This anticonvulsant activity occurred without overt side effects. GLUK5 antagonism also prevented epileptiform activity induced by electrical stimulation, both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, we propose that subtype-selective GLUK5 kainate receptor antagonists offer a potential new therapy for epilepsy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettler, B. & Mulle, C. AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 34, 123–139 (1995).
Bleakman, D. & Lodge, D. Neuropharmacology of AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 37, 1187–1204 (1998).
Nadler, J.V., Perry, B.W. & Cotman, C.W. Intraventricular kainic acid preferentially destroys hippocampal cells. Nature, 271, 676–677 (1978).
Ben-Ari, Y., Tremblay, E., Ottersen, O.P. & Meldrum, B.S. The role of epileptic activity in hippocampal and 'remote' cerebral lesions induced by kainic acid. Brain Res. 191, 79–97 (1980).
Ashwood, T.J., Lancaster, B. & Wheal, H.V. Intracellular electrophysiology of CA1 pyramidal neurones in slices of the kainic acid lesioned hippocampus of the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 62, 189–198 (1986).
Chittajallu, R. et al. Regulation of glutamate release by presynaptic kainate receptors in the hippocampus. Nature 379, 78–81 (1996).
Vignes, M. & Collingridge, G.L. The synaptic activation of kainate receptors. Nature 388, 179–182 (1997).
Vignes, M., Bleakman, D., Lodge, D. & Collingridge, G.L. The synaptic activation of the GluR5 subtype of kainate receptor in area CA3 of the rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 36, 1477–1481 (1997).
Castillo, P.E., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Kainate receptors mediate a slow postsynaptic current in hippocampal CA3 neurons. Nature 388, 182–186 (1997).
Clarke, V.R.J. et al. A hippocampal GluR5 kainate receptor regulating inhibitory synaptic transmission. Nature 389, 599–603 (1997).
Rodriguez-Moreno, A., Herrerras, O. & Lerma, J. Kainate receptors presynaptically downregulate GABAergic inhibition in the rat hippocampus. Neuron 19, 893–901 (1997).
O'Neill, M.J. et al. Decahydroisoquinolines: novel competitive AMPA/kainate antagonists with neuroprotective effects in global cerebral ischaemia. Neuropharmacology 37, 1211–1222 (1998).
Li, H. & Rogawski, M.A. GluR5 kainate receptor mediated synaptic transmission in rat basolateral amygdala in vitro. Neuropharmacology 37, 1279–1286 (1998).
Cossart, R. et al. GluR5 kainate receptor activation in interneurons increases tonic inhibition of pyramidal cells. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 470–478 (1998).
Frerking, M., Malenka, R.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Synaptic activation of kainate receptors on hippocampal interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 479–486 (1998).
Vignes, M. et al. The GluR5 subtype of kainate receptor regulates excitatory synaptic transmission in areas CA1 and CA3 of the rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 37, 1269–1277 (1998).
Mulle, C. et al. Altered synaptic physiology and reduced susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures in GluR6-deficient mice. Nature 392, 601–605 (1998).
Chittajallu, R., Braithwaite S.P., Clarke, V.R.J. & Henley, J.M. Kainate receptors: subunits, synaptic localization and function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20, 26–35 (1999).
Bortolotto, Z.A. et al. Kainate receptors are involved in synaptic plasticity. Nature 402, 297–301 (1999).
Min, M.Y., Melyan, Z. & Kullmann, D.M. Synaptically released glutamate reduces γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic inhibition in the hippocampus via kainate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 9932–9937 (1999).
Frerking, M., Petersen, C.C. & Nicoll, R.A. Mechanisms underlying kainate receptor-mediated disinhibition in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 12917–12922 (1999).
O'Neill, M.J. et al. LY377770, a novel iGluR5 kainate receptor antagonist with neuroprotective effects in global and focal cerebral ischaemia. Neuropharmacology 39, 1575–1588 (2000).
Rodriguez-Moreno, A., Lopez-Garcia, J.C. & Lerma, J. Two populations of kainate receptors with separate signaling mechanisms in hippocampal interneurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 1293–1298 (2000).
Paternain, A.V., Herrera, M.T., Nieto, M.A. & Lerma, J. GLUR5 and GLUR6 receptor subunits coexist in hippocampal neurons and coassemble to form functional receptors. J. Neurosci. 20, 196–205 (2000).
Li, H., Chen, A., Xing, G., Wei, M.L. & Rogawski, M.A. Kainate receptor-mediated heterosynaptic facilitation in the amygdala. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 612–620 (2001).
Huettner, J.E. Kainate receptors: knocking out plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 24, 365–366 (2001).
Schmitz, D., Mellor, J. & Nicoll, R.A. Presynaptic kainate receptor mediation of frequency facilitation at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Science 291, 1972–1975 (2001).
Contractor, A., Swanson, G. & Heinemann, S.F. Kainate receptors are involved in short- and long-term plasticity at mossy fiber synapses in the hippocampus. Neuron 29, 209–216 (2001).
Wilding, T.J. & Huettner, J.E. Functional diversity and developmental changes in rat neuronal kainate receptors. J. Physiol. 532.2, 411–421 (2001).
Lauri, S.E. et al. A critical role of a facilitatory presynaptic kainate receptor in mossy fiber LTP. Neuron 32, 697–709 (2001).
Bleakman, D. et al. Pharmacological discrimination of GluR5 and GluR6 kainate receptor subtypes by (3S,4aR,6R,8aR)-6-[2-(1(2)H-tetrazole-5-yl)ethyl]decahydro-isoquinoline-3 carboxylic acid. Mol. Pharmacol. 49, 581–585 (1996).
Lodge, D. & Dingledine, R. in The IUPHAR Compendium of Receptor Characterization and Classification 2nd edn. 189–194 (IUPHAR Media, London, 2000).
Kehl, S.J., McLennan, H. & Collingridge, G.L. Effects of folic and kainic acids on synaptic responses of hippocampal neurones. Neuroscience 11, 111–124 (1984).
Turski, L., Ikonomidou, C., Turski, W.A., Bortolotto, Z.A. & Cavalheiro, E.A. Review: cholinergic mechanisms and epileptogenesis. The seizures induced by pilocarpine: a novel experimental model of intractable epilepsy. Synapse 3, 154–171 (1989).
Smolders, I., Khan, G.M., Manil, J., Ebinger, G. & Michotte, Y. NMDA receptor-mediated pilocarpine-induced seizures: characterization in freely moving rats using microdialysis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 121, 1171–1179 (1997).
Rutecki, P.A. & Yang, Y. Ictal epileptiform activity in the CA3 region of hippocampal slices produced by pilocarpine. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 3019–3029 (1998).
Rogawski, M.A., Kurzman, P.S., Yamaguchi, S.I. & Li, H. Role of AMPA and GluR5 kainate receptors in the development and expression of amygdala kindling in the mouse. Neuropharmacology, 40, 28–35 (2001).
De Sarro, G. et al. Anticonvulsant activity and plasma level of 2,3-benzodiazepin-4-ones (CFMs) in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 63, 621–627 (1999).
Paternain, A.V., Morales, M. & Lerma, J. Selective antagonism of AMPA receptors unmasks kainate receptor-mediated responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 14, 185–189 (1995).
Wilding, T.J. & Huettner, J.E. Differential antagonism of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate-preferring and kainate-preferring receptors by 2,3-benzodiazepines. Mol. Pharmacol. 47, 582–587 (1995).
Stasheff, S.F., Bragdon, A.C. & Wilson, W.A. Induction of epileptiform activity in hippocampal slices by trains of electrical stimuli. Brain Res. 344, 296–302 (1985).
Krnjevic, K. in GABA Mechanisms in Epilepsy 47–87 (Wiley-Liss, New York, 1991).
Matagne, A. & Klitgaard, H. Validation of corneally kindled mice: a sensitive screening model for partial epilepsy in man. Epilepsy Res. 31, 59–71 (1998).
Lauri, S.E. et al. Synaptic activation of a presynaptic kainate receptor facilitates AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission at hippocampal mossy fibre synapses. Neuropharmacology 41, 907–915 (2001).
Mattson, R.H. Efficacy and adverse effects of established and new antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 36 suppl. 2, S13–S26 (1995).
Rogvi-Hansen, B. & Gram, L. Adverse effects of established and new antiepileptic drugs: an attempted comparison. Pharmacol. Ther. 68, 425–434 (1995).
Curry, W.J. & Kulling, D.L. Newer antiepileptic drugs: gabapentin, lamotrigine, felbamate, topiramate and fosphenytoin. Am. Fam. Physician 57, 513–524 (1998).
Sander, T. et al. Allelic association of juvenile absence epilepsy with a GluR5 kainate receptor gene (GRIK1) polymorphism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 74, 416–421 (1997).
Paxinos, G. & Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates 2nd edn. (Academic, San Diego, 1986).
Smolders, I., Sarre, S., Michotte, Y. & Ebinger, G. The analysis of excitatory, inhibitory and other amino acids in rat brain microdialysates using microbore liquid chromatography. J. Neurosci. Meth. 57, 47–53 (1995).
Acknowledgements
I. Smolders is a postdoctoral fellow of the FWO-Vlaanderen, Belgium. We thank C. Felder of Eli Lilly & Co. for help in profiling LY382884 and LY377770 in vitro and S. White and H. Wolf for help with the 6-Hz studies. We thank R. Berckmans, G. De Smet and C. De Rijck for technical assistance. Supported by the MRC, Wellcome Trust, FWO-Vlaanderen, VUB & the Koningin Elisabeth Stichting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Of the authors, Michael J. O'Neill, Paul L. Ornstein, David Bleakman, AnnMarie Ogden, Brianne Weiss, Ken H. Ho and David Lodge are employed by Eli Lilly & Co. Ltd. Ken H. Ho, worked for Allelix Biopharmaceuticals at the time some of these data were collected and Allelix Biopharmaceuticals had a collaborative financial agreement at that time.
Other than this, none of the authors or their institutions received any payment, financial support or other remuneration for this work from Eli Lilly & Co. Ltd, other than that the three compounds LY382884, LY377770 and GYKI53655 were provided free of charge.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smolders, I., Bortolotto, Z., Clarke, V. et al. Antagonists of GLUK5-containing kainate receptors prevent pilocarpine-induced limbic seizures. Nat Neurosci 5, 796–804 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn880
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn880
This article is cited by
-
Unbalanced dendritic inhibition of CA1 neurons drives spatial-memory deficits in the Ts2Cje Down syndrome model
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Susceptibility to Soman Toxicity and Efficacy of LY293558 Against Soman-Induced Seizures and Neuropathology in 10-Month-Old Male Rats
Neurotoxicity Research (2017)
-
Activation of Kainate GLUK5 Transmission Rescues Kindling-Induced Impairment of LTP in the Rat Lateral Amygdala
Neuropsychopharmacology (2008)