Abstract
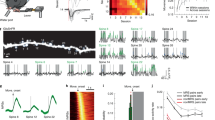
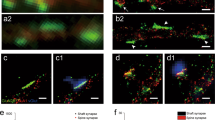
Synapse splitting is considered a viable mechanism for increasing synaptic coupling between neurons1,2,3,4,5. We investigated this issue by reconstructing dendrites, axons and synapses from hippocampus during long-term potentiation (LTP) and maturation. Long, mature axons passed between neighboring dendritic spine synapses, precluding their formation by splitting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlin, R.K. & Siekevitz, P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 3517–3521 (1983).
Lusher, C. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 545–550 (2000).
Jontes, J.D. & Smith, S. J. Neuron 27, 11–14 (2000).
Yuste, R. & Bonhoeffer, T. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1071–1089 (2001).
Hering, H. & Sheng, M. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 880–888 (2001).
Jones, D.G. & Harris, R.J. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 177–219 (1995).
Toni, N. et al. Nature 402, 421–425 (1999).
Toni, N. et al. J. Neurosci. 21, 6245–6251 (2001).
Sorra, K.E. & Harris, K.M. J. Neurosci. 18, 658–671 (1998).
Sorra, K.E. et al. J. Comp. Neurol. 398, 225–240 (1998).
Harris, K.M. et al. J. Neurosci. 12, 2685–2705 (1992).
Sorra, K.E. & Harris, K.M. J. Neurosci. 13, 3736–3745 (1993).
Engert, F. & Bonhoeffer, T. Nature 399, 66–70 (1999).
Maletic-Savatic, M. et al. Science 283, 1923–1927 (1999).
Fiala, J.C. et al. J. Neurosci. 18, 8900–8911 (1998).
Acknowledgements
Thanks to M. Feinberg, J. Cooney, A. Goddard, D. Castellano and E. Phillips for technical assistance. This work was supported by NIH grant NS33574 and by the Human Brain Project grant MH/DA57351 funded jointly by NIMH and NIDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiala, J., Allwardt, B. & Harris, K. Dendritic spines do not split during hippocampal LTP or maturation. Nat Neurosci 5, 297–298 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn830
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn830
This article is cited by
-
The Antidepressant Effects of Resveratrol are Accompanied by the Attenuation of Dendrite/Dendritic Spine Loss and the Upregulation of BDNF/p-cofilin1 Levels in Chronic Restraint Mice
Neurochemical Research (2021)
-
Single excitatory axons form clustered synapses onto CA1 pyramidal cell dendrites
Nature Neuroscience (2018)
-
Structure, Distribution, and Function of Neuronal/Synaptic Spinules and Related Invaginating Projections
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2015)
-
Multiple spine boutons are formed after long-lasting LTP in the awake rat
Brain Structure and Function (2014)
-
Repetitive motor learning induces coordinated formation of clustered dendritic spines in vivo
Nature (2012)