Abstract
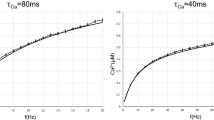
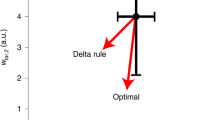
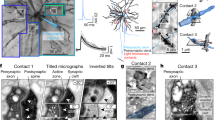
We provide a functional measure, the synaptic information efficacy (SIE), to assess the impact of synaptic input on spike output. SIE is the mutual information shared by the presynaptic input and postsynaptic output spike trains. To estimate SIE we used a method based on compression algorithms. This method detects the effect of a single synaptic input on the postsynaptic spike output in the presence of massive background synaptic activity in neuron models of progressively increasing realism. SIE increased with increases either in time locking between the input synapse activity and the output spike or in the average number of output spikes. SIE depended on the context in which the synapse operates. We also measured SIE experimentally. Systematic exploration of the effect of synaptic and dendritic parameters on the SIE offers a fresh look at the synapse as a communication device and a quantitative measure of how much the dendritic synapse informs the axon.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherrington, C. S. The central nervous system. in A Text-Book of Physiology 7th edn. Vol. 3 (ed. Foster, M.) (Macmillan, London, 1897).
Tsodyks, M. V. & Markram, H. The neural code between neocortical pyramidal neurons depends on neurotransmitter release probability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 719–723 (1997).
Abbott, L. F., Varela, J. A., Sen, K. & Nelson, S. B. Synaptic depression and cortical gain control. Science 275, 220–224 (1997).
Manwani, A. & Koch, C. Detecting and estimating signals over noisy and unreliable synapses: information-theoretic analysis. Neural Comput. 13, 1–33 (2001).
Fuhrmann, G., Segev, I., Markram, H. & Tsodyks, M. Coding of temporal information by activity-dependent synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 140–148 (2002).
Markram, H., Lubke, J., Frotscher, M., & Sakmann, B. Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275, 213–215 (1997).
Gil, Z., Connors, B. W. & Amitai, Y. Efficacy of thalamocortical and intracortical synaptic connections: quanta, innervation, and reliability. Neuron 23, 385–397 (1999).
Bernander, O., Douglas, R. J., Martin, K. A. C. & Koch, C. Synaptic background activity determines spatio-temporal integration in single pyramidal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 11569–11573 (1991).
Borg-Graham, L. J., Monier, C., & Fregnac, Y. Visual input evokes transient and strong shunting inhibition in visual cortical neurons. Nature 393, 369–373 (1998).
Destexhe, A. & Pare, D. Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 1531–1547 (1999).
London, M. & Segev, I. Synaptic scaling in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 853–855 (2001).
Fetz, E. E. & Gustafsson, B. Relation between shapes of post-synaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of cat motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 387–410 (1983).
Abeles, M. Corticonics. (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1991).
Hebb, D. O. The Organization of Behavior (Wiley, New York, 1949).
Hoppfield, J. J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2254–2258 (1982).
Yamada, S., Nakashima, M., Matsumoto, K. & Shiono, S. Information theoretic analysis of action potential trains. I. Analysis of correlation between two neurons. Biol. Cybern. 68, 215–220 (1993).
Rieke, F., Warland, D., de Ruyter van Steveninck, R. & Bialek, W. Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code. (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1997).
Borst, A. & Theunissen, F. E. Information theory and neural coding. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 947–957 (1999).
Willems, F. M. J., Shtarkov, Y. M. & Tjalkens, T. The context-tree weighting method: basic properties. IEEE Trans. Info. Theory Vol. IT-41, 653–664 (1995).
Pinsky, P. F. & Rinzel, J. Intrinsic and network rhythmogenesis in a reduced traub model for ca3 neurons J. Comput. Neurosci. 1, 39–60 (1994) [erratum in J. Comput. Neurosci. 2, 275 (1995)].
Mainen, Z. F. & Sejnowski, T. J. Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in model neocortical neurons. Nature 382, 363–366 (1996).
Segev, I. & London, M. Untangling dendrites with quantitative models. Science 290, 744–750 (2000).
Larkum, M. E., Zhu, J. J. & Sakmann, B. A new cellular mechanism for coupling inputs arriving at different cortical layers. Nature 398, 338–341 (1999).
Stuart, G. J. & Häusser, M. Dendritic coincidence detection of EPSPs and action potentials. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 63–71 (2001).
Stratford, R. D., Mason, A. J. R., Larkman, A. U., Major, G. & Jack, J. J. B. The modeling of pyramidal neurons in the visual cortex. in The Computing Neuron (eds. Durbin, R., Miall, C. & Mitchson, C.) Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts, 1989).
Nicoll, A., Larkman, A. & Blakemore, C. Modulation of EPSP shape and efficacy by intrinsic membrane conductances in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 468, 693–710 (1993).
Carnevale, N. T. & Johnston, D. Electrophysiological characterization of remote chemical synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 47, 606–621 (1982).
Oertel, D. Synaptic responses and electrical properties of cells in brain slices of the mouse anteroventral cochlear nucleus. J. Neurosci. 3, 2043–2053 (1983).
Bernander, O. & Koch, C. The effect of synchronized inputs at the single neuron level. Neural Comput. 6, 622–641 (1994).
Murthy, V. N. & Fetz, E. E. Effects of input synchrony on the firing rate of a three-conductance cortical neuron model. Neural Comput. 6, 1111–1126 (1994).
Rall, W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1138–1168 (1967).
Liao, D., Hessler, N. A. & Malinow, R. Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. Nature 375, 400–404 (1995).
Cook, E. P. & Johnston, D. Voltage-dependent properties of dendrites that eliminate location-dependent variability of synaptic input. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 535–543 (1999).
Iansek, R. & Redman, S. J. The amplitude, time course and charge of unitary excitatory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurone dendrites. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 665–688 (1973).
Levin, J. E. & Miller, J. P. Stochastic resonance enhances neural encoding of broadband stimuli in the cricket cercal sensory system. Nature 380, 165–168 (1996).
Rall, W. Theoretical significance of dendritic trees for neuronal input-output relations. in Neural Theory and Modeling (ed. Reiss, R.) 73–97 (Stanford Univ. Press, Stanford, 1964).
Rinzel, J. & Rall, W. Transient response in a dendritic neuron model for current injected at one branch. Biophys. J. 14, 759–790 (1974).
Häusser, M. & Clark, B. A. Tonic synaptic inhibition modulates neuronal output pattern and spatiotemporal synaptic integration. Neuron 19, 665–678 (1997).
Fricker, D. & Miles, R. EPSP amplification and the precision of spike timing in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 28, 559–569 (2001).
De Schutter, E. Dendritic voltage and calcium-gated channels amplify the variability of postsynaptic responses in a Purkinje cell model. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 504–519 (1998).
Reinagel, P., Godwin, D., Sherman, S. M. & Koch, C. Encoding of visual information by LGN bursts. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 2558–2569 (1999).
Magee, J. C. & Cook, E. P. Somatic EPSP amplitude is independent of synapse location in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 895–903 (2000).
Reyes, A. Influence of dendritic conductances on the input-output properties of neurons. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 653–675 (2001).
Magee, J. C. Dendritic lh normalizes temporal summation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 508–514 (1999).
Hines, M. L. & Carnevale, N. T. The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comput. 9, 1179–1209 (1997).
Cover, T. M. & Thomas, J. A. Elements of Information Theory (Wiley, New York, 1991).
Treves, A. & Panzeri, S. The upward bias in measures of information derived from limited data samples. Neural Comput. 7, 399–407 (1995).
Strong, S. P., Koberle, R., de Ruyter van Steveninck, R. & Bialek, W. Entropy and information in neuronal spike trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 197–201 (1997).
Schultz, S. R. & Panzeri, S. Temporal correlations and neural spike train entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5823–5826 (2001).
Contreras, D., Destexhe, A. & Steriade, M. Intracellular and computational characterization of the intracortical inhibitory control of synchronized thalamic inputs in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 78, 335–350 (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank R. El-Yaniv for his help in developing the entropy estimation method. This work was supported by grants from the ONR, NIMH, the US-Israel BSF, the Israel Science Foundation and the Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
London, M., Schreibman, A., Häusser, M. et al. The information efficacy of a synapse. Nat Neurosci 5, 332–340 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn826
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn826
This article is cited by
-
Human Purkinje cells outperform mouse Purkinje cells in dendritic complexity and computational capacity
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Illuminating dendritic function with computational models
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2020)
-
Spatiotemporal model of tripartite synapse with perinodal astrocytic process
Journal of Computational Neuroscience (2020)
-
Through synapses to spatial memory maps via a topological model
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Quantitative firing pattern phenotyping of hippocampal neuron types
Scientific Reports (2019)