Abstract
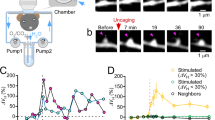
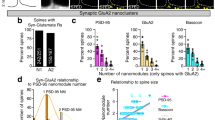
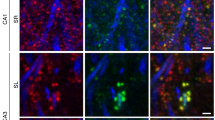
Dendritic spines serve as preferential sites of excitatory synaptic connections and are pleomorphic. To address the structure–function relationship of the dendritic spines, we used two-photon uncaging of glutamate to allow mapping of functional glutamate receptors at the level of the single synapse. Our analyses of the spines of CA1 pyramidal neurons reveal that AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid)-type glutamate receptors are abundant (up to 150/spine) in mushroom spines but sparsely distributed in thin spines and filopodia. The latter may be serving as the structural substrates of the silent synapses that have been proposed to play roles in development and plasticity of synaptic transmission. Our data indicate that distribution of functional AMPA receptors is tightly correlated with spine geometry and that receptor activity is independently regulated at the level of single spines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliss, T. V. & Collingridge, G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39 (1993).
Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Long-term potentiation—a decade of progress? Science 285, 1870–1874 (1999).
Ziff, E. B. Enlightening the postsynaptic density. Neuron 19, 1163–1174 (1997).
Naisbitt, S. et al. Interaction of the postsynaptic density-95/guanylate kinase domain-associated protein complex with a light chain of myosin-V and dynein. J. Neurosci. 20, 4524–4534 (2000).
Shen, L., Liang, F., Walensky, L. D. & Huganir, R. L. Regulation of AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit surface expression by a 4.1N-linked actin cytoskeletal association. J. Neurosci. 20, 7932–7940 (2000).
Song, I. et al. Interaction of the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor with AMPA receptors. Neuron 21, 393–400 (1998).
Lissin, D. V. et al. Activity differentially regulates the surface expression of synaptic AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7097–7102 (1998).
Luscher, C. et al. Role of AMPA receptor cycling in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Neuron 24, 649–658 (1999).
Turrigiano, G. G. AMPA receptors unbound: membrane cycling and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 26, 5–8 (2000).
Shi, S., Hayashi, Y., Esteban, J. A. & Malinow, R. Subunit-specific rules governing AMPA receptor trafficking to synapses in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell 105, 331–343 (2001).
Benke, T. A., Luthi, A., Isaac, J. T. & Collingridge, G. L. Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature 393, 793–797 (1998).
Lee, H. K., Barbarosie, M., Kameyama, K., Bear, M. F. & Huganir, R. L. Regulation of distinct AMPA receptor phosphorylation sites during bidirectional synaptic plasticity. Nature 405, 955–959 (2000).
Harris, K. M. & Stevens, J. K. Dendritic spines of CA 1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus: serial electron microscopy with reference to their biophysical characteristics. J. Neurosci. 9, 2982–2997 (1989).
Yuste, R. & Denk, W. Dendritic spines as basic functional units of neuronal integration. Nature 375, 682–684 (1995).
Svoboda, K., Tank, D. W. & Denk, W. Direct measurement of coupling between dendritic spines and shafts. Science 272, 716–719 (1996).
Shepherd, G. M. The dendritic spine: a multifunctional integrative unit. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 2197–2210 (1996).
Arbib, M. A. The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1995).
Cajal, R. y. Histologie du Systeme Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertebres (Maloine, Paris, 1911).
Nusser, Z. et al. Cell type and pathway dependence of synaptic AMPA receptor number and variability in the hippocampus. Neuron 21, 545–559 (1998).
Takumi, Y., Ramirez-Leon, V., Laake, P., Rinvik, E. & Ottersen, O.P. Different modes of expression of AMPA and NMDA receptors in hippocampal synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 618–624 (1999).
Segal, M., Korkotian, E. & Murphy, D. D. Dendritic spine formation and pruning: common cellular mechanisms? Trends Neurosci. 23, 53–57 (2000).
Halpain, S. Actin and the agile spine: how and why do dendritic spines dance? Trends Neurosci. 23, 141–146 (2000).
Liu, G., Choi, S. & Tsien, R. W. Variability of neurotransmitter concentration and nonsaturation of postsynaptic AMPA receptors at synapses in hippocampal cultures and slices. Neuron 22, 395–409 (1999).
Denk, W. Two-photon scanning photochemical microscopy: mapping ligand-gated ion channel distributions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 6629–6633 (1994).
Pettit, D. L., Wang, S. S., Gee, K. R. & Augustine, G. J. Chemical two-photon uncaging: a novel approach to mapping glutamate receptors. Neuron 19, 465–471 (1997).
Furuta, T. et al. Brominated 7-hydroxycoumarin-4-ylmethyls: photolabile protecting groups with biologically useful cross-sections for two photon photolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1193–1200 (1999).
Wang, S. S., Khiroug, L. & Augustine, G. J. Quantification of spread of cerebellar long-term depression with chemical two-photon uncaging of glutamate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8635–8640 (2000).
Rusakov, D. A. & Kullmann, D. M. Extrasynaptic glutamate diffusion in the hippocampus: ultrastructural constraints, uptake, and receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 18, 3158–3170 (1998).
Hopt, A. & Neher, E. Highly nonlinear photodamage in two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Biophys. J. 80, 2029–2036 (2001).
Xu, C. & Webb, W. W. Measurement of two-photon excitaiton cross sections of molecular fluorophores with data from 690 to 1050 nm. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 481–491 (1996).
Jonas, P. & Sakmann, B. Glutamate receptor channels in isolated patches from CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 455, 143–171 (1992).
Gomperts, S. N., Rao, A., Craig, A. M., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Postsynaptically silent synapses in single neuron cultures. Neuron 21, 1443–1451 (1998).
McAllister, A. K. & Stevens, C. F. Nonsaturation of AMPA and NMDA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6173–6178 (2000).
Durand, G. M., Kovalchuk, Y. & Konnerth, A. Long-term potentiation and functional synapse induction in developing hippocampus. Nature 381, 71–75 (1996).
Petralia, R. S. et al. Selective acquisition of AMPA receptors over postnatal development suggests a molecular basis for silent synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 31–36 (1999).
Sigworth, F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 307, 97–129 (1980).
Spruston, N., Jonas, P. & Sakmann, B. Dendritic glutamate receptor channels in rat hippocampal CA3 and CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 482, 325–352 (1995).
Silver, R. A., Cull-Candy, S. G. & Takahashi, T. Non-NMDA glutamate receptor occupancy and open probability at a rat cerebellar synapse with single and multiple release sites. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 494, 231–250 (1996).
Buchs, P. A. & Muller, D. Induction of long-term potentiation is associated with major ultrastructural changes of activated synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8040–8045 (1996).
Engert, F. & Bonhoeffer, T. Dendritic spine changes associated with hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Nature 399, 66–70 (1999).
Maletic-Savatic, M., Malinow, R. & Svoboda, K. Rapid dendritic morphogenesis in CA1 hippocampal dendrites induced by synaptic activity. Science 283, 1923–1927 (1999).
Lendvai, B., Stern, E. A., Chen, B. & Svoboda, K. Experience-dependent plasticity of dendritic spines in the developing rat barrel cortex in vivo. Nature 404, 876–881 (2000).
Shi, S. H. et al. Rapid spine delivery and redistribution of AMPA receptors after synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Science 284, 1811–1816 (1999).
Fiala, J. C., Feinberg, M., Popov, V. & Harris, K. M. Synaptogenesis via dendritic filopodia in developing hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 8900–8911 (1998).
Tsubokawa, H. & Ross, W. N. IPSPs modulate spike backpropagation and associated [Ca2+]i changes in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 76, 2896–2906 (1996).
Papageorgiou, G. & Corrie, J. E. T. Effects of aromatic substituents on the photocleavage of 1-acyl-7-nitroindolines. Tetrahedron 56, 8197–8205 (2001).
Nemoto, T. et al. Sequential-replenishment mechanism of exocytosis in pancreatic acini. Nat. Cell. Biol. 3, 253–258 (2001).
Brown, E. B., Shear, J. B., Adams, S. R., Tsien, R. Y. & Webb, W. W. Photolysis of caged calcium in femtoliter volumes using two-photon excitation. Biophys. J. 76, 489–499 (1999).
Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1975).
Diamond, J. S. & Jahr, C. E. Transporters buffer synaptically released glutamate on a submillisecond time scale. J. Neurosci. 17, 4672–4687 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Adams for a sample of azid-1, H. Tsubokawa for helpful suggestions on hippocampal slice experiments, R. Nichols for comments on the manuscript and R. Ijuin for technical assistance. This work was supported by CREST (Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology) of the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST); the Research for the Future program of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS); Grants-in-Aid from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology; and NIH (GM53395). M.M. was a JSPS research fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuzaki, M., Ellis-Davies, G., Nemoto, T. et al. Dendritic spine geometry is critical for AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 4, 1086–1092 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn736
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn736
This article is cited by
-
Activation of prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons ameliorates working memory deficit even under clinically comparable antipsychotic treatment in a mouse model of schizophrenia
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Disrupted Maturation of Prefrontal Layer 5 Neuronal Circuits in an Alzheimer’s Mouse Model of Amyloid Deposition
Neuroscience Bulletin (2023)
-
Initiation of dendritic NMDA spikes co-regulated via distance-dependent and dynamic distribution of the spine number and morphology in neuron dendrites
Science China Technological Sciences (2023)
-
The emergence of molecular systems neuroscience
Molecular Brain (2022)
-
Roles of neuroligins in central nervous system development: focus on glial neuroligins and neuron neuroligins
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)