Abstract
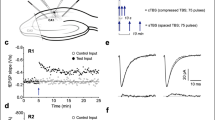
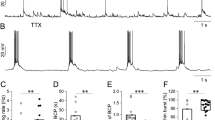
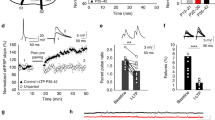
Hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) induced by theta-burst pairing of Schaffer collateral inputs and postsynaptic firing is associated with localized increases in synaptic strength and dendritic excitability. Using the same protocol, we now demonstrate a decrease in cellular excitability that was blocked by the h-channel blocker ZD7288. This decrease was also induced by postsynaptic theta-burst firing alone, yet it was blocked by NMDA receptor antagonists, postsynaptic Ca2+ chelation, low concentrations of tetrodotoxin, ω-conotoxin MVIIC, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitors and a protein synthesis inhibitor. Increasing network activity with high extracellular K+ caused a similar reduction of cellular excitability and an increase in h-channel HCN1 protein. We propose that backpropagating action potentials open glutamate-bound NMDA receptors, resulting in an increase in Ih and a decrease in overall excitability. The occurrence of such a reduction in cellular excitability in parallel with synaptic potentiation would be a negative feedback mechanism to normalize neuronal output firing and thus promote network stability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 December 2005
The PDF version of this article was corrected on December 14, 2005. Please see the PDF for details.
References
Bliss, T.V. & Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39 (1993).
Andersen, P., Sundberg, S.H., Sveen, O., Swann, J.W. & Wigstrom, H. Possible mechanisms for long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices from guinea-pigs. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 302, 463–482 (1980).
Bliss, T.V. & Lomo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 232, 331–356 (1973).
Zhang, W. & Linden, D.J. The other side of the engram: experience-driven changes in neuronal intrinsic excitability. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 885–900 (2003).
Frick, A., Magee, J. & Johnston, D. LTP is accompanied by an enhanced local excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 126–135 (2004).
Spitzer, N.C. A developmental handshake: neuronal control of ionic currents and their control of neuronal differentiation. J. Neurobiol. 22, 659–673 (1991).
Turrigiano, G.G. & Nelson, S.B. Homeostatic plasticity in the developing nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 97–107 (2004).
Cudmore, R.H. & Turrigiano, G.G. Long-term potentiation of intrinsic excitability in LV visual cortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 92, 341–348 (2004).
Desai, N.S., Rutherford, L.C. & Turrigiano, G.G. Plasticity in the intrinsic excitability of cortical pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 515–520 (1999).
Turrigiano, G., Abbott, L.F. & Marder, E. Activity-dependent changes in the intrinsic properties of cultured neurons. Science 264, 974–977 (1994).
Aizenman, C.D. & Linden, D.J. Rapid, synaptically driven increases in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar deep nuclear neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 109–111 (2000).
Wang, Z., Xu, N.L., Wu, C.P., Duan, S. & Poo, M.M. Bidirectional changes in spatial dendritic integration accompanying long-term synaptic modifications. Neuron 37, 463–472 (2003).
van Welie, I., van Hooft, J.A. & Wadman, W.J. Homeostatic scaling of neuronal excitability by synaptic modulation of somatic hyperpolarization-activated Ih channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 5123–5128 (2004).
Xu, J., Kang, N., Jiang, L., Nedergaard, M. & Kang, J. Activity-dependent long-term potentiation of intrinsic excitability in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 25, 1750–1760 (2005).
Daoudal, G., Hanada, Y. & Debanne, D. Bidirectional plasticity of excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)-spike coupling in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 14512–14517 (2002).
Marder, C.P. & Buonomano, D.V. Timing and balance of inhibition enhance the effect of long-term potentiation on cell firing. J. Neurosci. 24, 8873–8884 (2004).
Roberson, E.D., English, J.D. & Sweatt, J.D. A biochemist's view of long-term potentiation. Learn. Mem. 3, 1–24 (1996).
Watanabe, S., Hoffman, D.A., Migliore, M. & Johnston, D. Dendritic K+ channels contribute to spike-timing dependent long-term potentiation in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 8366–8371 (2002).
Magee, J.C. & Johnston, D. A synaptically controlled, associative signal for Hebbian plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Science 275, 209–213 (1997).
Buzsaki, G. Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron 33, 325–340 (2002).
Thomas, M.J., Watabe, A.M., Moody, T.D., Makhinson, M. & O'Dell, T.J. Postsynaptic complex spike bursting enables the induction of LTP by theta frequency synaptic stimulation. J. Neurosci. 18, 7118–7126 (1998).
Poolos, N.P., Migliore, M. & Johnston, D. Pharmacological upregulation of h-channels reduces the excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 767–774 (2002).
Shah, M.M., Anderson, A.E., Leung, V., Lin, X. & Johnston, D. Seizure-induced plasticity of h channels in entorhinal cortical layer III pyramidal neurons. Neuron 44, 495–508 (2004).
Maccaferri, G., Mangoni, M., Lazzari, A. & DiFrancesco, D. Properties of the hyperpolarization-activated current in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 69, 2129–2136 (1993).
Shin, K.S., Rothberg, B.S. & Yellen, G. Blocker state dependence and trapping in hyperpolarization-activated cation channels: evidence for an intracellular activation gate. J. Gen. Physiol. 117, 91–101 (2001).
Magee, J.C. Dendritic hyperpolarization-activated currents modify the integrative properties of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 18, 7613–7624 (1998).
Johnston, D., Magee, J.C., Colbert, C.M. & Christie, B.R. Active properties of neuronal dendrites. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 165–186 (1996).
Schiller, J., Schiller, Y. & Clapham, D.E. NMDA receptors amplify calcium influx into dendritic spines during associative pre- and postsynaptic activation. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 114–118 (1998).
Mackenzie, P.J. & Murphy, T.H. High safety factor for action potential conduction along axons but not dendrites of cultured hippocampal and cortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 2089–2101 (1998).
Magee, J.C. & Carruth, M. Dendritic voltage-gated ion channels regulate the action potential firing mode of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82, 1895–1901 (1999).
Robinson, R.B. & Siegelbaum, S.A. Hyperpolarization-activated cation currents: from molecules to physiological function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 65, 453–480 (2003).
Nolan, M.F. et al. A behavioral role for dendritic integration: HCN1 channels constrain spatial memory and plasticity at inputs to distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Cell 119, 719–732 (2004).
Saar, D. & Barkai, E. Long-term modifications in intrinsic neuronal properties and rule learning in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 2727–2734 (2003).
Vasilyev, D.V. & Barish, M.E. Postnatal development of the hyperpolarization-activated excitatory current Ih in mouse hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 22, 8992–9004 (2002).
Bender, R.A. et al. Differential and age-dependent expression of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel isoforms 1–4 suggests evolving roles in the developing rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 106, 689–698 (2001).
Zhu, J.J. Maturation of layer 5 neocortical pyramidal neurons: amplifying salient layer 1 and layer 4 inputs by Ca2+ action potentials in adult rat tuft dendrites. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 526, 571–587 (2000).
Yuan, L.L., Adams, J.P., Swank, M., Sweatt, J.D. & Johnston, D. Protein kinase modulation of dendritic K+ channels in hippocampus involves a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Neurosci. 22, 4860–4868 (2002).
Magee, J.C. Dendritic Ih normalizes temporal summation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 508 (1999).
Berger, T., Larkum, M.E. & Luscher, H.R. High I(h) channel density in the distal apical dendrite of layer V pyramidal cells increases bidirectional attenuation of EPSPs. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 855–868 (2001).
Berger, T. & Luscher, H.R. Associative somatodendritic interaction in layer V pyramidal neurons is not affected by the antiepileptic drug lamotrigine. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 1688–1693 (2004).
Frick, A., Magee, J., Koester, H.J., Migliore, M. & Johnston, D. Normalization of Ca2+ signals by small oblique dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 23, 3243–3250 (2003).
Berridge, M.J. Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron 21, 13–26 (1998).
Erondu, N.E. & Kennedy, M.B. Regional distribution of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 5, 3270–3277 (1985).
Shen, K. & Meyer, T. Dynamic control of CaMKII translocation and localization in hippocampal neurons by NMDA receptor stimulation. Science 284, 162–166 (1999).
Lisman, J., Schulman, H. & Cline, H. The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 175–190 (2002).
Santoro, B., Wainger, B.J. & Siegelbaum, S.A. Regulation of HCN channel surface expression by a novel C-terminal protein-protein interaction. J. Neurosci. 24, 10750–10762 (2004).
Bi, G. & Poo, M. Synaptic modification by correlated activity: Hebb's postulate revisited. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 139–166 (2001).
Bienenstock, E.L., Cooper, L.N. & Munro, P.W. Theory for the development of neuron selectivity: orientation specificity and binocular interaction in visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 2, 32–48 (1982).
Ganguly, K., Kiss, L. & Poo, M. Enhancement of presynaptic neuronal excitability by correlated presynaptic and postsynaptic spiking. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1018–1026 (2000).
Pouille, F. & Scanziani, M. Enforcement of temporal fidelity in pyramidal cells by somatic feed-forward inhibition. Science 293, 1159–1163 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Gray, N. Poolos and A. Frick for discussions and help with data acquisition and analysis software. We also thank W.S. She for technical help with western blotting. This work was supported by US NIH grants MH48432, MH44754 and NS37444 (D.J.) and NS48884 and AHA0465158Y (H.-C.L.); a fellowship from the American Heart Association (Y.F.); and a fellowship from the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (D.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
EPSP-spike transitions at an expanded time scale. (PDF 238 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Sag ratio increased after LTP. (PDF 372 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
TBP-LTP but not 100 Hz-LTP was accompanied by a decrease in RN. (PDF 683 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
TBF-induced decrease in excitability could be prevented by ZD7288. (PDF 1244 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Background synaptic inputs were less efficient after TBF. (PDF 769 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 6
A brief episode of extracellular high K+ challenge produced a reduction in input resistance similar to TBF. (PDF 1496 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 7
High extracellular K+ stimulated differential regulation of HCN protein levels. (PDF 1724 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Fricker, D., Brager, D. et al. Activity-dependent decrease of excitability in rat hippocampal neurons through increases in Ih. Nat Neurosci 8, 1542–1551 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1568
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1568
This article is cited by
-
Reduced expression of the psychiatric risk gene DLG2 (PSD93) impairs hippocampal synaptic integration and plasticity
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Effect of ivabradine on cognitive functions of rats with scopolamine-induced dementia
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The impact of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) and voltage-gated potassium KCNQ/Kv7 channels on primary microglia function
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2020)
-
An axon-specific expression of HCN channels catalyzes fast action potential signaling in GABAergic interneurons
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Intrinsic neuronal properties represent song and error in zebra finch vocal learning
Nature Communications (2020)