Abstract
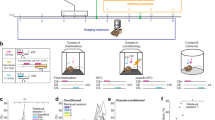
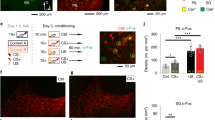
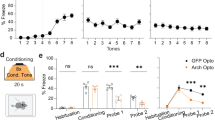
Defensive responses elicited by sensory experiences are critical for survival. Mice acquire a conditioned fear response rapidly to an auditory cue but slowly to a visual cue, a difference in learned behavior that is likely to be mediated by direct projections to the lateral amygdala from the auditory thalamus but mainly indirect ones from the visual thalamus. Here, we show that acquisition of visually cued conditioned fear is accelerated in 'rewired' mice that have retinal projections routed to the auditory thalamus. Visual stimuli induce expression of the immediate early gene Fos (also known as c-fos) in the auditory thalamus and the lateral amygdala in rewired mice, similar to the way auditory stimuli do in control mice. Thus, the rewired auditory pathway conveys visual information and mediates rapid activity-dependent plasticity in central structures that influence learned behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiesel, T.N. & Hubel, D.H. Single-cell responses in striate cortex of kittens deprived of vision in one eye. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 1003–1017 (1963).
Hubel, D.H. & Wiesel, T.N. & LeVay, S. Plasticity of ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 278, 377–409 (1977).
Merzenich, M.M. et al. Somatosensory cortical map changes following digit amputation in adult monkeys. J. Comp. Neurol. 224, 591–605 (1984).
Kaas, J.H. et al. Reorganization of retinotopic cortical maps in adult mammals after lesions of the retina. Science 248, 229–231 (1990).
Mitchell, D.E. The extent of visual recovery from early monocular or binocular visual deprivation in kittens. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 395, 639–660 (1988).
Mitchell, D.E. The long-term effectiveness of different regimens of occlusion on recovery from early monocular deprivation in kittens. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 333, 51–79 (1991).
Ramachandran, V.S., Stewart, M. & Rogers-Ramachandran, D.C. Perceptual correlates of massive cortical reorganization. Neuroreport 3, 583–586 (1992).
Dietrich, V., Nieschalk, M., Stoll, W., Rajan, R. & Pantev, C. Cortical reorganization in patients with high frequency cochlear hearing loss. Hear. Res. 158, 95–101 (2001).
von Melchner, L., Pallas, S.L. & Sur, M. Visual behaviour mediated by retinal projections directed to the auditory pathway. Nature 404, 871–876 (2000).
Fendt, M. & Fanselow, M.S. The neuroanatomical and neurochemical basis of conditioned fear. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 23, 743–760 (1999).
LeDoux, J.E. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 155–184 (2000).
Heldt, S., Sundin, V., Willott, J.F. & Falls, W.A. Posttraining lesions of the amygdala interfere with fear-potentiated startle to both visual and auditory conditioned stimuli in C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Neurosci. 114, 749–759 (2000).
Rogan, M.T. & LeDoux, J.E. LTP is accompanied by commensurate enhancement of auditory-evoked responses in a fear conditioning circuit. Neuron 15, 127–136 (1995).
Doron, N.N. & LeDoux, J.E. Organization of projections to the lateral amygdala from auditory and visual areas of the thalamus in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 412, 383–409 (1999).
Namura, S., Takada, M., Kikuchi, H. & Mizuno, N. Collateral projections of single neurons in the posterior thalamic region to both the temporal cortex and the amygdala: a fluorescent retrograde double-labeling study in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 384, 59–70 (1997).
LeDoux, J.E., Sakaguchi, A. & Reis, D.J. Subcortical efferent projections of the medial geniculate nucleus mediate emotional responses conditioned to acoustic stimuli. J. Neurosci. 4, 683–698 (1984).
Quirk, G.J., Repa, C. & LeDoux, J.E. Fear conditioning enhances short-latency auditory responses of lateral amygdala neurons: parallel recordings in the freely behaving rat. Neuron 15, 1029–1039 (1995).
Quirk, G.J., Armony, J.L. & LeDoux, J.E. Fear conditioning enhances different temporal components of tone-evoked spike trains in auditory cortex and lateral amygdala. Neuron 19, 613–624 (1997).
Shi, C. & Davis, M. Visual pathways involved in fear conditioning measured with fear-potentiated startle: behavioral and anatomic studies. J. Neurosci. 21, 9844–9855 (2001).
Lyckman, A.W. et al. Enhanced plasticity of retinothalamic projections in an ephrin-A2/A5 double mutant. J. Neurosci. 21, 7684–7690 (2001).
Sur, M., Garraghty, P.E. & Roe, A.W. Experimentally induced visual projections into auditory thalamus and cortex. Science 242, 1437–1441 (1988).
Roe, A.W., Pallas, S.L., Hahm, J.O. & Sur, M. A map of visual space induced in primary auditory cortex. Science 250, 818–820 (1990).
Roe, A.W., Pallas, S.L., Kwon, Y.H. & Sur, M. Visual projections routed to the auditory pathway in ferrets: receptive fields of visual neurons in primary auditory cortex. J. Neurosci. 12, 3651–3664 (1992).
Roe, A.W., Garraghty, P.E., Esguerra, M. & Sur, M. Experimentally induced visual projections to the auditory thalamus in ferrets: evidence for a W cell pathway. J. Comp. Neurol. 334, 263–280 (1993).
Sharma, J., Angelucci, A. & Sur, M. Induction of visual orientation modules in auditory cortex. Nature 404, 841–847 (2000).
Schneider, G.E. Early lesions of superior colliculus: factors affecting the formation of abnormal retinal projections. Brain Behav. Evol. 8, 73–109 (1973).
Kalil, R.E. & Schneider, G.E. Abnormal synaptic connections of the optic tract in the thalamus after midbrain lesions in newborn hamsters. Brain Res. 100, 690–698 (1975).
Frost, D.O. Anomalous visual connections to somatosensory and auditory systems following brain lesions in early life. Brain Res. 255, 627–635 (1982).
Frost, D.O. & Metin, C. Induction of functional retinal projections to the somatosensory system. Nature 317, 162–164 (1985).
Kim, S.D., Rivers, S., Bevins, R.A. & Ayres, J.J.B. Conditioned stimulus determinants of conditioned response form in pavlovian fear conditioning. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 22, 87–104 (1996).
Angelucci, A., Clasca, F. & Sur, M. Brainstem inputs to the ferret medial geniculate nucleus and the effect of early deafferentation on novel retinal projections to the auditory thalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 400, 417–439 (1998).
Fanselow, M.S. & LeDoux, J.E. Why we think plasticity underlying Pavlovian fear conditioning occurs in the basolateral amygdala. Neuron 23, 229–232 (1999).
Rogan, M.T., Staubli, U.V. & LeDoux, J.E. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala. Nature 390, 604–607 (1997).
Tang, Y.P. et al. Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401, 63–69 (1999).
Katz, L.C. & Shatz, C.J. Synaptic activity and the construction of cortical circuits. Science 274, 1133–1138 (1996).
Newton, J.R. & Sur, M. Plasticity of cerebral cortex in development. in Encyclopedia of Neuroscience edn. 3 (eds. Adelman, G. & Smith, B.H.) (Elsevier, New York, 2004).
Damasio, A.R. et al. Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1049–1056 (2000).
Buchel, C., Morris, J., Dolan, R.J. & Friston, K.J. Brain systems mediating aversive conditioning: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron 20, 947–957 (1998).
LaBar, K.S., Gatenby, J.C., Gore, J.C., LeDoux, J.E. & Phelps, E.A. Human amygdala activation during conditioned fear acquisition and extinction: a mixed-trial fMRI study. Neuron 20, 937–945 (1998).
Adolphs, R., Tranel, D., Damasio, H. & Damasio, A. Impaired recognition of emotion in facial expressions following bilateral damage to the human amygdala. Nature 372, 669–672 (1994).
Bechara, A. et al. Double dissociation of conditioning and declarative knowledge relative to the amygdala and hippocampus in humans. Science 269, 1115–1118 (1995).
Miyakawa, T., Yamada, M., Duttaroy, A. & Wess, J. Hyperactivity and intact hippocampus-dependent learning in mice lacking the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Neurosci. 21, 5239–5250 (2001).
Williams, R.W. & Rakic, P. Three-dimensional counting: an accurate and direct method to estimate numbers of cells in sectioned material. J. Comp. Neurol. 278, 344–352 (1988).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Majewska and A. Lyckman for their assistance with the c-fos experiments. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (F32 EY13900 to J.R.N., R01 NS32925 and P50 MH58880 to S.T., and R01 EY14134 and R01 EY15068 to M.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Lesion site. Coronal sections are shown at the same level of the inferior colliculus for (a) a sham lesion and (b) a rewired mouse. Dark label in dorsal part of A shows retinal projections to the far posterior superior colliculus following bilateral intraocular injection of cholera toxin subunit B. Scale bar, 1 mm. D, dorsal, M, medial, IC = inferior colliculus. (JPG 18 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Retinothalamic projections. Coronal sections are shown at the same level of the thalamus for (a) a sham lesion, (b) a rewired and (c) a SC lesion mouse. Retinal projections were labeled by intraocular injection of cholera toxin subunit B. Scale bar, 0.1 mm. D, dorsal, M, medial, LP = lateral posterior nucleus, MGN = medial geniculate nucleus. (JPG 42 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Summary of the number of mice in each group. (PDF 9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newton, J., Ellsworth, C., Miyakawa, T. et al. Acceleration of visually cued conditioned fear through the auditory pathway. Nat Neurosci 7, 968–973 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1306
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1306
This article is cited by
-
Hippocampus as a sorter and reverberatory integrator of sensory inputs
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Light-induced charge generation in polymeric nanoparticles restores vision in advanced-stage retinitis pigmentosa rats
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Sound check, stage design and screen plot – how to increase the comparability of fear conditioning and fear extinction experiments
Psychopharmacology (2019)
-
The Challenges of Integrating Behavioral and Neural Data: Bridging and Breaking Boundaries Across Levels of Analysis
The Behavior Analyst (2017)
-
Probing perceptual decisions in rodents
Nature Neuroscience (2013)