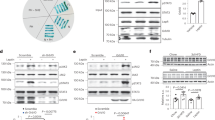
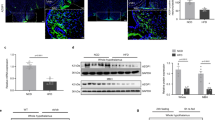
Abstract
Leptin regulates energy balance. However, knowledge of the critical intracellular transducers of leptin signaling remains incomplete. We found that Rho-kinase 1 (ROCK1) regulates leptin action on body weight homeostasis by activating JAK2, an initial trigger of leptin receptor signaling. Leptin promoted the physical interaction of JAK2 and ROCK1, thereby increasing phosphorylation of JAK2 and downstream activation of Stat3 and FOXO1. Mice lacking ROCK1 in either pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) or agouti-related protein neurons, mediators of leptin action, displayed obesity and impaired leptin sensitivity. In addition, deletion of ROCK1 in the arcuate nucleus markedly enhanced food intake, resulting in severe obesity. Notably, ROCK1 was a specific mediator of leptin, but not insulin, regulation of POMC neuronal activity. Our data identify ROCK1 as a key regulator of leptin action on energy homeostasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjørbaek, C. Central leptin receptor action and resistance in obesity. J. Investig. Med. 57, 789–794 (2009).
Morton, G.J., Cummings, D.E., Baskin, D.G., Barsh, G.S. & Schwartz, M.W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443, 289–295 (2006).
Myers, M.G., Cowley, M.A. & Munzberg, H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 70, 537–556 (2008).
Elmquist, J.K., Coppari, R., Balthasar, N., Ichinose, M. & Lowell, B.B. Identifying hypothalamic pathways controlling food intake, body weight, and glucose homeostasis. J. Comp. Neurol. 493, 63–71 (2005).
Elmquist, J.K., Elias, C.F. & Saper, C.B. From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22, 221–232 (1999).
Myers, M.G. Jr., Munzberg, H., Leinninger, G.M. & Leshan, R.L. The geometry of leptin action in the brain: more complicated than a simple ARC. Cell Metab. 9, 117–123 (2009).
Cheung, C.C., Clifton, D.K. & Steiner, R.A. Proopiomelanocortin neurons are direct targets for leptin in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 138, 4489–4492 (1997).
Wilson, B.D. et al. Physiological and anatomical circuitry between Agouti-related protein and leptin signaling. Endocrinology 140, 2387–2397 (1999).
van den Top, M., Lee, K., Whyment, A.D., Blanks, A.M. & Spanswick, D. Orexigen-sensitive NPY/AgRP pacemaker neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 493–494 (2004).
Mizuno, T.M. et al. Hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA is reduced by fasting and [corrected] in ob/ob and db/db mice, but is stimulated by leptin. Diabetes 47, 294–297 (1998).
Schwartz, M.W. et al. Leptin increases hypothalamic pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA expression in the rostral arcuate nucleus. Diabetes 46, 2119–2123 (1997).
Thornton, J.E., Cheung, C.C., Clifton, D.K. & Steiner, R.A. Regulation of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin mRNA by leptin in ob/ob mice. Endocrinology 138, 5063–5066 (1997).
Balthasar, N. et al. Leptin receptor signaling in POMC neurons is required for normal body weight homeostasis. Neuron 42, 983–991 (2004).
van de Wall, E. et al. Collective and individual functions of leptin receptor modulated neurons controlling metabolism and ingestion. Endocrinology 149, 1773–1785 (2008).
Matsui, T. et al. Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J. 15, 2208–2216 (1996).
Hu, E. & Lee, D. Rho kinase as potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases: opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 9, 715–736 (2005).
Chun, K.H. et al. In vivo activation of ROCK1 by insulin is impaired in skeletal muscle of humans with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 300, E536–E542 (2011).
Begum, N., Sandu, O.A., Ito, M., Lohmann, S.M. & Smolenski, A. Active Rho kinase (ROK-alpha) associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and inhibits insulin signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6214–6222 (2002).
Furukawa, N. et al. Role of Rho-kinase in regulation of insulin action and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2, 119–129 (2005).
Lee, D.H. et al. Targeted disruption of ROCK1 causes insulin resistance in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 11776–11780 (2009).
Chun, K.H. et al. Regulation of glucose transport by ROCK1 differs from that of ROCK2 and is controlled by actin polymerization. Endocrinology 153, 1649–1662 (2012).
Hill, J.W. et al. Acute effects of leptin require PI3K signaling in hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neurons in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 1796–1805 (2008).
Al-Qassab, H. et al. Dominant role of the p110beta isoform of PI3K over p110alpha in energy homeostasis regulation by POMC and AgRP neurons. Cell Metab. 10, 343–354 (2009).
Plum, L. et al. Enhanced PIP3 signaling in POMC neurons causes KATP channel activation and leads to diet-sensitive obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1886–1901 (2006).
Cota, D. et al. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science 312, 927–930 (2006).
Fukuda, M. et al. Monitoring FoxO1 localization in chemically identified neurons. J. Neurosci. 28, 13640–13648 (2008).
Coppari, R. et al. The hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: a key site for mediating leptin's effects on glucose homeostasis and locomotor activity. Cell Metab. 1, 63–72 (2005).
Mesaros, A. et al. Activation of Stat3 signaling in AgRP neurons promotes locomotor activity. Cell Metab. 7, 236–248 (2008).
Huo, L. et al. Leptin-dependent control of glucose balance and locomotor activity by POMC neurons. Cell Metab. 9, 537–547 (2009).
Cowley, M.A. et al. Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 411, 480–484 (2001).
Ren, D., Li, M., Duan, C. & Rui, L. Identification of SH2-B as a key regulator of leptin sensitivity, energy balance and body weight in mice. Cell Metab. 2, 95–104 (2005).
Bates, S.H. et al. STAT3 signaling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 421, 856–859 (2003).
Xu, A.W., Ste-Marie, L., Kaelin, C.B. & Barsh, G.S. Inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in proopiomelanocortin (Pomc) neurons causes decreased pomc expression, mild obesity, and defects in compensatory refeeding. Endocrinology 148, 72–80 (2007).
Dhillon, H. et al. Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight homeostasis. Neuron 49, 191–203 (2006).
Yoshii, A. & Constantine-Paton, M. Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB signaling in synapse maturation, plasticity, and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 70, 304–322 (2010).
Mellon, P.L. et al. Immortalization of hypothalamic GnRH neurons by genetically targeted tumorigenesis. Neuron 5, 1–10 (1990).
Bjørbaek, C., Uotani, S., da Silva, B. & Flier, J.S. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32686–32695 (1997).
Bacia, K., Kim, S.A. & Schwille, P. Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy in living cells. Nat. Methods 3, 83–89 (2006).
Tong, Q., Ye, C.P., Jones, J.E., Elmquist, J.K. & Lowell, B.B. Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 998–1000 (2008).
van den Pol, A.N. et al. Neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide excite arcuate nucleus neuropeptide Y neurons in a novel transgenic mouse expressing strong Renilla green fluorescent protein in NPY neurons. J. Neurosci. 29, 4622–4639 (2009).
Huo, L., Grill, H.J. & Bjorbaek, C. Divergent regulation of proopiomelanocortin neurons by leptin in the nucleus of the solitary tract and in the arcuate hypothalamic nucleus. Diabetes 55, 567–573 (2006).
Balthasar, N. et al. Divergence of melanocortin pathways in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. Cell 123, 493–505 (2005).
Kim, M.S. et al. Role of hypothalamic Foxo1 in the regulation of food intake and energy homeostasis. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 901–906 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank B. Kahn and T. Flier for valuable suggestions; L. Huo, S.D. Ha, S. Baver, S. Yee, T. Liu, S.-M. Hong, N. Wang, D. Kim, B. Enkhjargal for technical assistance, and L. Wei for DN-Rock1 cDNA. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (1R01DK083567 to Y.-B.K., 5R01CA127247 to S.W.L. and P30DK057521 to D.K.) and the American Diabetes Association (1-09-RA-87 to Y.-B.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.-B.K., H.H. and B.B.L. designed the study. J.M.Z. and C.B. provided conceptual advice. H.H. performed most of the mice experiments and some of the in vitro studies. D.K. generated several lines of model mice. K.H.B. and B.L. performed most of the in vitro studies, including PLA and FCCS experiments. C.Y. was responsible for the electrophysiology studies. S.K. carried out AAV injection experiments. D.H.L. bred and maintained Rock1loxP/loxP mice. S.W.L. generated adenovirus encoding ROCK1. B.-C.O. performed immunoblotting analyses. M.S.K. performed food intake studies with adenovirus. C.B. carried out immunohistochemistry experiments. All of the authors analyzed and interpreted experimental data. J.M.Z., C.B., B.B.L. and Y.-B.K. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9 (PDF 3445 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Kong, D., Byun, K. et al. Rho-kinase regulates energy balance by targeting hypothalamic leptin receptor signaling. Nat Neurosci 15, 1391–1398 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3207
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3207
This article is cited by
-
Hypothalamic Grb10 enhances leptin signalling and promotes weight loss
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
Hypothalamic control of energy expenditure and thermogenesis
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Signaling pathways in obesity: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
RhoA/Rock activation represents a new mechanism for inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the aging-associated bone loss
Cell Regeneration (2021)
-
POMC neuronal heterogeneity in energy balance and beyond: an integrated view
Nature Metabolism (2021)