Abstract
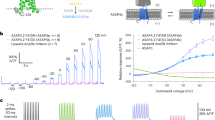
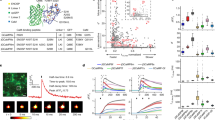
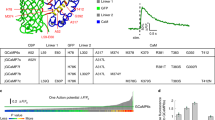
We present a noninvasive approach to track activation of ATP-gated P2X receptors and potentially other transmitter-gated cation channels that show calcium fluxes. We genetically engineered rat P2X receptors to carry calcium sensors near the channel pore and tested this as a reporter for P2X2 receptor opening. The method has several advantages over previous attempts to image P2X channel activation by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET): notably, it reports channel opening rather than a conformation change in the receptor protein. Our FRET-based imaging approach can be used as a general method to track, in real time, the location, regional expression variation, mobility and activation of transmitter-gated P2X channels in living neurons in vitro and in vivo. This approach should help to determine when, where and how different receptors are activated during physiological processes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes 3rd edn (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 2001).
Burnstock, G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol. Rev. 24, 509–581 (1972).
Burnstock, G. Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol. Rev. 87, 659–797 (2007).
Khakh, B.S. & North, R.A. P2X receptors as cell surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature 442, 527–532 (2006).
North, R.A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 82, 1013–1067 (2002).
Chiu, C.-S., Kartalov, E., Unger, M., Quake, S. & Lester, H.A. Single-molecule measurements calibrate green fluorescent protein surface densities on transparent beads for use with 'knock-in' animals and other expression systems. J. Neurosci. Methods 105, 55–63 (2001).
Sugiyama, Y., Kawabata, I., Sobue, K. & Okabe, S. Determination of absolute protein numbers in single synapses by a GFP-based calibration technique. Nat. Methods 2, 677–684 (2005).
Fisher, J.A., Girdler, G. & Khakh, B.S. Time resolved measurement of state specific P2X ion channel cytosolic gating motions. J. Neurosci. 24, 10475–10487 (2004).
Egan, T.M. & Khakh, B.S. Contribution of calcium ions to P2X channel responses. J. Neurosci. 24, 3413–3420 (2004).
Guerrero, G. et al. Heterogeneity in synaptic transmission along a Drosophila larval motor axon. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1188–1196 (2005).
Lee, M.Y. et al. Local subplasma membrane Ca2+ signals detected by a tethered Ca2+ sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13232–13237 (2006).
Tour, O. et al. Calcium Green FlAsH as a genetically targeted small-molecule calcium indicator. Nat. Chem. Biol. 3, 423–431 (2007).
Miyawaki, A. Innovations in the imaging of brain functions using fluorescent proteins. Neuron 48, 189–199 (2005).
Palmer, A.E. & Tsien, R.Y. Measuring calcium signaling using genetically targetable fluorescent indicators. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1057–1065 (2006).
Demuro, A. & Parker, I. 'Optical patch-clamping': single-channel recording by imaging Ca2+ flux through individual muscle acetylcholine receptor channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 126, 179–192 (2005).
Miyawaki, A., Griesbeck, O., Heim, R. & Tsien, R.Y. Dynamic and quantitative Ca2+ measurements using improved cameleons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2135–2140 (1999).
Khakh, B.S. et al. Activation-dependent changes in receptor distribution and dendritic morphology in hippocampal neurons expressing P2X2–green fluorescent protein receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5288–5293 (2001).
Egan, T.M., Samways, D.S. & Li, Z. Biophysics of P2X receptors. Pflugers Arch. 452, 501–512 (2006).
Kanjhan, R. et al. Distribution of the P2X2 receptor subunit of the ATP-gated ion channels in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 407, 11–32 (1999).
Rubio, M.E. & Soto, F. Distinct localisation of P2X receptors at excitatory postsynaptic specializations. J. Neurosci. 21, 641–653 (2001).
Lippincott-Schwartz, J., Snapp, E. & Kenworthy, A. Studying protein dynamics in living cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 444–456 (2001).
Wieraszko, A., Goldsmith, G. & Seyfried, T.N. Stimulation-dependent release of adenosine triphosphate from hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 485, 244–250 (1989).
Pankratov, Y., Castro, E., Miras-Portugal, M.T. & Krishtal, O. A purinergic component of the excitatory postsynaptic current mediated by P2X receptors in the CA1 neurons of the rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3898–3902 (1998).
Pankratov, Y.V., Lalo, U.V. & Krishtal, O.A. Role for P2X receptors in long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 22, 8363–8369 (2002).
Harata, N.C., Aravanis, A.M. & Tsien, R.W. Kiss-and-run and full-collapse fusion as modes of exo-endocytosis in neurosecretion. J. Neurochem. 97, 1546–1570 (2006).
Norton, W.H., Rohr, K.B. & Burnstock, G. Embryonic expression of a P2X(3) receptor encoding gene in zebrafish. Mech. Dev. 99, 149–152 (2000).
Egan, T.M., Cox, J.A. & Voigt, M.M. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the zebrafish ATP-gated ionotropic receptor P2X3 subunit. FEBS Lett. 475, 287–290 (2000).
Boué-Grabot, E., Akimenko, M.A. & Séguéla, P. Unique functional properties of a sensory neuronal P2X ATP-gated channel from zebrafish. J. Neurochem. 75, 1600–1607 (2000).
Diaz-Hernandez, M. et al. Cloning and characterization of two novel zebrafish P2X receptor subunits. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 295, 849–853 (2002).
Kucenas, S., Li, Z., Cox, J.A., Egan, T.M. & Voigt, M.M. Molecular characterization of the zebrafish P2X receptor subunit gene family. Neuroscience 121, 935–945 (2003).
Kucenas, S., Soto, F., Cox, J.A. & Voigt, M.M. Selective labeling of central and peripheral sensory neurons in the developing zebrafish using P2X3 receptor subunit transgenes. Neuroscience 138, 641–652 (2006).
Appelbaum, L., Skariah, G., Mourrain, P. & Mignot, E. Comparative expression of P2X receptors and ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 in hypocretin and sensory neurons in zebrafish. Brain Res. 1174, 66–75 (2007).
Sagasti, A., Guido, M.R., Raible, D.W. & Schier, A.F. Repulsive interactions shape the morphologies and functional arrangement of zebrafish peripheral sensory arbors. Curr. Biol. 15, 804–814 (2005).
Khakh, B.S. et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIV. Current status of the nomenclature and properties of P2X receptors and their subunits. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 107–118 (2001).
Greenwood, D. et al. P2X receptor signaling inhibits BDNF-mediated spiral ganglion neuron development in the neonatal rat cochlea. Development 134, 1407–1417 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank A.F. Schier (Harvard University) for cloning of the Fugu P2X3 enhancer; R.Y. Tsien (University of California San Diego) for providing YC3.1 cDNA; H. Singh and E. Toulme for comments and discussions; J. Fisher for an early version of Supplementary Figure 3; and F. Schweizer and G. David for advice on working with hippocampal neurons and reagents. E.R. was supported by a Molecular Cellular Integrative Physiology Predoctoral Fellowship, a Buschwald Fellowship and a Neural Repair Training Grant Predoctoral Fellowship. E.S. was supported by the Uehara Memorial Foundation (Japan). Zebrafish work was supported by a Burroughs-Wellcome Career Award in the Biomedical Sciences to A.S. The laboratory (B.S.K.) was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Human Frontiers Science Program, the Whitehall Foundation and a Stein/Oppenheimer Endowment Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.R., S.C., E.S. and B.S.K. designed and did the experiments, contributed data, helped to make the figures, and wrote the paper. A.S. contributed laboratory space, made the vectors for the zebrafish work, and helped to make the figures and to write the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8, Supplementary Notes 1–2, Supplementary Methods (PDF 2961 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richler, E., Chaumont, S., Shigetomi, E. et al. Tracking transmitter-gated P2X cation channel activation in vitro and in vivo. Nat Methods 5, 87–93 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1144
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1144
This article is cited by
-
Calcium-dependent regulation of Rab activation and vesicle fusion by an intracellular P2X ion channel
Nature Cell Biology (2014)
-
Measurement of purine release with microelectrode biosensors
Purinergic Signalling (2012)
-
Purinergic signaling: a novel mechanism in immune surveillance
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2010)
-
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
Nature Neuroscience (2010)