Abstract
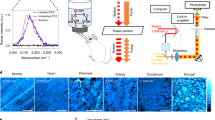
Sensitive and specific visualization of small biomolecules in living systems is highly challenging. We report stimulated Raman-scattering imaging of alkyne tags as a general strategy for studying a broad spectrum of small biomolecules in live cells and animals. We demonstrate this technique by tracking alkyne-bearing drugs in mouse tissues and visualizing de novo synthesis of DNA, RNA, proteins, phospholipids and triglycerides through metabolic incorporation of alkyne-tagged small precursors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, J., Campbell, R.E., Ting, A.Y. & Tsien, R.Y. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 906–918 (2002).
Sasic, S. & Ozaki, Y. Raman, Infrared, and Near-infrared Chemical Imaging (Wiley, 2011).
Cheng, J.-X. & Xie, X.S. Coherent Raman Scattering Microscopy (CRC Press, 2012).
Masters, B.R. & So, P.T.C. Handbook of Biomedical Nonlinear Optical Microscopy (Oxford University Press, 2008).
Prescher, J.A. & Bertozzi, C.R. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 13–21 (2005).
Grammel, M. & Hang, H.C. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9, 475–484 (2013).
Salic, A. & Mitchison, T.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 2415–2420 (2008).
Jao, C.Y. & Salic, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 15779–15784 (2008).
Beatty, K.E. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7364–7367 (2006).
Jao, C.Y., Roth, M., Welti, R. & Salic, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 15332–15337 (2009).
Hang, H.C., Wilson, J.P. & Charron, G. Acc. Chem. Res. 44, 699–708 (2011).
Baskin, J.M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16793–16797 (2007).
Lin-Vien, D., Colthup, N.B., Fateley, W.G. & Grasselli, J.G. The Handbook of Infrared and Raman Characteristic Frequencies of Organic Molecules 95–104 (Academic Press, 1991).
Wei, L., Shen, Y., Yong, Y., Wang, M. & Min, W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 11226–11231 (2013).
Yamakoshi, H. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 6102–6105 (2011).
Yamakoshi, H. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20681–20689 (2012).
Min, W., Freudiger, C.W., Lu, S. & Xie, X.S. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 62, 507–530 (2011).
Freudiger, C.W. et al. Science 322, 1857–1861 (2008).
Moore, K.J. & Tabas, I. Cell 145, 341–355 (2011).
Ashrafi, K. et al. Nature 421, 268–272 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Zhang, L. Brus, V.W. Cornish, D. Peterka and R. Yuste for helpful discussions. We are grateful to Y. Shin and X. Gao for technical assistance. W.M. acknowledges support from Columbia University, a US National Institutes of Health Director's New Innovator Award, the US Army Research Office (W911NF-12-1-0594) and an Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.W., F.H., Y.S., Z.C., Y.Y., C.-C.L. and M.C.W. performed experiments and analyzed data. L.W. and W.M. conceived the concept, designed the experiments and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Columbia University, which L.W., F.H., Y.S., Z.C. and W.M. are affiliated with, has filed a patent application based on this work.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 (PDF 5947 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Hu, F., Shen, Y. et al. Live-cell imaging of alkyne-tagged small biomolecules by stimulated Raman scattering. Nat Methods 11, 410–412 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2878
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2878
This article is cited by
-
Mapping enzyme activity in living systems by real-time mid-infrared photothermal imaging of nitrile chameleons
Nature Methods (2024)
-
Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Transient stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy and imaging
Light: Science & Applications (2024)
-
Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Fast Real-Time Brain Tumor Detection Based on Stimulated Raman Histology and Self-Supervised Deep Learning Model
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine (2024)