Abstract
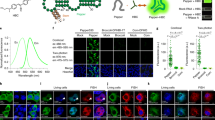
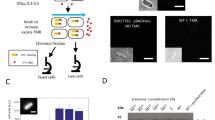
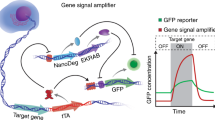
The difficulties in imaging the dynamics of protein expression in live bacterial cells can be overcome by using fluorescent sensors based on Spinach, an RNA that activates the fluorescence of a small-molecule fluorophore. These RNAs selectively bind target proteins and exhibit fluorescence increases that enable protein expression to be imaged in living Escherichia coli. These sensors are key components of a generalizable strategy to image protein expression in a single bacterium in real time.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paige, J.S., Nguyen-Duc, T., Song, W. & Jaffrey, S.R. Science 335, 1194 (2012).
Paige, J.S., Wu, K.Y. & Jaffrey, S.R. Science 333, 642–646 (2011).
Hermann, T. & Patel, D.J. Science 287, 820–825 (2000).
Srisawat, C. & Engelke, D.R. RNA 7, 632–641 (2001).
White, R. et al. Mol. Ther. 4, 567–573 (2001).
Lowary, P.T. & Uhlenbeck, O.C. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 10483–10493 (1987).
Viñuela, E., Algranati, I.D. & Ochoa, S. Eur. J. Biochem. 1, 3–11 (1967).
Ishihama, Y. et al. BMC Genomics 9, 102 (2008).
Wilson, D.S. & Szostak, J.W. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 611–647 (1999).
Tycowski, K.T., Shu, M.D., Borah, S., Shi, M. & Steitz, J.A. Cell Rep. 2, 26–32 (2012).
Aucoin, M.G. et al. Microb. Cell Fact. 5, 27 (2006).
Miroux, B. & Walker, J.E. J. Mol. Biol. 260, 289–298 (1996).
Huang, C.J., Lin, H. & Yang, X. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39, 383–399 (2012).
Makino, T., Skretas, G. & Georgiou, G. Microb. Cell Fact. 10, 32 (2011).
Zuker, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415 (2003).
Ponchon, L. & Dardel, F. Nat. Methods 4, 571–576 (2007).
Howarth, M. et al. Nat. Methods 3, 267–273 (2006).
Brosius, J., Erfle, M. & Storella, J. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3539–3541 (1985).
Adams, M.H. Bacteriophages (Interscience Publishers, New York, 1959).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.S. Paige for useful comments and suggestions and F. Dardel (Université Paris Descartes) for providing plasmids containing the tRNA scaffold sequence. This work was supported by the US National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health, EB010249 (S.R.J.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.S., R.L.S. and S.R.J. conceived and designed the experiments, W.S. and R.L.S. performed experiments and analyzed data, and W.S., R.L.S. and S.R.J. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
S.R.J. and W.S. are authors of a patent application related to technology described in this manuscript.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1-7, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Note (PDF 565 kb)
Source data
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Strack, R. & Jaffrey, S. Imaging bacterial protein expression using genetically encoded RNA sensors. Nat Methods 10, 873–875 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2568
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2568
This article is cited by
-
Unconventional roles of chromatin remodelers and long non-coding RNAs in cell division
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Nucleic acid-based fluorescent sensor systems: a review
Polymer Journal (2022)
-
Optogenetic control of RNA function and metabolism using engineered light-switchable RNA-binding proteins
Nature Biotechnology (2022)
-
Visualizing RNA dynamics in live cells with bright and stable fluorescent RNAs
Nature Biotechnology (2019)
-
Structural basis for activation of fluorogenic dyes by an RNA aptamer lacking a G-quadruplex motif
Nature Communications (2018)