Abstract
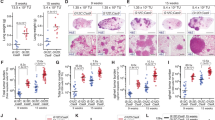
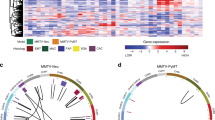
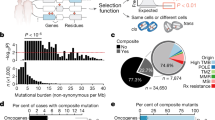
We here establish a mouse cancer model called Multi-Hit that allows for the evaluation of oncogene cooperativities in tumor development. The model is based on the stochastic expression of oncogene combinations ('hits') that are mediated by Cre in a given tissue. Cells with cooperating hits are positively selected and give rise to tumors. We used this approach to evaluate the requirement of Ras downstream effector pathways in tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R.A. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011).
Downward, J. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 11–22 (2003).
Malumbres, M. & Barbacid, M. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 459–465 (2003).
Giehl, K. Biol. Chem. 386, 193–205 (2005).
Repasky, G.A., Chenette, E.J. & Der, C.J. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 639–647 (2004).
Khosravi-Far, R. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 3923–3933 (1996).
Blaas, L. et al. Biotechniques 43, 659–660, 662, 664 (2007).
Zhang, Y., Buchholz, F., Muyrers, J.P. & Stewart, A.F. Nat. Genet. 20, 123–128 (1998).
Rangarajan, A., Hong, S.J., Gifford, A. & Weinberg, R.A. Cancer Cell 6, 171–183 (2004).
DuPage, M., Dooley, A.L. & Jacks, T. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1064–1072 (2009).
McCormick, F. J. Surg. Oncol. 103, 464–467 (2011).
Gupta, S. et al. Cell 129, 957–968 (2007).
Doehn, U. et al. Mol. Cell 35, 511–522 (2009).
Mishra, P.J. et al. Oncogene 29, 2449–2456 (2010).
Drosten, M. et al. EMBO J. 29, 1091–1104 (2010).
Joneson, T., White, M.A., Wigler, M.H. & Bar-Sagi, D. Science 271, 810–812 (1996).
White, M.A. et al. Cell 80, 533–541 (1995).
Chappell, S.A., Edelman, G.M. & Mauro, V.P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9590–9594 (2004).
Yusufzai, T.M. & Felsenfeld, G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8620–8624 (2004).
Hochedlinger, K., Yamada, Y., Beard, C. & Jaenisch, R. Cell 121, 465–477 (2005).
Hameyer, D. et al. Physiol. Genomics 31, 32–41 (2007).
Suzuki, A. et al. Immunity 14, 523–534 (2001).
Vasioukhin, V., Degenstein, L., Wise, B. & Fuchs, E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8551–8556 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Downward (London Research Institute) for Ras effector mutants, A. Berns (Netherlands Cancer Institute) for Rosa26CreERT2 mice and G. Felsenfeld (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, USA) for chicken 2xHS4 insulator sequences. We thank M. Sibilia and E.F. Wagner for critical reading of the manuscript and M. Mair and D. Khan for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Ludwig Boltzmann Gesellschaft (LBG), the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) grant SFB F28 to M. Müller, R.M. and R.E., the FWF Doktoratskolleg-plus grant 'Inflammation and Immunity' to M. Müller and R.E., the CCC Vienna Research grant to E.C. and R.E. and the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science and Research GENAU grant 'Austromouse' to M. Müller, T.R., J.M.P., E.C. and R.E. J.M.P. is supported by the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) and an advanced European Research Council (ERC) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Musteanu performed the study and interpreted data. L.B., R.Z., J.S., T.H., B.G. and D.S. provided major technical support. H.-P.K., M. Müller, T.K., T.R., R.M., L.K., D.S. and J.M.P. provided technical support. H.P. provided histopathological support and interpreted data. E.C. designed and supervised the study. R.E. designed and supervised the study, interpreted data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9. (PDF 2749 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musteanu, M., Blaas, L., Zenz, R. et al. A mouse model to identify cooperating signaling pathways in cancer. Nat Methods 9, 897–900 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2130
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2130
This article is cited by
-
Atypical goblet cell hyperplasia occurs in CPAM 1, 2, and 3, and is a probable precursor lesion for childhood adenocarcinoma
Virchows Archiv (2020)
-
Pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinomas: architectural patterns in correlation with genetic changes, prognosis and survival
Virchows Archiv (2015)
-
Evaluating oncogene cooperativities
Nature Reviews Genetics (2012)