Abstract
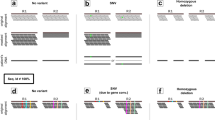
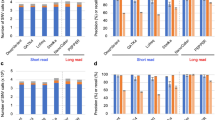
We report an algorithm to detect structural variation and indels from 1 base pair (bp) to 1 Mbp within exome sequence data sets. Splitread uses one end–anchored placements to cluster the mappings of subsequences of unanchored ends to identify the size, content and location of variants with high specificity and sensitivity. The algorithm discovers indels, structural variants, de novo events and copy number–polymorphic processed pseudogenes missed by other methods.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Church, D.M. et al. Nat. Genet. 42, 813–814 (2010).
Sherry, S.T. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 308–311 (2001).
Mills, R.E. et al. Nature 470, 59–65 (2011).
Kidd, J.M. et al. Cell 143, 837–847 (2010).
Ng, S.B. et al. Nature 461, 272–276 (2009).
O'Roak, B.J. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 585–589 (2011).
Depristo, M.A. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 491–498 (2011).
Li, H. et al. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079 (2009).
Ye, K., Schulz, M.H., Long, Q., Apweiler, R. & Ning, Z. Bioinformatics 25, 2865–2871 (2009).
Hach, F. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 576–577 (2010).
Mills, R.E. et al. Genome Res. 21, 830–839 (2011).
Nguyen, T.V. et al. World J. Gastroenterol. 12, 6021–6025 (2006).
Renton, A.E. et al. Neuron 72, 257–268 (2011).
Pearson, C.E., Nichol Edamura, K. & Cleary, J.D. Natl. Rev. 6, 729–742 (2005).
Kidd, J.M. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 365–371 (2010).
Ye, K., Schulz, M.H., Long, Q., Apweiler, R. & Ning, Z. Bioinformatics 25, 2865–2871 (2009).
Hach, F. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 576–577 (2010).
Hamming, R.W. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 29, 147–160 (1950).
Kidd, J.M. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 365–371 (2010).
Hajirasouliha, I. et al. Bioinformatics 26, 1277–1283 (2010).
Karp, R.M. in Complexity of Computer Computations (J.W.T.R.E. Miller, ed.) 85–103 (Plenum, New York, 1972).
Chvatal, V. Math. Oper. Res. 4, 233–235 (1979).
International HapMap Consortium.. Nature 437, 1299–1320 (2005).
O'Roak, B.J. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 585–589 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Brown and S. Girirajan for helpful comments during manuscript preparation. This work was supported by Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative award SFARI191889 (E.E.E.) and US National Institutes of Health grants HD065285 (E.E.E.), HHSN273200800010C (D.A.N.) and HL 102926 (D.A.N.). E.E.E. is funded by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.K. designed and implemented the Splitread algorithm; E.K. and C.A. analyzed data; B.J.O., L.V., M.J.R. and D.A.N. generated sequencing data; M.Y.D. and K.M. carried out validation experiments and analyzed processed pseudogenes and E.K., C.A. and E.E.E. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
E.E.E. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Pacific Biosciences.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1 and 2, Supplementary Tables 1–6 and Supplementary Note (PDF 2526 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karakoc, E., Alkan, C., O'Roak, B. et al. Detection of structural variants and indels within exome data. Nat Methods 9, 176–178 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1810
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1810
This article is cited by
-
Understanding Horizontal Gene Transfer network in human gut microbiota
Gut Pathogens (2020)
-
Deep learning for HGT insertion sites recognition
BMC Genomics (2020)
-
IMSindel: An accurate intermediate-size indel detection tool incorporating de novo assembly and gapped global-local alignment with split read analysis
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
CLOVE: classification of genomic fusions into structural variation events
BMC Bioinformatics (2017)
-
The association of insertions/deletions (INDELs) and variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) with obesity and its related traits and complications
Journal of Physiological Anthropology (2017)