Abstract
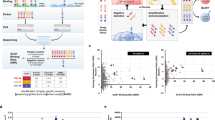
We describe a method for mapping the epitopes recognized by antibodies, based on bacterial surface expression of antigen protein fragments followed by antibody-based flow-cytometric sorting. We analyzed the binding sites of both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies directed to three human protein targets: (i) the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), (ii) ephrin-B3 and (iii) the transcription factor SATB2. All monoclonal antibodies bound a single epitope, whereas the polyclonal antibodies showed, in each case, a binding pattern with one to five separate epitopes. A comparison of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies raised to the same antigen showed overlapping binding epitopes. We also demonstrated that bacterial cells with displayed protein fragments can be used as affinity ligands to generate epitope-specific antibodies. Our approach shows a path forward for systematic validation of antibodies for epitope specificity and cross-reactivity on a whole-proteome level.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhlén, M. Mapping the human proteome using antibodies. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 1455–1456 (2007).
Barlow, D.J., Edwards, M.S. & Thornton, J.M. Continuous and discontinuous protein antigenic determinants. Nature 322, 747–748 (1986).
van Zonneveld, A.J., van den Berg, B.M., van Meijer, M. & Pannekoek, H. Identification of functional interaction sites on proteins using bacteriophage-displayed random epitope libraries. Gene 167, 49–52 (1995).
Geysen, H.M., Meloen, R.H. & Barteling, S.J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 3998–4002 (1984).
Reineke, U., Kramer, A. & Schneider-Mergener, J. Antigen sequence- and library-based mapping of linear and discontinuous protein-protein-interaction sites by spot synthesis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 243, 23–36 (1999).
Christmann, A., Wentzel, A., Meyer, C., Meyers, G. & Kolmar, H. Epitope mapping and affinity purification of monospecific antibodies by Escherichia coli cell surface display of gene-derived random peptide libraries. J. Immunol. Methods 257, 163–173 (2001).
Petersen, G., Song, D., Hugle-Dorr, B., Oldenburg, I. & Bautz, E.K. Mapping of linear epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies with gene-fragment phage display libraries. Mol. Gen. Genet. 249, 425–431 (1995).
Pizzi, E., Cortese, R. & Tramontano, A. Mapping epitopes on protein surfaces. Biopolymers 36, 675–680 (1995).
Cunningham, B.C. & Wells, J.A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science 244, 1081–1085 (1989).
Sidhu, S.S. & Koide, S. Phage display for engineering and analyzing protein interaction interfaces. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 17, 481–487 (2007).
Weiss, G.A., Watanabe, C.K., Zhong, A., Goddard, A. & Sidhu, S.S. Rapid mapping of protein functional epitopes by combinatorial alanine scanning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8950–8954 (2000).
Chao, G., Cochran, J.R. & Wittrup, K.D. Fine epitope mapping of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies through random mutagenesis and yeast surface display. J. Mol. Biol. 342, 539–550 (2004).
Levy, R. et al. Fine and domain-level epitope mapping of botulinum neurotoxin type A neutralizing antibodies by yeast surface display. J. Mol. Biol. 365, 196–210 (2007).
Götz, F. Staphylococcus carnosus: a new host organism for gene cloning and protein production. Soc. Appl. Bacteriol. Symp. Ser. 19, 49S–53S (1990).
Wernérus, H. & Ståhl, S. Biotechnological applications for surface-engineered bacteria. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 40, 209–228 (2004).
Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 228, 1315–1317 (1985).
Smith, G.P. & Petrenko, V.A. Phage display. Chem. Rev. 97, 391–410 (1997).
Wittrup, K.D. Protein engineering by cell-surface display. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 395–399 (2001).
Schechter, A.L. et al. The neu gene: an erbB-homologous gene distinct from and unlinked to the gene encoding the EGF receptor. Science 229, 976–978 (1985).
Yarden, Y. & Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 127–137 (2001).
Löfblom, J., Kronqvist, N., Uhlén, M., Ståhl, S. & Wernérus, H. Optimization of electroporation-mediated transformation: Staphylococcus carnosus as model organism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 102, 736–747 (2007).
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W. & Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990).
Agaton, C. et al. Affinity proteomics for systematic protein profiling of chromosome 21 gene products in human tissues. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2, 405–414 (2003).
Benson, M.D. et al. Ephrin-B3 is a myelin-based inhibitor of neurite outgrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10694–10699 (2005).
Wang, X.X., Cho, Y.K. & Shusta, E.V. Mining a yeast library for brain endothelial cell-binding antibodies. Nat. Methods 4, 143–145 (2007).
Feldhaus, M.J. et al. Flow-cytometric isolation of human antibodies from a nonimmune Saccharomyces cerevisiae surface display library. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 163–170 (2003).
Margulies, M. et al. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 437, 376–380 (2005).
Michaud, G.A. et al. Analyzing antibody specificity with whole proteome microarrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1509–1512 (2003).
Flicek, P. et al. Ensembl 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D707–D714 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to P.-Å. Nygren and J. Lundeberg for comments and advice. M. Hansson and H. Johannesson at Atlas Antibodies AB are acknowledged for funding the generation of SATB2 monoclonals. This work was supported by funding from the ProNova center (project B3) and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation. J.L. was partially supported by grant 621-2003-2876 from the Swedish Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Methods (PDF 1241 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rockberg, J., Löfblom, J., Hjelm, B. et al. Epitope mapping of antibodies using bacterial surface display. Nat Methods 5, 1039–1045 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1272
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1272
This article is cited by
-
Staphylococcus carnosus: from starter culture to protein engineering platform
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2017)
-
Stratification of responders towards eculizumab using a structural epitope mapping strategy
Scientific Reports (2016)