Abstract
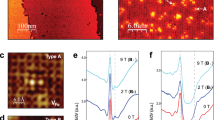
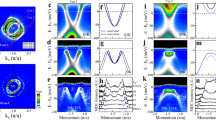
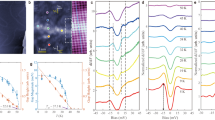
Superconducting and topological states are two most intriguing quantum phenomena in solid materials. The entanglement of these two states, the topological superconducting state, will give rise to even more exotic quantum phenomena. While many materials are found to be either a superconductor or a topological insulator, it is very rare that both states exist in one material. Here, we demonstrate by first-principles theory as well as scanning tunnelling spectroscopy and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy experiments that the recently discovered ‘two-dimensional (2D) superconductor’ of single-layer FeSe also exhibits 1D topological edge states within an energy gap of ∼40 meV at the M point below the Fermi level. It is the first 2D material that supports both superconducting and topological states, offering an exciting opportunity to study 2D topological superconductors through the proximity effect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Q. et al. Interface-induced high-temperature superconductivity in single unit-cell FeSe Films on SrTiO3 . Chin. Phys. Lett. 29, 037402 (2012).
Liu, D. et al. Electronic origin of high-temperature superconductivity in single-layer FeSe superconductor. Nature Commun. 3, 931 (2012).
He, S. et al. Phase diagram and electronic indication of high-temperature superconductivity at 65 K in single-layer FeSe films. Nature Mater. 12, 605–610 (2013).
Tan, S. et al. Interface-induced superconductivity and strain-dependent spin density waves in FeSe/SrTiO3 thin films. Nature Mater. 12, 634–640 (2013).
Lee, J. J. et al. Interfacial mode coupling as the origin of the enhancement of Tc in FeSe films on SrTiO3 . Nature 515, 245–248 (2014).
Zhang, W. et al. Direct observation of high-temperature superconductivity in one-unit-cell FeSe films. Chin. Phys. Lett. 31, 017401 (2014).
Ge, J.-F. et al. Superconductivity above 100 K in single-layer FeSe films on doped SrTiO3 . Nature Mater. 14, 285–289 (2015).
Hao, N. & Hu, J. Topological phases in the single-layer FeSe. Phys. Rev. X 4, 031053 (2014).
Wang, Z. et al. Topological nature of the FeSe0.5Te0.5 superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 92, 115119 (2015).
Hao, N. & Shen, S.-Q. Topological superconducting states in monolayer FeSe/SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. B 92, 165104 (2015).
Coh, S., Cohen, M. L. & Louie, S. G. Large electron–phonon interactions from FeSe phonons in a monolayer. New J. Phys. 17, 073027 (2015).
Liu, K., Lu, Z.-Y. & Xiang, T. Atomic and electronic structures of FeSe monolayer and bilayer thin films on SrTiO3(001): first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 85, 235123 (2013).
Berlijn, T. et al. Doping effects of Se vacancies in monolayer FeSe. Phys. Rev. B 89, 020501(R) (2014).
Bazhirov, T. & Cohen, M. L. Effects of charge doping and constrained magnetization on the electronic structure of an FeSe monolayer. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 25, 105506 (2013).
Zheng, F., Wang, Z., Kang, W. & Zhang, P. Antiferromagnetic FeSe monolayer on SrTiO3: the charge doping and electric field effects. Sci. Rep. 3, 2213 (2013).
Hor, Y. S. et al. Superconductivity in CuxBi2Se3 and its implications for pairing in the undoped topological insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 057001 (2010).
Novak, M. et al. Unusual nature of fully gapped superconductivity in In-doped SnTe. Phys. Rev. B 88, 140502(R) (2013).
Kane, C. L. & Mele, E. J. Quantum spin Hall effect in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 226801 (2005).
Wang, Z. F., Su, N. & Liu, F. Prediction of a two-dimensional organic topological insulator. Nano Lett. 13, 2842–2845 (2013).
Bernevig, B. A., Hughes, T. L. & Zhang, S.-C. Quantum spin Hall effect and topological phase transition in HgTe quantum wells. Science 314, 1757–1761 (2006).
König, M. et al. Quantum spin Hall insulator state in HgTe quantum wells. Science 318, 766–770 (2007).
Mong, R. S. K., Essin, A. M. & Moore, J. E. Antiferromagnetic topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 81, 245209 (2010).
Essin, A. M. & Gurarie, V. Antiferromagnetic topological insulators in cold atomic gases. Phys. Rev. B 85, 195116 (2012).
Guo, H., Feng, S. & Shen, S.-Q. Quantum spin Hall effect induced by nonmagnetic and magnetic staggered potentials. Phys. Rev. B 83, 045114 (2011).
Mostofi, A. A. et al. Wannier90: a tool for obtaining maximally-localised Wannier functions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 178, 685–699 (2008).
Wang, Z. F., Liu, Z. & Liu, F. Organic topological insulators in organometallic lattices. Nature Commun. 4, 1471 (2013).
Wang, Z. F., Chen, L. & Liu, F. Tuning topological edge states of Bi (111) bilayer film by edge adsorption. Nano Lett. 14, 2879–2883 (2014).
Yang, F. et al. Spatial and energy distribution of topological edge states in single Bi(111) bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 016801 (2012).
Tamai, A. et al. Strong electron correlations in the normal state of the iron-based FeSe0.42Te0.58 superconductor observed by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 097002 (2010).
Maletz, J. et al. Unusual band renormalization in the simplest iron-based superconductor FeSe1−x . Phys. Rev. B 89, 220506(R) (2014).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 47, 558–561(R) (1993).
Acknowledgements
Z.F.W. and F.Liu acknowledge financial support from DOE-BES (No. DE-FG02-04ER46148). Z.F.W. acknowledges additional financial support from the Chinese Youth 1000 Talents Program and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. X.J.Z. acknowledges financial support from the NSFC (No. 11190022 and 11334010) and the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of CAS (No. XDB07020300). Q.K.X. and X.M. acknowledge financial support from the MOST of China (No. 2009CB929400 and 2012CB921702). We also thank the Supercomputing Center at USTC, NERSC and CHPC at University of Utah for providing the computing resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.F.W. and F.Liu conceived the project, and Z.F.W. carried out the theoretical calculation. H.Z., C.L., C.T., C.S., Y.Z., J.P., F.Li, C.N., L.W., X.M. and Q.K.X. carried out the MBE thin-film growth and STS measurement. D.L. and X.J.Z. carried out the ARPES measurement. Z.F.W. and F.Liu prepared the manuscript with input from X.J.Z., X.M. and Q.K.X.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 3241 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, D. et al. Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO3(001) film. Nature Mater 15, 968–973 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4686
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4686
This article is cited by
-
A hybrid topological quantum state in an elemental solid
Nature (2024)
-
Identifying topological corner states in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Pair density wave state in a monolayer high-Tc iron-based superconductor
Nature (2023)
-
Two-dimensional superconductors with intrinsic p-wave pairing or nontrivial band topology
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
Fragile topological band in the checkerboard antiferromagnetic monolayer FeSe
npj Computational Materials (2022)