Abstract
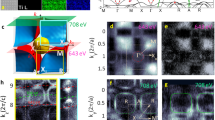
The development of interface-based magnetoelectric devices necessitates an understanding of polarization-mediated electronic phenomena and atomistic polarization screening mechanisms. In this work, the LSMO/BFO interface is studied on a single unit-cell level through a combination of direct order parameter mapping by scanning transmission electron microscopy and electron energy-loss spectroscopy. We demonstrate an unexpected ~5% lattice expansion for regions with negative polarization charge, with a concurrent anomalous decrease of the Mn valence and change in oxygen K-edge intensity. We interpret this behaviour as direct evidence for screening by oxygen vacancies. The vacancies are predominantly accumulated at the second atomic layer of BFO, reflecting the difference of ionic conductivity between the components. This vacancy exclusion from the interface leads to the formation of a tail-to-tail domain wall. At the same time, purely electronic screening is realized for positive polarization charge, with insignificant changes in lattice and electronic properties. These results underline the non-trivial role of electrochemical phenomena in determining the functional properties of oxide interfaces. Furthermore, these behaviours suggest that vacancy dynamics and exclusion play major roles in determining interface functionality in oxide multilayers, providing clear implications for novel functionalities in potential electronic devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C. H. et al. Local, nonvolatile electronic writing of epitaxial Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3/SrRuO3 heterostructures. Science 276, 1100–1103 (1997).
Lee, J. H. et al. A strong ferroelectric ferromagnet created by means of spin-lattice coupling. Nature 466, 954–958 (2010).
Miller, S. L. & McWhorter, P. J. Physics of the ferroelectric nonvolatile memory field-effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 5999–6010 (1992).
Molegraaf, H. J. A. et al. Magnetoelectric effects in complex oxides with competing ground states. Adv. Mater. 21, 3470–3474 (2009).
Imada, M., Fujimori, A. & Tokura, Y. Metal-insulator transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 1039–1263 (1998).
Bibes, M., Villegas, J. E. & Barthelemy, A. Ultrathin oxide films and interfaces for electronics and spintronics. Adv. Phys. 60, 5–84 (2011).
Cheng, G. L. et al. Sketched oxide single-electron transistor. Nature Nanotech. 6, 343–347 (2011).
Fiebig, M. Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D 38, R123–R152 (2005).
Burton, J. D. & Tsymbal, E. Y. Prediction of electrically induced magnetic reconstruction at the manganite/ferroelectric interface. Phys. Rev. B 80, 174406 (2009).
Rondinelli, J. M., Stengel, M. & Spaldin, N. A. Carrier-mediated magnetoelectricity in complex oxide heterostructures. Nature Nanotech. 3, 46–50 (2008).
Yamauchi, K., Sanyal, B. & Picozzi, S. Interface effects at a half-metal/ferroelectric junction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 062506 (2007).
Brivio, S. et al. Effects of Au nanoparticles on the magnetic and transport properties of La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 ultrathin layers. Phys. Rev. B 81, 094410 (2010).
Estrade, S. et al. Effect of the capping on the local Mn oxidation state in buried (001) and (110) SrTiO3/La2/3Ca1/3MnO3 interfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 103903–103905 (2011).
Ferguson, J. D. et al. Epitaxial oxygen getter for a brownmillerite phase transformation in manganite films. Adv. Mater. 23, 1226–1230 (2011).
Kim, Y., Disa, A. S., Babakol, T. E. & Brock, J. D. Strain screening by mobile oxygen vacancies in SrTiO3 . Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 251901 (2010).
Schneider, C. W. et al. The origin of oxygen in oxide thin films: Role of the substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 192107 (2010).
Lankhorst, M. H. R., Bouwmeester, H. J. M. & Verweij, H. Use of the rigid band formalism to interpret the relationship between O chemical potential and electron concentration in La1 − xSrxCoO3 − δ . Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2989–2992 (1996).
Pennycook, S. J. & Nellist, P. D. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy: Imaging and Analysis (Springer, 2011).
Jia, C. L. et al. Atomic-scale study of electric dipoles near charged and uncharged domain walls in ferroelectric films. Nature Mater. 7, 57–61 (2008).
Chisholm, M. F., Luo, W. D., Oxley, M. P., Pantelides, S. T. & Lee, H. N. Atomic-scale compensation phenomena at polar interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 197602 (2010).
Chang, H. J. et al. Atomically resolved mapping of polarization and electric fields across ferroelectric/oxide interfaces by Z-contrast Imaging. Adv. Mater. 23, 2474–2479 (2011).
Jia, C. L. et al. Effect of a single dislocation in a heterostructure layer on the local polarization of a ferroelectric layer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 117601 (2009).
Nelson, C. T. et al. Spontaneous vortex nanodomain arrays at ferroelectric heterointerfaces. Nano Lett. 11, 828–834 (2011).
Jia, C. L., Urban, K. W., Alexe, M., Hesse, D. & Vrejoiu, I. Direct observation of continuous electric dipole rotation in flux-closure domains in ferroelectric Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 . Science 331, 1420–1423 (2011).
Gruverman, A. & Kholkin, A. Nanoscale ferroelectrics: Processing, characterization and future trends. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 2443–2474 (2006).
Balke, N., Bdikin, I., Kalinin, S. V. & Kholkin, A. L. Electromechanical imaging and spectroscopy of ferroelectric and piezoelectric materials: State of the art and prospects for the future. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1629–1647 (2009).
Kalinin, S. V., Morozovska, A. N., Chen, L. Q. & Rodriguez, B. J. Local polarization dynamics in ferroelectric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 73, 056502 (2010).
Kim, Y-M. et al. Interplay of octahedral tilts and polar order in BiFeO3 films. Adv. Mater. 25, 2497–2504 (2013).
Yu, P. et al. Interface control of bulk ferroelectric polarization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 9710–9715 (2012).
Jia, C. L. et al. Unit-cell scale mapping of ferroelectricity and tetragonality in epitaxial ultrathin ferroelectric films. Nature Mater. 6, 64–69 (2007).
Kim, Y. M. et al. Probing oxygen vacancy concentration and homogeneity in solid-oxide fuel-cell cathode materials on the subunit-cell level. Nature Mater. 11, 888–894 (2012).
Borisevich, A. Y. et al. Suppression of octahedral tilts and associated changes in electronic properties at epitaxial oxide heterostructure interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 087204 (2010).
Pruneda, J. M. et al. Ferrodistortive instability at the (001) surface of half-metallic manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 226101 (2007).
Botton, G. A., Appel, C. C., Horsewell, A. & Stobbs, W. M. Quantification of the EELS near-edge structures to study Mn doping in oxides. J. Microsc. 180, 211–216 (1995).
Cavé, L., Al, T., Loomer, D., Cogswell, S. & Weaver, L. A STEM/EELS method for mapping iron valence ratios in oxide minerals. Micron 37, 301–309 (2006).
Maurice, J. L., Imhoff, D., Contoury, J. P. & Colliex, C. Interfaces in {100} epitaxial heterostructures of perovskite oxides. Phil. Mag. 86, 2127–2146 (2006).
Oxley, M. P. & Pennycook, S. J. Image simulation for electron energy loss spectroscopy. Micron 39, 676–684 (2008).
Samet, L. et al. EELS study of interfaces in magnetoresistive LSMO/STO/LSMO tunnel junctions. Eur. Phys. J. B 34, 179–192 (2003).
Wang, Z. L., Yin, J. S. & Jiang, Y. D. EELS analysis of cation valence states and oxygen vacancies in magnetic oxides. Micron 31, 571–580 (2000).
De Jong, M. P. et al. Evidence for Mn2+ ions at surfaces of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 71, 014434 (2005).
De Jong, M. P. et al. Valence electronic states related to Mn2+ at La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 surfaces characterized by resonant photoemission. Phys. Rev. B 73, 052403 (2006).
Adler, S. B. Chemical expansivity of electrochemical ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 2117–2119 (2001).
Chen, X. Y., Yu, J. S. & Adler, S. B. Thermal and chemical expansion of Sr-doped lanthanum cobalt oxide (La1 − xSrxCoO3 − δ). Chem. Mater. 17, 4537–4546 (2005).
Zeches, R. J. et al. A strain-driven morphotropic phase boundary in BiFeO3 . Science 326, 977–980 (2009).
Selbach, S. M., Tybell, T., Einarsrud, M-A. & Grande, T. Structure and properties of multiferroic oxygen hyperstoichiometric BiFe1 − xMnxO3 + δ . Chem. Mater. 21, 5176–5186 (2009).
Masó, N. & West, A. R. Electrical properties of Ca-doped BiFeO3 ceramics: From p-type semiconduction to oxide-ion conduction. Chem. Mater. 24, 2127–2132 (2012).
Yang, C. H. et al. Electric modulation of conduction in multiferroic Ca-doped BiFeO3 films. Nature Mater. 8, 485–493 (2009).
Gerra, G., Tagantsev, A. K. & Setter, N. Ferroelectricity in asymmetric metal-ferroelectric–metal heterostructures: A combined first-principles-phenomenological approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 207601 (2007).
Morozovska, A. N. et al. Finite size and intrinsic field effect on the polar-active properties of ferroelectric-semiconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 81, 205308 (2010).
Eliseev, E. A. et al. Surface effect on domain wall width in ferroelectrics. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 084102 (2009).
Sheldon, B. W. & Shenoy, V. B. Space charge induced surface stresses: Implications in ceria and other ionic solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 216104 (2011).
Eliseev, E. A., Morozovska, A. N., Svechnikov, G. S., Maksymovych, P. & Kalinin, S. V. Domain wall conduction in multiaxial ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 85, 045312 (2012).
Fridkin, V. M. Ferroelectric Semiconductors (Springer, 1980).
Gureev, M. Y., Tagantsev, A. K. & Setter, N. Head-to-head and tail-to-tail 180 degrees domain walls in an isolated ferroelectric. Phys. Rev. B 83, 184104 (2011).
Vul, B. M., Guro, G. M. & Ivanchik, I. I. Encountering domains in ferroelectrics. Ferroelectrics 6, 29–31 (1973).
Riess, I. I–V relations in semiconductors with ionic motion. J. Electroceram. 17, 247–253 (2006).
Maier, J. Thermodynamics of nanosystems with a special view to charge carriers. Adv. Mater. 21, 2571–2585 (2009).
Vaz, C. A. F. et al. Origin of the magnetoelectric coupling effect in Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3/La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 multiferroic heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 127202 (2010).
Chien, T. Y., Liu, J. A., Chakhalian, J., Guisinger, N. P. & Freeland, J. W. Visualizing nanoscale electronic band alignment at the La2/3Ca1/3MnO3/Nb:SrTiO3 interface. Phys. Rev. B 82, 041101 (2010).
Huang, B. C. et al. Direct observation of ferroelectric polarization-modulated band bending at oxide interfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 122903 (2012).
Acknowledgements
The work is supported in part (A.Y.B., Y-M.K., S.V.K., R.M. and S.T.P.) by the Materials Science and Engineering Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences of the US DOE and through a user project supported by Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, which is sponsored at Oak Ridge National Laboratory by the Scientific User Facilities Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, US Department of Energy. M.P.O. acknowledges support from DOE grant DE-FG02-09ER46554. The authors thank P. Yu (Tsinghua University, Beijing, China), Y-H. Chu (National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan) and R. Ramesh (University of California Berkeley) for providing BiFeO3 films for the study. A.M. and E.E. acknowledge support via a bilateral SFFR-NSF project, namely US National Science Foundation under NSF-DMR-1210588 and State Fund of Fundamental Research of Ukraine, grant UU48/002. This research used resources of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, which is supported by the Office of Science of the US Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-M.K. conducted STEM/EELS study and data analysis; A.M. and E.E. carried out LGD modelling; M.P.O. carried out EELS profile simulations; R.M. and S.T.P. conducted first-principles calculations; S.M.S. and T.G. provided solid state chemistry reasoning; A.Y.B. and S.V.K. conceived and directed the project. All authors contributed to writing the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1836 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YM., Morozovska, A., Eliseev, E. et al. Direct observation of ferroelectric field effect and vacancy-controlled screening at the BiFeO3/LaxSr1−xMnO3 interface. Nature Mater 13, 1019–1025 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4058
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4058
This article is cited by
-
Machine learning in scanning transmission electron microscopy
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2022)
-
Direct observation of elemental fluctuation and oxygen octahedral distortion-dependent charge distribution in high entropy oxides
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Twisted oxide lateral homostructures with conjunction tunability
Nature Communications (2022)
-
AtomAI framework for deep learning analysis of image and spectroscopy data in electron and scanning probe microscopy
Nature Machine Intelligence (2022)
-
Ensemble learning-iterative training machine learning for uncertainty quantification and automated experiment in atom-resolved microscopy
npj Computational Materials (2021)