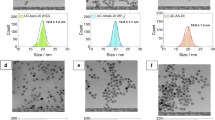
Abstract
The induction of autophagy on exposure of cells to a variety of nanoparticles represents both a safety concern and an application niche for engineered nanomaterials. Here, we show that a short synthetic peptide, RE-1, identified by means of phage display, binds to lanthanide (LN) oxide and upconversion nanocrystals (UCN), forms a stable coating layer on the nanoparticles’ surface, and effectively abrogates their autophagy-inducing activity. Furthermore, RE-1 peptide variants exhibit a differentially reduced binding capability, and correspondingly, a varied ability to reduce the autophagic response. We also show that the addition of an arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD) motif to RE-1 enhances autophagy for LN UCN through the interaction with integrins. RE-1 and its variants provide a versatile tool for tuning material–cell interactions to achieve the desired level of autophagy, and may prove useful for the various diagnostic and therapeutic applications of LN-based nanomaterials and nanodevices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klionsky, D. J. Autophagy: From phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 931–937 (2007).
Mizushima, N. Autophagy: Process and function. Genes Dev. 21, 2861–2873 (2007).
Ravikumar, B. et al. Regulation of mammalian autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Phys. Rev. 90, 1383–1435 (2010).
Mizushima, N., Levine, B., Cuervo, A. M. & Klionsky, D. J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451, 1069–1075 (2008).
Levine, B. Cell biology—autophagy and cancer. Nature 446, 745–747 (2007).
Pan, T. H., Kondo, S., Le, W. & Jankovic, J. The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131, 1969–1978 (2008).
Levine, B., Mizushima, N. & Virgin, H. W. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 469, 323–335 (2011).
Zabirnyk, O., Yezhelyev, M. & Seleverstov, O. Nanoparticles as a novel class of autophagy activators. Autophagy 3, 278–281 (2007).
Stern, S. T. et al. Induction of autophagy in porcine kidney cells by quantum dots: a common cellular response to nanomaterials? Toxicol. Sci. 106, 140–152 (2008).
Man, N., Yu, L., Yu, S. H. & Wen, L. P. Rare earth oxide nanocrystals as a new class of autophagy inducers. Autophagy 6, 310–311 (2010).
Seleverstov, O. et al. Quantum dots for human mesenchymal stem cells labeling. A size-dependent autophagy activation. Nano Lett. 6, 2826–2832 (2006).
Zhang, Q. et al. Autophagy-mediated chemosensitization in cancer cells by fullerene 60C nanocrystal. Autophagy 5, 1107–1117 (2009).
Wei, P. F., Zhang, L., Lu, Y., Man, N. & Wen, L. P. 60C (Nd) nanoparticles enhance chemotherapeutic susceptibility of cancer cells by modulation of autophagy. Nanotechnology 21, 5101–5111 (2010).
Liu, H. L. et al. A functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube-induced autophagic cell death in human lung cells through Akt-TSC2-mTOR signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2, 159–165 (2011).
Chen, Y., Yang, L., Feng, C. & Wen, L. P. Nano neodymium oxide induces massive vacuolization and autophagic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H460 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 337, 52–60 (2005).
Yu, L., Lu, Y., Yu, S. H. & Wen, L. P. Rare earth oxide nanocrystals induce autophagy in HeLa cells. Small 5, 2784–2787 (2009).
Zhang, Y., Yu, C., Huang, G., Wang, C. & Wen, L. P. Nano rare-earth oxides induced size-dependent vacuolization: An independent pathway from autophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 5, 601–609 (2010).
Li, C. G. et al. PAMAM nanoparticles promote acute lung injury by inducing autophagic cell death through the Akt-TSC2-mTOR signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 37–45 (2009).
Li, J. J., Hartono, D., Ong, C. N., Bay, B. H. & Yung, L. Y. Autophagy and oxidative stress associated with gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31, 5996–6003 (2010).
Wu, Y. N. et al. The selective growth inhibition of oral cancer by iron core–gold shell nanoparticles through mitochondria-mediated autophagy. Biomaterials 32, 4565–4573 (2011).
Ma, X. W. et al. Gold nanoparticles induce autophagosome accumulation through size-dependent nanoparticle uptake and lysosome impairment. ACS Nano 5, 8629–8639 (2011).
Yu, J. X. & Li, T. H. Distinct biological effects of different nanoparticles commonly used in cosmetics and medicine coatings. Cell Biosci. 1, 19–27 (2011).
Stern, S. T. & Johnson, D. N. Role for nanomaterial–autophagy interaction in neurodegenerative disease. Autophagy 4, 1097–1100 (2008).
Li, H. Y., Li, Y. H., Jiao, J. & Hu, H. M. Alpha–alumina nanoparticles induce efficient autophagy-dependent cross-presentation and potent antitumour response. Nature Nanotech. 6, 645–650 (2011).
Verma, A. & Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle–cell interactions. Small 6, 12–21 (2010).
Nel, A. E. et al. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nature Mater. 8, 543–557 (2009).
Dutta, D. et al. Adsorbed proteins influence the biological activity and molecular targeting of nanomaterials. Toxicol. Sci. 100, 303–315 (2007).
Bakota, E. L., Aulisa, L., Tsyboulski, D. A., Weisman, R. B. & Hartgerink, J. D. Multidomain peptides as single-walled carbon nanotube surfactants in cell culture. Biomacromolecules 10, 2201–2206 (2009).
Whaley, S. R., English, D. S., Hu, E. L., Barbara, P. F. & Belcher, A. M. Selection of peptides with semiconductor binding specificity for directed nanocrystal assembly. Nature 405, 665–668 (2000).
Naik, R. R., Stringer, S. J., Agarwal, G., Jones, S. E. & Stone, M. O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nature Mater. 1, 169–172 (2002).
Wang, S. Q. et al. Peptides with selective affinity for carbon nanotubes. Nature Mater. 2, 196–200 (2003).
Kriplani, U. & Kay, B. K. Selecting peptides for use in nanoscale materials using phage-displayed combinatorial peptide libraries. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 16, 470–475 (2005).
Lee, S. W., Mao, C., Flynn, C. E. & Belcher, A. M. Ordering of quantum dots using genetically engineered viruses. Science 296, 892–895 (2002).
Chen, H. B., Su, X., Neoh, K. G. & Choe, W. S. Probing the interaction between peptides and metal oxides using point mutants of a TiO2-binding peptide. Langmuir 24, 6852–6857 (2008).
Goede, K., Busch, P. & Grundmann, M. Binding specificity of a peptide on semiconductor surfaces. Nano Lett. 4, 2115–2120 (2004).
Cho, N. H. et al. A multifunctional core–shell nanoparticle for dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Nature Nanotech. 6, 675–682 (2011).
Barth, S., Glick, D. & Macleod, K. F. Autophagy: Assays and artifacts. J. Pathol. 221, 117–24 (2010).
Xiong, L., Yang, T., Yang, Y., Xu, C. & Li, F. Long-term in vivo biodistribution imaging and toxicity of polyacrylic acid-coated upconversion nanophosphors. Biomaterials 31, 7078–7085 (2010).
Abdul, J. R. & Zhang, Y. Biocompatibility of silica coated NaYF4 upconversion fluorescent nanocrystals. Biomaterials 29, 4122–4128 (2008).
Johnson-Lyles, D. N. et al. Fullerenol cytotoxicity in kidney cells is associated with cytoskeleton disruption, autophagic vacuole accumulation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 248, 249–58 (2010).
Monick, M. M. et al. Identification of an autophagy defect in smokers’ alveolar macrophages. J. Immunol. 185, 5425–35 (2010).
Cho, E. C., Zhang, Q. & Xia, Y. N. The effect of sedimentation and diffusion on cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles. Nature Nanotech. 6, 385–391 (2011).
Chen, K. & Chen, X. Y. Integrin targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics. Theranostics 1, 189–200 (2011).
Van Vlerken, L. E., Vyas, T. K. & Amiji, M. M. Poly(ethylene glycol)-modified nanocarriers for tumor-targeted and intracellular delivery. Pharmaceutical Res. 24, 1405–1414 (2007).
Xie, J., Xu, C., Kohler, N., Hou, Y. & Sun, S. Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv. Mater. 19, 3163–3166 (2007).
Bretscher, M. S. Endocytosis and recycling of the fibronectin receptor in CHO cells. EMBO J. 8, 1341–1348 (1989).
Zhang, Y. & Li, Z. Q. An efficient and user-friendly method for the synthesis of hexagonal-phase NaYF4:Yb, Er/Tm nanocrystals with controllable shape and upconversion fluorescence. Nanotechnology 19, 606–610 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Chinese Ministry of Sciences 973 Program (2010CB912804), Natural Science Foundation of China (#30830036, #31170966, #31071211), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK2070000008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yunjiao Z. and L-P.W. conceived and designed the experiments. Yunjiao Z., F.Z., T.Y., Y.L., W.Z., N.M., L.Z. and N.J. performed the experiments. Q.D., Yong Z. and Z.L. synthesized the UCN nanocrystals. Yunjiao Z. and L-P.W. analysed the data and wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 6357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zheng, F., Yang, T. et al. Tuning the autophagy-inducing activity of lanthanide-based nanocrystals through specific surface-coating peptides. Nature Mater 11, 817–826 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3363
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3363
This article is cited by
-
A pyroptosis nanotuner for cancer therapy
Nature Nanotechnology (2022)
-
Molecular recognition and specificity of biomolecules to titanium dioxide from molecular dynamics simulations
npj Computational Materials (2020)
-
Reduction of the Cytotoxicity of Copper (II) Oxide Nanoparticles by Coating with a Surface-Binding Peptide
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2020)
-
Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Harnessing copper-palladium alloy tetrapod nanoparticle-induced pro-survival autophagy for optimized photothermal therapy of drug-resistant cancer
Nature Communications (2018)