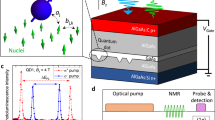
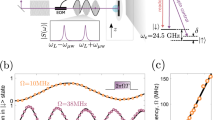
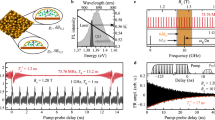
Abstract
Highly polarized nuclear spins within a semiconductor quantum dot induce effective magnetic (Overhauser) fields of up to several Tesla acting on the electron spin1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, or up to a few hundred mT for the hole spin13,14. Recently this has been recognized as a resource for intrinsic control of quantum-dot-based spin quantum bits. However, only static long-lived Overhauser fields could be used10,11. Here we demonstrate fast redirection on the microsecond timescale of Overhauser fields on the order of 0.5 T experienced by a single electron spin in an optically pumped GaAs quantum dot. This has been achieved using coherent control of an ensemble of 105 optically polarized nuclear spins by sequences of short radiofrequency pulses. These results open the way to a new class of experiments using radiofrequency techniques to achieve highly correlated nuclear spins in quantum dots, such as adiabatic demagnetization in the rotating frame15 leading to sub-μK nuclear spin temperatures, rapid adiabatic passage15, and spin squeezing16.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eble, B. et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization of a single charge-tunable InAs/GaAs quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 74, 081306(R) (2006).
Tartakovskii, A. I. et al. Nuclear spin switch in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 026806 (2007).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Dynamics of optically induced nuclear spin polarization in individual InP/GaInP quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 81, 245308 (2010).
Xu, X. et al. Optically controlled locking of the nuclear field via coherent dark-state spectroscopy. Nature 459, 1105–1109 (2009).
Latta, C. et al. Confluence of resonant laser excitation and bidirectional quantum-dot nuclear-spin polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 758–763 (2009).
Nikolaenko, A. E. et al. Suppression of nuclear spin diffusion at a GaAs/AlxGa1−xAs interface measured with a single quantum-dot nanoprobe. Phys. Rev. B 79, 081303(R) (2009).
Gammon, D. et al. Nuclear spectroscopy in single quantum dots: Nanoscopic Raman scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance. Science 277, 85–88 (1997).
Makhonin, M. N. et al. Optically tunable nuclear magnetic resonance in a single quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 82, 161309(R) (2010).
Chekhovich, E. A., Krysa, A. B., Skolnick, M. S. & Tartakovskii, A. I. Direct measurement of the hole-nuclear spin interaction in single InP/GaInP quantum dots using photoluminescence spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 027402 (2011).
Foletti, S., Bluhm, H., Mahalu, D., Umansky, V. & Yacoby, A. Universal quantum control of two-electron spin quantum bits using dynamic nuclear polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 903–908 (2009).
Kloeffel, C. et al. Controlling the interaction of electron and nuclear spins in a tunnel-coupled quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 046802 (2011).
Kalevich, V. K., Kavokin, K. V. & Merkulov, I. A. in Spin Physics in Semiconductors (ed. Dyakonov, M. I.) (Springer, 2008).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Pumping of nuclear spins by optical excitation of spin-forbidden transitions in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 066804 (2010).
Fallahi, P., Yilmaz, S. T. & Imamoglu, A. Measurement of a heavy-hole hyperfine interaction in InGaAs quantum dots using resonance fluorescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 257402 (2010).
Slichter, C. P. Principles of Magnetic Resonance (Springer, 1990).
Rudner, M. S., Vandersypen, L. M. K., Vuletic, V. & Levitov, L. S. Generating entanglement and squeezed states of nuclear spins in quantum dots. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/1101.3370 (2010).
Erlingsson, S. I., Nazarov, Y. V. & Falko, V. I. Nucleus-mediated spin-flip transitions in GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 64, 195306 (2001).
Khaetskii, A. V., Loss, D. & Glazman, L. Electron spin decoherence in quantum dots due to interaction with nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 186802 (2002).
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Control and detection of singlet–triplet mixing in a random nuclear field. Science 309, 1346 (2005).
Vink, I. T. et al. Locking electron spins into magnetic resonance by electron–nuclear feedback. Nature Phys. 5, 764–768 (2009).
Bluhm, H. et al. Dephasing time of GaAs electron-spin qubits coupled to a nuclear bath exceeding 200 μs. Nature Phys. 7, 109 (2011).
Yusa, G., Muraki, K., Takashina, K., Hashimoto, K. & Hirayama, Y. Controlled multiple quantum coherences of nuclear spins in a nanometre-scale device. Nature 434, 1001 (2005).
Machida, T., Yamazaki, T., Ikushima, K. & Komiyama, S. Coherent control of nuclear-spin system in a quantum-Hall device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 409 (2003).
Sanada, H. et al. Optical pump–probe measurements of local nuclear spin coherence in semiconductor quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 067602 (2006).
Peter, E. et al. Exciton-photon strong-coupling regime for a single quantum dot embedded in a microcavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 067401 (2005).
Ramsey, N. F. A molecular beam resonance method with separated oscillating fields. Phys. Rev. 78, 695–699 (1950).
Abragam, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetism (Oxford Univ. Press, 1961).
Torrey, H. C. Transient nutations in nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Rev. 76, 1059–1068 (1949).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. M. K. Vandersypen, V. I. Fal’ko, E. A. Chekhovich and A. D. Andreev for discussions, and D. Martrou for help with the sample growth. This work has been supported by the EPSRC Programme Grant EP/G601642/1, ITN Spin-Optronics and the Royal Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.L. and P.S. developed and grew the sample. M.N.M. and A.I.T. conceived the experiments. M.N.M. designed and carried out the experiments. M.N.M, K.V.K. and A.I.T. analysed the data. A.I.T. and M.N.M. wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 739 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makhonin, M., Kavokin, K., Senellart, P. et al. Fast control of nuclear spin polarization in an optically pumped single quantum dot. Nature Mater 10, 844–848 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3102
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3102
This article is cited by
-
Fabrication and Optical Properties of Strain-free Self-assembled Mesoscopic GaAs Structures
Nanoscale Research Letters (2017)
-
Suppression of nuclear spin bath fluctuations in self-assembled quantum dots induced by inhomogeneous strain
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Longitudinal wave function control in single quantum dots with an applied magnetic field
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Manipulation of the nuclear spin ensemble in a quantum dot with chirped magnetic resonance pulses
Nature Nanotechnology (2014)
-
Quantum control of hybrid nuclear–electronic qubits
Nature Materials (2013)