Abstract
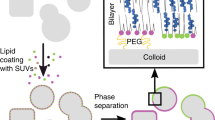
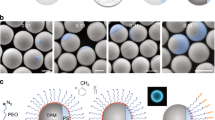
Selective binding of multivalent ligands within a mixture of polyvalent amphiphiles provides, in principle, a simple mechanism for driving domain formation in self-assemblies. Divalent cations are shown here to crossbridge polyanionic amphiphiles, which thereby demix from neutral amphiphiles and form spots or rafts within vesicles as well as stripes within cylindrical micelles. Calcium- and copper-crossbridged domains of synthetic block copolymers or natural lipid (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate) possess tunable sizes, shapes and/or spacings that can last for years. Lateral segregation in these ‘ligand-responsive Janus assemblies’ couples weakly to curvature and proves to be restricted within phase diagrams to narrow regimes of pH and cation concentration that are centred near the characteristic binding constants for polyacid interactions. Remixing at high pH is surprising, but a theory for strong lateral segregation shows that counterion entropy dominates electrostatic crossbridges, thus illustrating the insights gained into ligand-induced pattern formation within self-assemblies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Discher, D. E. & Eisenberg, A. Polymer vesicles. Science 297, 967–973 (2002).
Pochan, D. J. et al. Toroidal triblock copolymer assemblies. Science 306, 94–97 (2004).
Won, Y. Y., Davis, H. T. & Bates, F. S. Giant wormlike rubber micelles. Science 283, 960–963 (1999).
Zhang, L. F., Yu, K. & Eisenberg, A. Ion-induced morphological changes in ‘crew-cut’ aggregates of amphiphilic block copolymers. Science 272, 1777–1779 (1996).
Fraaije, J., van Sluis, C. A., Kros, A., Zvelindovsky, A. V. & Sevink, G. J. A. Design of chimaeric polymersomes. Faraday Discuss. 128, 355–361 (2005).
Srinivas, G. & Pitera, J. W. Soft patchy nanoparticles from solution-phase self-assembly of binary diblock copolymers. Nano Lett. 8, 611–618 (2008).
Walther, A. & Muller, A. H. E. Janus particles. Soft Matter 4, 663–668 (2008).
Glotzer, S. C. & Solomon, M. J. Anisotropy of building blocks and their assembly into complex structures. Nature Mater. 6, 557–562 (2007).
Alexeev, A., Uspal, W. E. & Balazs, A. C. Harnessing Janus nanoparticles to create controllable pores in membranes. ACS Nano 2, 1117–1122 (2008).
Cui, H. G., Chen, Z. Y., Zhong, S., Wooley, K. L. & Pochan, D. J. Block copolymer assembly via kinetic control. Science 317, 647–650 (2007).
Wang, H., Wang, X. S., Winnik, M. A. & Manners, I. Redox-mediated synthesis and encapsulation of inorganic nanoparticles in shell-cross-linked cylindrical polyferrocenylsilane block copolymer micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 12921–12930 (2008).
Li, Z. B., Kesselman, E., Talmon, Y., Hillmyer, M. A. & Lodge, T. P. Multicompartment micelles from ABC miktoarm stars in water. Science 306, 98–101 (2004).
Wang, X. S. et al. Cylindrical block copolymer micelles and co-micelles of controlled length and architecture. Science 317, 644–647 (2007).
Baumgart, T., Hess, S. T. & Webb, W. W. Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature 425, 821–824 (2003).
Korlach, J., Schwille, P., Webb, W. W. & Feigenson, G. W. Characterization of lipid bilayer phases by confocal microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8461–8466 (1999).
Veatch, S. L. & Keller, S. L. Separation of liquid phases in giant vesicles of ternary mixtures of phospholipids and cholesterol. Biophys. J. 85, 3074–3083 (2003).
Clapham, D. E. Calcium signalling. Cell 131, 1047–1058 (2007).
Haverstick, D. M. & Glaser, M. Visualization of Ca2+-induced phospholipid domains. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4475–4479 (1987).
Shoemaker, S. D. & Vanderlick, T. K. Calcium modulates the mechanical properties of anionic phospholipid membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 266, 314–321 (2003).
Geng, Y., Ahmed, F., Bhasin, N. & Discher, D. E. Visualizing worm micelle dynamics and phase transitions of a charged diblock copolymer in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 3772–3779 (2005).
Horkay, F., Tasaki, I. & Basser, P. J. Effect of monovalent–divalent cation exchange on the swelling of polyacrylate hydrogels in physiological salt solutions. Biomacromolecules 2, 195–199 (2001).
Konradi, R. & Ruhe, J. Interaction of poly(methacrylic acid) brushes with metal ions: Swelling properties. Macromolecules 38, 4345–4354 (2005).
Discher, B. M. et al. Cross-linked polymersome membranes: Vesicles with broadly adjustable properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 2848–2854 (2002).
Gell, C. B., Graessley, W. W. & Fetters, L. J. Viscoelasticity and self-diffusion in melts of entangled linear polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B 35, 1933–1942 (1997).
Velichko, Y. S. & de la Cruz, M. O. Pattern formation on the surface of cationic–anionic cylindrical aggregates. Phys. Rev. E 72, 041920 (2005).
Grason, G. M. & Santangelo, C. D. Undulated cylinders of charged diblock copolymers. Eur. Phys. J. E 20, 335–346 (2006).
Borisov, O. V. & Zhulina, E. B. Reentrant morphological transitions in copolymer micelles with pH-sensitive corona. Langmuir 21, 3229–3231 (2005).
McLaughlin, S. & Murray, D. Plasma membrane phosphoinositide organization by protein electrostatics. Nature 438, 605–611 (2005).
Oosawa, F. Polyelectrolytes (M. Dekker, 1971).
Acknowledgements
The NSF-MRSEC at the University of Pennsylvania provided primary support. Further support from the NIH (D.E.D., P.A.J.), DOE (A.J.L.) and NSF (T.B.) is very gratefully acknowledged. We thank J. D. Pajerowski for his help with correlation length and periodicity analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.A.C., A.T., I.L., P.A.J., T.B. and D.E.D. designed experiments and analysed data; D.A.C., A.T. and I.L. carried out experiments; W.G.E. and A.J.L. developed the SSL theory; K.R. contributed new reagents; D.A.C., W.G.E., A.J.L., T.B. and D.E.D. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 2443 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christian, D., Tian, A., Ellenbroek, W. et al. Spotted vesicles, striped micelles and Janus assemblies induced by ligand binding. Nature Mater 8, 843–849 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2512
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2512
This article is cited by
-
Dynamic metastable polymersomes enable continuous flow manufacturing
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Morphogenesis of starfish polymersomes
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Fluorescent label-free quantitative detection of nano-sized bioparticles using a pillar array
Nature Communications (2018)
-
In situ synthesis of block copolymer nano-assemblies by polymerization-induced self-assembly under heterogeneous condition
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science (2017)