Abstract
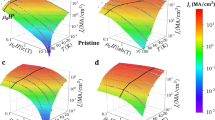
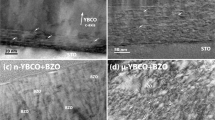
Power applications of superconductors will be tremendously boosted if an effective method for magnetic flux immobilization is discovered. Here, we report the most efficient vortex-pinning mechanism reported so far which, in addition, is based on a low-cost chemical solution deposition technique. A dense array of defects in the superconducting matrix is induced in YBa2Cu3O7−x–BaZrO3 nanocomposites where BaZrO3 nanodots are randomly oriented. Non-coherent interfaces are the driving force for generating a new type of nanostructured superconductor. Angle-dependent critical-current measurements demonstrate that a strong and isotropic flux-pinning mechanism is extremely effective at high temperatures and high magnetic fields leading to high-temperature superconductors with record values of pinning force. The maximum vortex-pinning force achieved at 65 K, 78 GN m−3, is 500% higher than that of the best low-temperature NbTi superconductors at 4.2 K and so a great wealth of high-field applications will be possible at high temperatures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larbalestier, D. C., Gurevich, A., Feldmann, D. M. & Polyanskii, A. High-Tc superconducting materials for electric power applications. Nature 414, 368–377 (2001).
Parans Paranthaman, M. & Izumi, T. High-performance YBCO-coated superconductor wires. Mater. Res. Soc. Bull. 29, 533–541 (2004).
Dam, B. et al. Origin of high critical currents in YBa2Cu3O7−δ superconducting thin films. Nature 399, 439–442 (1999).
Puig, T. et al. in Flux Pinning and AC Loss Studies on YBCO Coated Conductors (eds Parans Paranthaman, M. & Selvamanickam, V.) (Nova Science, New York, in the press).
Joos, C., Warthmann, R. & Kronmuller, H. Pinning mechanism of vortices at antiphase boundaries in YBa2Cu3O7−d . Phys. Rev. B 61, 12433–12446 (2000).
Van der Beek, C. J. et al. Strong pinning in high-temperature superconducting films. Phys. Rev. B 66, 024523 (2002).
MacManus-Driscoll, J. L. et al. Strongly enhanced current densities in superconducting coated conductors of YBa2Cu3O7−x+BaZrO3 . Nature Mater. 3, 439–443 (2004).
Haugan, T., Barnes, P. N., Wheeler, R., Meisenkothen, F. & Sumption, M. Addition of nanoparticle dispersions to enhance flux pinning of the YBa2Cu3O7−x superconductor. Nature 430, 867–870 (2004).
Kang, S. et al. High-performance high-Tc superconducting wires. Science 311, 1911–1914 (2006).
Yamada, Y. et al. Epitaxial nanostructure and defects effective for pinning in (Y,RE)Ba2Cu3O7−x coated conductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 132502 (2005).
Song, X. et al. Evidence for strong flux pinning by small, dense nanoprecipitates in a Sm-doped YBa2Cu3O7−x coated conductor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 212508 (2006).
Figueras, J. et al. The loss of vortex line tension sets an upper limit to the irreversibility line in YBa2Cu3O7 . Nature Phys. 2, 402–407 (2006).
Civale, L. et al. Vortex confinement by columnar defects in YBa2Cu3O7 crystals: enhanced pinning at high fields and temperatures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 648–651 (1991).
Obradors, X. et al. Progress towards all-chemical superconducting YBa2Cu3O7−x coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, S13–S26 (2006).
Pomar, A. et al. All-chemical high-Jc YBa2Cu3O7 multilayers with SrTiO3 as cap layer. J. Mater. Res. 21, 1106–1116 (2006).
Goyal, A. et al. Irradiation-free, columnar defects comprised of self-assembled nanodots and nanorods resulting in strongly enhanced flux-pinning in YBa2Cu3O7−δ films. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 18, 1533–1538 (2005).
Hänisch, J., Cai, C., Hühne, R., Schultz, L. & Holzapfel, B. Formation of nanosized BaIrO3 precipitates and their contribution to flux pinning in Ir-doped YBa2Cu3O7−δ quasi-multilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 122508 (2005).
Puig, T. et al. Influence of growth conditions on the microstructure and critical currents of TFA-MOD YBa2Cu3O7 films. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 18, 1141–1150 (2005).
Bals, S. et al. Transmission electron microscopy on interface engineered superconducting thin films. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 13, 2834–2837 (2003).
Haage, T. et al. Transport properties and flux pinning by self-organization in YBa2Cu3O7 films on vicinal SrTiO3 (001). Phys. Rev. B 56, 8404–8418 (1997).
Berenov, A. et al. Microstructural characterization of YBa2Cu3O7−δ thick films grown at very high rates and high temperatures by pulsed laser deposition. J. Mater. Res. 18, 956–964 (2003).
Jiang, H. G., Rühle, M. & Lavernia, E. J. On the applicability of the x-ray diffraction line profile analysis in extracting grain size and microstrain in nanocrystalline materials. J. Mater. Res. 14, 549–559 (1999).
Pomar, A., Gutiérrez, J., Palau, A., Puig, T. & Obradors, X. Porosity induced magnetic granularity in epitaxial YBa2Cu3O7 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 73, 214522 (2006).
Coll, M. et al. Stress-induced spontaneous dewetting of heteroepitaxial YBa2Cu3O7 thin films. Phys. Rev. B 73, 075420 (2006).
Zheng, H et al. Self-Assembled growth of BiFeO3–CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 18, 2747–2752 (2006).
Xie, Q., Madhukar, A., Chen, P. & Kobayashi, N. P. Vertically self-organized InAs quantum box islands on GaAs(100). Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2542–2545 (1995).
Thomson, C. V. Structure evolution during processing of polycrystalline films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 159–190 (2000).
Sutton, A. & Balluffi, R. Interfaces in Crystalline Materials (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1996).
Yoshizumi, M., Seleznev, I. & Cima, M. J. Reactions of oxyfluoride precursors for the preparation of barium yttrium cuprate films. Physica C 403, 191–199 (2004).
Gázquez, J. et al. Precursor evolution and nucleation mechanism of YBa2Cu3Ox films by TFA metal-organic decomposition. Chem. Mater. 18, 6211–6219 (2006).
Moshnyaga, V. et al. Structural phase transition at the percolation threshold in epitaxial (La0.7Ca0.3MnO3)1−x:(MgO)x nanocomposite films. Nature Mater. 2, 247–252 (2003).
Wan, J. G. et al. Magnetoelectric CoFe2O4–Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composite thin films derived by a sol-gel process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 122501 (2005).
Vucinic-Vasic, M. et al. Zn,Ni ferrite/NiO nanocomposite powder obtained from acetylacetonato complexes. Nanotechnology 17, 4877–4884 (2006).
Meingast, C. & Larbalestier, D. Quantitative description of a very high critical density Nb-Ti superconductor during its final optimization strain. II Flux pinning mechanisms. J. Appl. Phys. 66, 5971–5083 (1989).
Miura, M. et al. Addition of low-Tc nanoparticles dispersions to enhance flux pinning of Sm1+xBa2−xCu3Oy thin films. Physica C 445–448, 643–647 (2006).
Foltyn, S. & Civale, L. Understanding and pushing the limits of critical current in coated conductors. Ann. Peer Rev. US Supercond. Program Electric Syst. (2006) (www.energetics.com/supercon06).
Blatter, G., Geshkenbein, V. B. & Larkin, A. I. From isotropic to anisotropic superconductors: a scaling approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 875–879 (1992).
Civale, L. et al. Angular-dependent vortex pinning mechanisms in YBa2Cu3O7 coated conductors and thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2121–2123 (2004).
Schilling, A., Welp, U., Kwok, W. K. & Crabtree, G. W. Vortex-lattice melting in untwinned YBa2Cu3O7−δ for H⊥c. Phys. Rev. B 65, 054505 (2002).
Puig, T. & Obradors, X. Anisotropic vortex plasticity in the liquid state of YBa2Cu3O7: Evidence for quenched c-axis vortex correlation length. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1571–1574 (2000).
Gutierrez, J., Puig, T. & Obradors, X. Anisotropy and strength of vortex pinning centers in YBa2Cu3O7−x coated conductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. (in the press).
Blatter, G., Feigelman, M. V., Geshkenbein, V. B., Larkin, A. I. & Vinokur, V. M. Vortices in high-temperature superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125–1388 (1994).
Nelson, D. R. & Vinokur, V. M. Boson localization and correlated pinning of superconducting vortex arrays. Phys. Rev. B 48, 13060–13097 (1993).
Plain, J., Puig, T., Sandiumenge, F., Obradors, X. & Rabier, J. Microstructural influence on critical currents and irreversibility line in melt-textured YBa2Cu3O7−δ reannealed at high oxygen pressure. Phys. Rev. B 65, 104526 (2002).
Kim, S. I. et al. Mechanisms of weak thickness dependence of the critical current density in strong-pinning ex situ metal-organic-deposition-route YBa2Cu3O7 coated conductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, 968–979 (2006).
Palau, A. et al. Crossover between channeling and pinning at twin boundaries in YBa2Cu3O7 thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 257002 (2006).
Ijaduola, A. O. et al. Critical currents of ex situ YBa2Cu3O7−δ thin films on rolling assisted biaxially textured substrates: Thickness, field, and temperature dependencies. Phys. Rev. B 73, 134502 (2006).
Romà, N. et al. Acid anhydrides: A simple route to highly pure organometallic solutions for superconducting films. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 19, 521–527 (2006).
Zalamova, K. et al. Smooth stress relief of trifluoroacetate metal-organic solutions for YBa2Cu3O7 film growth. Chem. Mater. 18, 5897–5906 (2006).
Kliem, H., Weyers, A. & Lijtzner, J. Self-field limited currents in ceramic YBaCuO. J. Appl. Phys. 69, 1534–1537 (1991).
Sanchez, A. & Navau, C. Critical-current density from magnetization loops of finite high-Tc superconductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 14, 444–447 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from MEC (NANOARTIS, MAT2005-02047; NANOFUNCIONA, NAN2004-09133-CO3-01; FPU and RyC), Generalitat de Catalunya (Catalan Pla de Recerca SGR-0029 and CeRMAE), CSIC (PIF-CANNAMUS) and EU (HIPERCHEM, NMP4-CT2005-516858; SUPER3C, SES6-CT-2004-502615). The support of J. Santiso and C. Frontera in the X-ray diffraction analysis is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez, J., Llordés, A., Gázquez, J. et al. Strong isotropic flux pinning in solution-derived YBa2Cu3O7−x nanocomposite superconductor films. Nature Mater 6, 367–373 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1893
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1893
This article is cited by
-
Exploring the Effect of the Density of \(\textbf{Y}_{0.5} \textrm{Gd}_{0.5} \textrm{Ba}_2 \textrm{Cu}_3 \textrm{O}_{7-\delta }\) Target on Superconducting Thin Films
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2024)
-
Vertical nanoscale strain-induced electronic localization in epitaxial La2/3Sr1/3MnO3 films with ZrO2 nanopillar inclusions
Nano Convergence (2023)
-
Impact of high growth rates on the microstructure and vortex pinning of high-temperature superconducting coated conductors
Nature Reviews Physics (2023)
-
Development of metal-organic deposition-derived second-generation high-temperature superconductor tapes and artificial flux pinning
Advances in Manufacturing (2023)
-
Structural, electrical and mechanical properties of the (NdFeO3)x/(CuTl)-1223 superconductor phase
Applied Physics A (2023)