Abstract
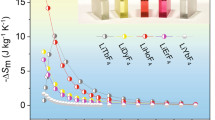
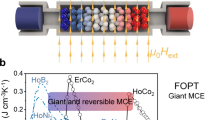
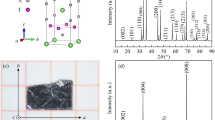
The magnetocaloric effect (MCE) is the basis for magnetic refrigeration, and can replace conventional gas compression technology due to its superior efficiency and environment friendliness1,2,3. MCE materials must exhibit a large temperature variation in response to an adiabatic magnetic-field variation and a large isothermal entropic effect is also expected. In this respect, MnAs shows the colossal MCE, but the effect appears under high pressures4. In this work, we report on the properties of Mn1−xFexAs that exhibit the colossal effect at ambient pressure. The MCE peak varies from 285 K to 310 K depending on the Fe concentration. Although a large thermal hysteresis is observed, the colossal effect at ambient pressure brings layered magnetic regenerators with huge refrigerating power closer to practical applications around room temperature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tishin, A. M. & Spichkin, I. The Magnetocaloric Effect and its Applications (Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol, 2003).
Gschneidner, K. A. Jr, Pecharsky, V. K. & Tsokol, A. O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 1479–1539 (2005).
Brück, E. Developments in magnetocaloric refrigeration. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, R381–R391 (2005).
Gama, S. et al. Pressure-induced colossal magnetocaloric effect in MnAs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 237202 (2004).
Pecharsky, V. K., Gschneidner, K. A. Jr, Pecharsky, A. O. & Tishin, A. M. Thermodynamics of the magnetocaloric effect. Phys. Rev. B 64, 144406 (2001).
Pecharsky, V. K. & Gschneidner, K. A. Jr. Giant Magnetocaloric Effect in Gd5(Si2Ge1−x)4 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4494–4497 (1997).
Tegus, O., Brück, E., Buschow, K. H. J. & de Boer, F. R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 415, 150–152 (2002).
Fujita, A., Fujieda, S., Hasegawa, Y. & Fukamichi, K. Itinerant-electron metamagnetic transition and large magnetocaloric effects in La(Fe1−xSix)13 compounds and their hydrides. Phys. Rev. B 67, 104416–104418 (2003).
Wada, H. & Tanabe, Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect of MnAs1−xSbx . Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3302–3304 (2001).
Wada, H., Taniguchi, K. & Tanabe, Y. Extremely large magnetic entropy change of MnAs1−xSbx near room temperature. Mater. Trans. 43, 73–77 (2002).
Pecharsky, V. K., Holm, A. P., Gschneidner, K. A. Jr & Rink, R. Massive magnetic-field-induced structural transformation in Gd5Ge4 and the nature of the first order transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 197204 (2003).
Morellon, L. et al. Pressure enhancement of the giant magnetocaloric effect in Tb5Si2Ge2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 137201 (2004).
von Ranke, P. J. et al. Theoretical description of the colossal entropic magnetocaloric effect: Application to MnAs. Phys. Rev. B 73, 014415 (2006).
von Ranke, P. J., de Oliveira, N. A., Mello, C., Carvalho, A. M. G. & Gama, S. Analytical model to understand the colossal magnetocaloric effect. Phys. Rev. B 71, 054410 (2004).
Richard, M. A., Rowe, A. M. & Chahine, R. Magnetic refrigeration: Single and multimaterial active magnetic regenerators experiments. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 2146–2150 (2004).
Carvalho, A. M. G. et al. The magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Gd5Ge2Si2 compound under hydrostatic pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10M320 (2005).
Rocco, D. L. et al. Magnetocaloric effect of La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 compound under pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10M317 (2005).
Fujita, A. & Fukamichi, K. Proc. First IIR Int. Conf. On Magnetic Refrigeration at Room Temperature (Montreux, Switzerland, 27–30 Sept. 2005) 201–209 (International Institute of Refrigeration, Paris, 2005).
Massalski, T. B. (ed.) in Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams 2nd edn (ASM International, Materials Park, 1990).
Menyuk, N., Kafalas, J. A., Dwight, K. & Goodenough, J. B. Effects of pressure on the magnetic properties of MnAs. Phys. Rev. 177, 942–951 (1969).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from Fapesp—Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de S. Paulo, CNPq—Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico and from Capes—Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento do Pessoal de Nível Superior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Campos, A., Rocco, D., Carvalho, A. et al. Ambient pressure colossal magnetocaloric effect tuned by composition in Mn1−xFexAs. Nature Mater 5, 802–804 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1732
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1732
This article is cited by
-
Large barocaloric effect in intermetallic La1.2Ce0.8Fe11Si2H1.86 materials driven by low pressure
NPG Asia Materials (2022)
-
Magnetic refrigeration material operating at a full temperature range required for hydrogen liquefaction
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Sintering Temperature Effects on Structural, Magnetic, Magnetocaloric and Critical Properties of Nd0.67Pb0.33Mn0.9Al0.1O3 Manganites
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2020)
-
Magnetism and Magnetocaloric Efffects of R3Pd4 (R = Nd and Pr) Compounds
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2020)
-
Ultrafast giant magnetic cooling effect in ferromagnetic Co/Pt multilayers
Nature Communications (2017)