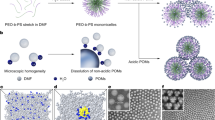
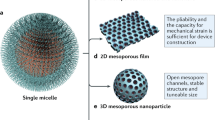
Abstract
Mesoporous materials are of technological interest because of their applications ranging from catalysts, molecular sieves, separation technology and gas sensors, to batteries and electronics1,2,3,4. Here we demonstrate a synthetic methodology that allows us to create an ordered mesoporous nanocomposite with a crystalline oxide framework. We design a 'nanocrystal–glass' configuration to build a nanoarchitecture by means of surfactant-templated self-assembly followed by the controlled in-situ crystallization of materials. Functional nanocrystals are used as the building blocks of ordered mesopores, and the glass phase can act both as the 'glue' between nanocrystals and as a functionalized component in the composites. Specifically, we demonstrate this methodology for ordered mesoporous nanocomposites consisting of electrochemically active nanocrystals and semiconductive glass in the TiO2–P2O5–MxOy systems (where M is a metal ion). This approach could be applied to many other multicomponent oxides to fabricate mesoporous nanocomposites for numerous uses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, M.E. Ordered porous materials for emerging applications. Nature 417, 813–821 (2002).
Yamata, T. et al. Surface photo voltage NO gas sensing properties dependent on the structure of self ordered mesoporous silicate film. Adv. Mater. 14, 812–815 (2002).
Kavan, L., Rathousky, J., Gratzel, M., Shklover, V. & Zukal, A. Mesoporous thin film TiO2 electrodes. Micro. Meso. Mater. 44–45, 653–659 (2001).
Miller, R.D. In search of low-k dielectrics. Science 286, 421–423 (1999).
Kresge, C.T., Leonowicz, M.E., Roth, W.J., Vartuli, J.C. & Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359, 710–712 (1992).
Attard, G.S., Glyde, J.C. & Goltner, C.G. Liquid-crystalline phases as templates for the synthesis of mesoporous silica. Nature 378, 366–378 (1995).
Zhao, D. et al. Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 279, 548–552 (1998).
Templin, M. et al. Organically modified aluminosilicate mesostructures from block copolymer phases. Science 278, 1795–1798 (1997).
Bhaumik, A. & Inagaki, S. Mesoporous titanium phosphate molecular sieves with ion-exchange capacity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 691–696 (2001).
Tian, B. et al. Self-adjusted synthesis of ordered stable mesoporous minerals by acid–base pairs. Nature Mater. 2, 159–163 (2003).
Attard, G.S. et al. Science 278, 838–841 (1997).
Bartlett, P.N., Birkin, P.N., Ghanem, M.A., de Groot, P. & Sawicki, M. The electrochemical deposition of nanostructured Ccobalt film from lyotropic liquid crystalline media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, C119–C123 (2001).
Tressler, J.F., Alkoy, S., Dogan, A. & Newnham, R.E. Functional composites for sensors, actuators and transducers. Composites A 30, 477–482 (1997).
Zen, H., Li, J., Liu, J.P., Wang, Z.L. & Sun, S. Exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnets by nanoparticle self-assembly. Nature 420, 395–398 (2002).
Yang, P., Zhao, D., Margolese, D.I., Chmelka, B.F. & Stucky, G.D. Generalized syntheses of large-pore mesoporous metal oxides with semicrystalline frameworks. Nature 396, 152–155 (1998).
Lee, B., Lu, D., Kondo, J.N. & Domen, K. Three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous niobium oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 11256–11257 (2002).
Hwang, Y.K., Lee, K.-C. & Kwon, Y.-U. Nanoparticle route to mesoporous titania thin films. Chem. Commun. 1738–1739 (2001).
Yun, H.S., Miyazawa, K., Zhou, H.S., Honma, I. & Kuwabara, M. Synthesis of mesoporous thin TiO2 films with hexagonal pore structure using triblock copolymer templates. Adv. Mater. 13, 1377–1380 (2001).
Mcmillan, P.W. Glass-Ceramics (Academic, London, 1979).
Gaskell, P.H. Structure, glass formation and properties. J. Non-Crystal. Solids 192/193, 9–22 (1995).
Lu, Y. et al. Self-assembly of mesoscopically ordered chromatic polydiacetylene/silica nanocomposites. Nature 410, 913–917 (2001).
Inagaki, S., Guan, S., Ohsuna, T. & Terasaki, O. An ordered mesoporous organosilica hybrid material with a crystal-like wall structure. Nature 416, 304–307 (2002).
Li, D., Kong, L., Zhang, L. & Yao, X. Sol-gel preparation and characterization of transparent KTiOPO4/SiO2 nanocomposite glass for second harmonic generation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 271, 45–55 (2000).
James, P.F., Iqbal, Y., Jais, U.S., Jordery, S. & Lee, W.E. Crystallisation of silicate and phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 219, 17–29 (1997).
Pinckney, L.R. & Beall, G.H. Nanocrystalline non-alkali glass-ceramics. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 219, 219–227 (1997).
Fujishima, A. & Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238, 37–38 (1972).
O'Regan, B. & Gratzel, M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 film. Nature 353, 737–739 (1991).
Bach, U. et al. Solid-state dye-sensitized mesoporous TiO2 solar cells with high photon-to-electron conversion efficiencies. Nature 395, 583–585 (1998).
Wagemaker, M., Kentgens, A.P.M. & Mulder, F.M. Equilibrium lithium transport between nanocrystalline phases in intercalated TiO2 anatase. Nature 418, 397–399 (2002).
Talavera, R.R., Vargas, S., Arroyo-Murillo, R., Montiel-Campos, R. & Haro-Poniatowski, E. Modification of the phase transition temperatures in titania doped with various cations. J. Mater. Res. 12, 439–443 (1997).
Schmutz, C. et al. EXAFS, Raman and 31P NMR study of amorphous titanium phosphates. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 170, 250–262 (1994).
Acknowledgements
D.L. acknowledges the financial support of the Japanese Society of the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Fellowship for work carried out at the Energy Electronics Institute, AIST. H.Z. thanks M. Ichihara for help in TEM observations, and acknowledges partial research funding from JSPS, Japan Science and Technology Agency, AIST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Zhou, H. & Honma, I. Design and synthesis of self-ordered mesoporous nanocomposite through controlled in-situ crystallization. Nature Mater 3, 65–72 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1043
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1043
This article is cited by
-
Mesoporous TiO2 mixed crystals for photocatalytic pure water splitting
Science China Materials (2020)
-
Sonochemically synthesized Na2Ti6O13 nanorod: an efficient electrode material for Na-ion battery
Bulletin of Materials Science (2020)
-
Effects of nano-voids and nano-cracks on the elastic properties of a host medium: XFEM modeling with the level-set function and free surface energy
Acta Mechanica Sinica (2019)
-
Preparation of 3D ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2 and their photocatalytic activity
Rare Metals (2019)
-
CuO–ZnO nanocomposite films with efficient interfacial charge transfer characteristics for optoelectronic applications
SN Applied Sciences (2019)