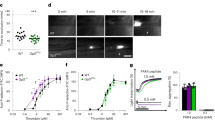
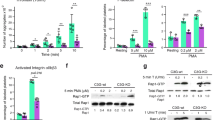
Abstract
Platelet activation at sites of vascular injury is essential for primary hemostasis, but also underlies arterial thrombosis leading to myocardial infarction or stroke1,2. Platelet activators such as adenosine diphosphate, thrombin or thromboxane A2 (TXA2) activate receptors that are coupled to heterotrimeric G proteins1,3. Activation of platelets through these receptors involves signaling through Gq, Gi and Gz (refs. 4–6). However, the role and relative importance of G12 and G13, which are activated by various platelet stimuli7,8,9, are unclear. Here we show that lack of Gα13, but not Gα12, severely reduced the potency of thrombin, TXA2 and collagen to induce platelet shape changes and aggregation in vitro. These defects were accompanied by reduced activation of RhoA and inability to form stable platelet thrombi under high shear stress ex vivo. Gα13 deficiency in platelets resulted in a severe defect in primary hemostasis and complete protection against arterial thrombosis in vivo. We conclude that G13-mediated signaling processes are required for normal hemostasis and thrombosis and may serve as a new target for antiplatelet drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruggeri, Z.M. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat. Med. 8, 1227–1234 (2002).
Bhatt, D.L. & Topol, E.J. Scientific and therapeutic advances in antiplatelet therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 15–28 (2003).
Abrams, C.S. & Brass, L.F. Platelet signal transduction. in Hemostasis and Thrombosis (eds. Colman, R.W., Hirsh, J., Marder, V.J., Clowes, A.W. & George, J.N.) 541–559 (Lippincott William & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001).
Offermanns, S., Toombs, C.F., Hu, Y.-H. & Simon, M.I. Defective platelet activation in Gαq deficient mice. Nature 389, 183–186 (1997).
Jin, J. & Kunapuli, S.P. Coactivation of two different G protein-coupled receptors is essential for ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8070–8074 (1998).
Yang, J. et al. Signaling through Gi family members in platelets. Redundancy and specificity in the regulation of adenylyl cyclase and other effectors. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46035–46042 (2002).
Klages, B., Brandt, U., Simon, M.I., Schultz, G. & Offermanns, S. Activation of G12/G13 results in shape change and Rho/Rho-kinase-mediated myosin light chain phosphorylation in mouse platelets. J. Cell Biol. 144, 745–754 (1999).
Offermanns, S., Laugwitz, K.-L., Spicher, K. & Schultz, G. G proteins of the G12 family are activated via thromboxane A2 and thrombin receptors in human platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 504–508 (1994).
Manganello, J.M., Djellas, Y., Borg, C., Antonakis, K. & Le Breton, G.C. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of thromboxane A(2) receptor-associated Galpha(13). J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28003–28010 (1999).
Offermanns, S., Mancino, V., Revel, J.-P. & Simon, M.I. Vascular system defects and impaired cell chemokinesis as a result of Gα13 deficiency. Science 275, 533–536 (1997).
Gu, J.L., Müller, S., Mancino, V., Offermanns, S. & Simon, M.I. Interaction of Gα12 with Gα13 and Gαq signaling pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9352–9357 (2002).
Lakso, M. et al. Efficient in vivo manipulation of mouse genomic sequences at the zygote stage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5860–5865 (1996).
Kühn, R., Schwenk, F., Aguet, M. & Rajewsky, K. Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269, 1427–1429 (1995).
Nieswandt, B., Schulte, V., Zywietz, A., Gratacap, M.-P. & Offermanns, S. Costimulation of Gi- and G12/G13-mediated signaling pathways induces integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 activation in platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 39493–39498 (2002).
Sambrano, G.R., Weiss, E.J., Zheng, Y.W., Huang, W. & Coughlin, S.R. Role of thrombin signaling in platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis. Nature 413, 74–82 (2001).
Savage, B., Cattaneo, M. & Ruggeri, Z.M. Mechanisms of platelet aggregation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 8, 270–276 (2001).
Sah, V.P., Seasholtz, T.M., Sagi, S.A. & Brown, J.H. The role of Rho in G protein-coupled receptor signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 459–489 (2000).
Paul, B.Z., Daniel, J.L. & Kunapuli, S.P. Platelet shape change is mediated by both calcium-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Role of p160 Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase in platelet shape change. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28293–28300 (1999).
Bauer, M. et al. Dichotomous regulation of myosin phosphorylation and shape change by Rho-kinase and calcium in intact human platelets. Blood 94,1665–1672 (1999).
Missy, K. et al. Rho-kinase is involved in the sustained phosphorylation of myosin and the irreversible platelet aggregation induced by PAR1 activating peptide. Thromb. Haemost. 85, 514–520 (2001).
Schoenwaelder, S.M. et al. RhoA sustains integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 adhesion contacts under high shear. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 14738–14746 (2002).
Jantzen, H.M., Milstone, D.S., Gousset, L., Conley, P.B. & Mortensen, R.M. Impaired activation of murine platelets lacking G alpha(i2). J. Clin. Invest. 108, 477–483 (2001).
Yang, J. et al. Loss of signaling through the G protein, Gz, results in abnormal platelet activation and altered responses to psychoactive drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9984–9989 (2000).
Dorsam, R.T., Kim, S., Jin, J. & Kunapuli, S.P. Coordinated signaling through both G12/13 and G(i) pathways is sufficient to activate GPIIb/IIIa in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47588–47595 (2002).
Kuner, R., Swiercz, J., Zywietz, A., Tappe, A. & Offermanns, S. Characterization of the expression of PDZ-RhoGEF, LARG and Gα12/Gα13 proteins in the murine nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 16, 2333–2341 (2002).
Ren, X.D. & Schwartz, M.A. Determination of GTP loading on Rho. Methods Enzymol. 325, 264–272 (2000).
Kuijpers, M.J. et al. Complementary roles of platelet glycoprotein VI and integrin alpha2beta1 in collagen-induced thrombus formation in flowing whole blood ex vivo. FASEB J. 17, 685–687 (2003).
Massberg, S. et al. A crucial role of glycoprotein VI for platelet recruitment to the injured arterial wall in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 197, 41–49 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Rogatzki and A. Rippberger for expert technical help and B. Arnold for kind help with bone marrow transplantation experiments. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Volkswagen Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moers, A., Nieswandt, B., Massberg, S. et al. G13 is an essential mediator of platelet activation in hemostasis and thrombosis. Nat Med 9, 1418–1422 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm943
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm943
This article is cited by
-
Targeting Gα13-integrin interaction ameliorates systemic inflammation
Nature Communications (2021)
-
GNA13 regulates BCL2 expression and the sensitivity of GCB-DLBCL cells to BCL2 inhibitors in a palmitoylation-dependent manner
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Gα13 Contributes to LPS-Induced Morphological Alterations and Affects Migration of Microglia
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Platelet integrin αIIbβ3: signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2019)
-
Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing
Nature Communications (2018)