Abstract
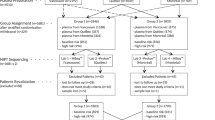
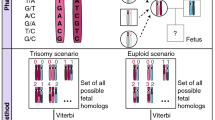
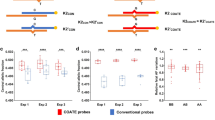
Current methods for prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal aneuploidies involve the invasive sampling of fetal materials using procedures such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling and constitute a finite risk to the fetus. Here, we outline a strategy for fetal chromosome dosage assessment that can be performed noninvasively through analysis of placental expressed mRNA in maternal plasma. We achieved noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal trisomy 21 by determining the ratio between alleles of a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in PLAC4 mRNA, which is transcribed from chromosome 21 and expressed by the placenta, in maternal plasma. PLAC4 mRNA in maternal plasma was fetal derived and cleared after delivery. The allelic ratios in maternal plasma correlated with those in the placenta. Fetal trisomy 21 was detected noninvasively in 90% of cases and excluded in 96.5% of controls.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfirevic, Z., Sundberg, K. & Brigham, S. Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling for prenatal diagnosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. CD003252 (2003).
Malone, F.D. et al. First-trimester or second-trimester screening, or both, for Down's syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 2001–2011 (2005).
Wapner, R. et al. First-trimester screening for trisomies 21 and 18. N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 1405–1413 (2003).
Bianchi, D.W., Flint, A.F., Pizzimenti, M.F., Knoll, J.H. & Latt, S.A. Isolation of fetal DNA from nucleated erythrocytes in maternal blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3279–3283 (1990).
Cheung, M.C., Goldberg, J.D. & Kan, Y.W. Prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell anaemia and thalassaemia by analysis of fetal cells in maternal blood. Nat. Genet. 14, 264–268 (1996).
Bianchi, D.W. et al. PCR quantitation of fetal cells in maternal blood in normal and aneuploid pregnancies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 61, 822–829 (1997).
Bianchi, D.W. et al. Fetal gender and aneuploidy detection using fetal cells in maternal blood: analysis of NIFTY I data. National Institute of Child Health and Development Fetal Cell Isolation Study. Prenat. Diagn. 22, 609–615 (2002).
Lo, Y.M.D. et al. Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet 350, 485–487 (1997).
Lo, Y.M.D. et al. Quantitative analysis of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum: implications for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62, 768–775 (1998).
Kaiser, J. Prenatal diagnosis. An earlier look at baby's genes. Science 309, 1476–1478 (2005).
Lo, Y.M.D. et al. Increased fetal DNA concentrations in the plasma of pregnant women carrying fetuses with trisomy 21. Clin. Chem. 45, 1747–1751 (1999).
Lee, T. et al. Down syndrome and cell-free fetal DNA in archived maternal serum. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 187, 1217–1221 (2002).
Farina, A. et al. Evaluation of cell-free fetal DNA as a second-trimester maternal serum marker of Down syndrome pregnancy. Clin. Chem. 49, 239–242 (2003).
Ng, E.K.O. et al. mRNA of placental origin is readily detectable in maternal plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 4748–4753 (2003).
Ferguson-Smith, M.A. Placental mRNA in maternal plasma: prospects for fetal screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 4360–4362 (2003).
Oudejans, C.B. et al. Detection of chromosome 21-encoded mRNA of placental origin in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 49, 1445–1449 (2003).
Tsui, N.B.Y. et al. Systematic micro-array based identification of placental mRNA in maternal plasma: towards non-invasive prenatal gene expression profiling. J. Med. Genet. 41, 461–467 (2004).
Chim, S.S.C. et al. Detection of the placental epigenetic signature of the maspin gene in maternal plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 14753–14758 (2005).
Lui, Y.Y.N. et al. Predominant hematopoietic origin of cell-free DNA in plasma and serum after sex-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Clin. Chem. 48, 421–427 (2002).
Kido, S. et al. D21S418E identifies a cAMP-regulated gene located on chromosome 21q22.3 that is expressed in placental syncytiotrophoblast and choriocarcinoma cells. Genomics 17, 256–259 (1993).
Ding, C., Maier, E., Roscher, A.A., Braun, A. & Cantor, C.R. Simultaneous quantitative and allele-specific expression analysis with real competitive PCR. BMC Genet. 5, 8 (2004).
Wapner, R.J. Invasive prenatal diagnostic techniques. Semin. Perinatol. 29, 401–404 (2005).
Amor, D.J. et al. Health and developmental outcome of children following prenatal diagnosis of confined placental mosaicism. Prenat. Diagn. 26, 443–448 (2006).
Anker, P., Mulcahy, H. & Stroun, M. Circulating nucleic acids in plasma and serum as a noninvasive investigation for cancer: time for large-scale clinical studies? Int. J. Cancer 103, 149–152 (2003).
Jurinke, C., Oeth, P. & van den Boom, D. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: a versatile tool for high-performance DNA analysis. Mol. Biotechnol. 26, 147–164 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Innovation and Technology Fund of the Hong Kong SAR Government (ITS/195/01) and the Li Ka Shing Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Y.M.D.L., N.B.Y.T., R.W.K.C., C.R.C. and C.D. have filed a patent application on the RNA-SNP allelic ratio technology described in this paper.
Y.M.D.L. has equity in Plasmagene Biosciences Limited.
C.R.C. and C.D. have equity in Sequenom Inc.
C.R.C. is the Chief Scientific Officer of Sequenom Inc.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
MS tracings of the PLAC4 SNP genotype in DNA samples of maternal blood cells and placentas and RNA samples of placentas and maternal plasma. (PDF 1523 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Transcripts from chromosome 21 with high relative and absolute placental tissue expression as identified by the micorarray data mining strategy. (PDF 73 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Sequences and allelic frequencies of four polymorphic SNPs located in the transcribed regions of PLAC4. (PDF 100 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
PLAC4 SNP genotype analysis using maternal blood cell and placental DNA as well as placental and maternal plasma RNA obtained from pregnant women carrying euploid fetuses. (PDF 73 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Primer sequences of the RNA-SNP allelic ratio assay involving the PLAC4 SNP, rs8130833. (PDF 108 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
PCR primers for direct sequencing of PLAC4. (PDF 81 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, Y., Tsui, N., Chiu, R. et al. Plasma placental RNA allelic ratio permits noninvasive prenatal chromosomal aneuploidy detection. Nat Med 13, 218–223 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1530
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1530
This article is cited by
-
Women’s experiences with non-invasive prenatal testing in Switzerland: a qualitative analysis
BMC Medical Ethics (2023)
-
Bringing precision medicine to the management of pregnancy in women with glucokinase-MODY: a study of diagnostic accuracy and feasibility of non-invasive prenatal testing
Diabetologia (2023)
-
A dPCR-NIPT assay for detections of trisomies 21, 18 and 13 in a single-tube reaction-could it replace serum biochemical tests as a primary maternal plasma screening tool?
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Non-invasive characterization of human bone marrow stimulation and reconstitution by cell-free messenger RNA sequencing
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Prenatal diagnosis of 4953 pregnant women with indications for genetic amniocentesis in Northeast China
Molecular Cytogenetics (2019)