Abstract
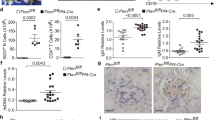
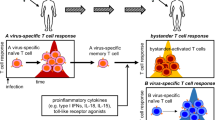
We found that platelet depletion reduces intrahepatic accumulation of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and organ damage in mouse models of acute viral hepatitis. Transfusion of normal but not activation-blocked platelets in platelet-depleted mice restored accumulation of CTLs and severity of disease. In contrast, anticoagulant treatment that prevented intrahepatic fibrin deposition without reducing platelet counts did not avert liver injury. Thus, activated platelets contribute to CTL-mediated liver immunopathology independently of procoagulant function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guidotti, L.G. & Chisari, F.V. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 65–91 (2001).
Wilson, J.M. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46, 205–209 (2001).
Weyrich, A.S., Lindemann, S. & Zimmerman, G.A. J. Thromb. Haemost. 1, 1897–1905 (2003).
Weyrich, A.S. & Zimmerman, G.A. Trends Immunol. 25, 489–495 (2004).
Ando, K. et al. J. Immunol. 152, 3245–3253 (1994).
Guidotti, L.G. et al. Immunity 4, 25–36 (1996).
Kakimi, K. et al. J. Exp. Med. 194, 1755–1766 (2001).
Sitia, G. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 1158–1167 (2004).
McClary, H., Koch, R., Chisari, F.V. & Guidotti, L.G. J. Virol. 74, 2255–2264 (2000).
Ware, J., Russell, S. & Ruggeri, Z.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2803–2808 (2000).
Chisari, F.V. & Ferrari, C. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 29–60 (1995).
Shoukry, N.H., Cawthon, A.G. & Walker, C.M. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 58, 391–424 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to S. Wieland for providing the pCMV-lacZ plasmid and for discussions. We also thank S. Medrano and M. Chadwell for technical assistance. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants HL31950, HL42846, HL78784 (to Z.M.R.), CA40489 (to F.V.C.) and AI40696 (to L.G.G.). Work in the Board of Governors Gene Therapy Research Institute is funded by the Board of Governors at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the US National Institutes of Health and the Bram and Elaine Goldsmith Chair in Gene Therapeutics. This is manuscript number 16807-MEM from the Scripps Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Platelets accumulate within necroinflammatory foci of the liver. (PDF 2379 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Reduced levels of IFN-γ expression and inhibition of viral replication reflect the homing of fewer but functional CTLs in the liver of thrombocytopenic HBV transgenic mice. (PDF 412 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
TKK-PLTs are recognized by α-PLT both in vitro and in vivo. (PDF 845 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Restoration of liver disease severity, CTL accumulation and intrahepatic IFN-γ expression in platelet-depleted mice upon TKK-PLT transfusion. (PDF 727 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Platelet-dependent fibrin deposition within the inflamed liver. (PDF 2428 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
α-PLT treatment selectively depletes platelets in vivo. (PDF 20 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
CTLs interact with activated platelets in vitro. (MOV 41155 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iannacone, M., Sitia, G., Isogawa, M. et al. Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte–induced liver damage. Nat Med 11, 1167–1169 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1317
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1317
This article is cited by
-
Does aspirin reduce the incidence, recurrence, and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma? A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2023)
-
The GPIb-IX complex on platelets: insight into its novel physiological functions affecting immune surveillance, hepatic thrombopoietin generation, platelet clearance and its relevance for cancer development and metastasis
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection
Nature Reviews Immunology (2022)
-
The phosphatase PTEN links platelets with immune regulatory functions of mouse T follicular helper cells
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Elevated mean platelet volume in oral lichen planus and increased blood urea nitrogen level in its red-form: an observational study
BMC Oral Health (2021)