Abstract
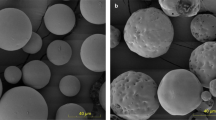
An injectable sustained–release form of human growth hormone (hGH) was developed by stabilizing and encapsulating the protein, without altering its integrity, into biodegradable microspheres using a novel cryogenic process. A single injection of microspheres in monkeys resulted in elevated serum levels of recombinant hCH (rhGH) for more than one month. Insulin–like growth factor–I (ICF–I) and its binding protein IGFBP–3, both of which are induced by hGH, were also elevated for four weeks by the rhGH containing microspheres to a level greater than that induced by the same amount of rhGH administered by daily injections. These results show that, by using appropriate methods of stabilization and encapsulation, the advantages of sustained–release formulations previously demonstrated for low–molecular–weight drugs can now be extended to protein therapeutics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langer, R. New methods of drug delivery. Science 249, 1527–1533 (1990).
Mulligan, R.C. The basic science of gene therapy. Science 260, 926–932 (1993).
Wise, D.L., Jackanics, T.M., Nash, H.A. & Gregory, J.B. Polylactic acid as a biodegradable carrier for contraceptive steroids. Contraception 8, 227–234 (1973).
Beck, L.R., Pope, V.Z., Cowsar, D.R., Lewis, D.H. & Tice, T.R. Evaluation of a new three-month contraceptive microsphere system in primates. J. Contracept. Delhi. Sys. 1, 79–82 (1980).
Pitt, G.C., Marks, A. & Schindler, A. Biodegradable drug delivery systems based on aliphatic polymers: Application to contraceptives and narcotic antagonists. in Controlled Release of Bioactive Agents. (ed. Baker, R.W.) 19–43 (Academic Press, New York, 1980).
Hutchinson, F.G. & Furr, B.J.A. Biodegradable polymers for sustained release of peptides. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 13, 520–523 (1985).
Ogawa, Y., Okada, H., Yamamota, M. & Shimamoto, T. In vivo release profiles of leuprolide acetate from microcapsules prepared with polylactic acids or copoly (lactic/glycolic) acids and in vivo degradation of these polymers. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36, 2576–2581 (1988).
Sanders, L.M., Kell, B.A., McRae, G.I. & Whitehead, G.W. Prolonged controlled release of nafarelin, a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue, from biodegradable polymeric implants: Influence of composition and molecular weight of polymer. J. Pharm. Sci. 75, 356–360 (1986).
Austin, P.E. et al. Subcuticular sutures and the rate of inflammation in noncon-taminated wounds. Ann. Emerg. Med. 25, 328–330 (1995).
Pihlajamaki, H., Bostman, O., Hirvensalo, E., Tormala, P. & Rokkanen, P. Absorbable pins of self-reinforced poly-L-lactic acid for fixation of fractures and osteotomies. J. Bone Joint Surg, 74, 853–857 (1992).
Winde, G. et al. Clinical and functional results of abdominal rectopexy with absorbable mesh-graft for treatment of complete rectal prolapse. Eur. J. Surg. 159, 301–305 (1993).
Cohen, S. et al. Ionically cross-linkable polyphosphazene: A novel polymer for microencapsulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 7832–7833 (1990).
Ogawa, Y., Yamamoto, M., Okada, H., Yashiki, T. & Shimamoto, T. A new technique to efficiently entrap leuprolide acetate into microcapsules of polylactic acid or copoly (lactic/glycolic) acid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 5, 1095–1103 (1988).
Cohen, S., Yoshioka, T., Lucarelii, M., Hwang, L.H. & Langer, R. Controlled delivery systems for proteins based on poly (lactic/glycolic acid) microspheres. Pharm. Research 8, 713–720 (1991).
Mathiowitz, E., Saltzman, W.M., Domb, A., Dor, P. & Langer, R. Polyanhydride microspheres as drug carriers. II. Microencapsulation by solvent removal. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 35, 755–774 (1988).
Daughaday, W.F. Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors and acromegaly. in Endocrinology, (ed. DeGroot, L.J.) 303–329 (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1995).
Pearlman, R. & Bewley, T.A. Stability and characterization of human growth hormone, in Stability and Characterization of Protein and Peptide Drugs: Case Histories, (eds. Wang, Y.J. & Pearlman, R.) 1–58 (Plenum, New York, 1993).
Laursen, T., Jorgensen, O.L., Jakobsen, G., Hansen, B.L. & Christiansen, J.S. Continuous infusion versus daily injections of growth hormone (GH) for 4 weeks in GH-deficient patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 2410–2418 (1995).
Tauber, H., De Bouet du Portal, H., Sallerin-Caute, B., Rochiccioli, P. & Bastide, R. Differential regulation of serum growth hormone (GH)-binding protein during continuous infusion vs. daily injection of recombinant human GH in GH-deficient children. J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab. 76, 1135–1139 (1993).
Thorlacius-Ussing, O. Zinc in the anterior pituitary of the rat: A histochemical and analytical work. Neuroendocrinology 45, 233–242 (1987).
Cunningham, B.C., Mulkerrin, M.G. & Wells, J.A. Dimerization of human growth hormone by zinc. Science 253, 545–548 (1991).
Coleman, J.E. Zinc proteins: Enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 897–946 (1992).
Steiner, D.F., Bell, G.I., Tager, H.S. & Rubenstein, A.H. Chemistry and biosynthesis of the islet hormones: Insulin, islet amyloid polypeptide (amylin), glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. in Endocrinology. (ed. DeGroot, L.J.) 1296–1328 (Saunders, Philadelphia, 1995).
Mathews, L.S., Norstedt, G. & Palmiter, R.D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by growth hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 9343–9347 (1986).
Hardouin, S. et al. Molecular forms of serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins in man: Relationships with growth hormone and IGFs and physiological significance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 69, 1291–1301 (1989).
Wilson, M.E. & Tanner, J.M. Long-term effects of recombinant human growth hormone treatment on skeletal maturation and growth in female rhesus monkeys with normal pituitary function. J. Endocrinol. 130, 435–441. (1991).
Li, C.H., Lahm, H.W. & Stein, S. The primary structure of monkey pituitary growth hormone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 245, 287–291 (1986).
Schwendeman, S.P., Cardamone, M., Brandon, M.R., Klibanov, A. & Langer, R. Stability of proteins and their delivery from biodegradable polymer microspheres. in Microspheres/Microparticles: Characterization and Pharmaceutical Application. (eds. Cohen, S. & Bernstein, H.) 1–49 (Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1996).
Cleland, J.L. & Yang, J. In vitro release of bioactive recombinant human interferon from PLGA microspheres. Proc. Int. Symp. Control. Rel. Bioact. Mater. 22, 518–519 (1995).
Pitt, C.G. The controlled parenteral delivery of polypeptides and proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 59, 173–196 (1990).
Shah, S.S., Cha, Y. & Pitt, C.G. Poly (glycolic acid-CO-DL-lactic acid): Diffusion or degradation controlled delivery? J. Control. Rel. 18, 261–270 (1992).
Cleland, J.L. et al. Characterization of recombinant human growth hormone-PLGA formulations in animals. Proc. Int. Symp. Control. Rel. Bioact. Mater. 22, 143–144 (1995).
Physician's Desk Reference. 2502–2506 (Medical Economics Data, Montvale, New Jersey, 1995).
Eckhardt, B.M., Oeswein, J.Q. & Bewley, T.A. Effect of freezing on aggregation of human growth hormone. Pharm. Res. 8, 1360–1364 (1991).
Battersby, J.E., Hancock, W.S., Canova-Davis, E., Oeswein, J. & O'Connor, B. Diketopiperazine formation and N-terminal degradation in recombinant human growth hormone. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 44, 215–222 (1994).
Battersby, J.E., Mukku, V.R., Clark, R.G. & Hancock, W.S. Affinity purification and microcharacterization of recombinant DNA-derived human growth hormone isolated from an in vivo model. Anal. Chem. 67, 447–455 (1995).
Canova-Davis, E. et al. Properties of a cleaved two-chain form of recombinant human growth hormone. Int. J Peptide Protein Res. 35, 17–24 (1990).
Teshima, G., Stults, J.T., Ling, V. & Canova-Davis, E. Isolation and characterization of a succinimide variant of methionyl human growth hormone. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 13544–13547 (1991).
Teshima, G. & Canova-Davis, E. Separation of oxidized human growth hormone variants by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 625, 207–215 (1992).
Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, O., Cleland, J., Lee, H. et al. A month–long effect from a single injection of microencapsulated human growth hormone. Nat Med 2, 795–799 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0796-795
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0796-795
This article is cited by
-
Shape-specific microfabricated particles for biomedical applications: a review
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2022)
-
Optimal Design of Needle Array for Effective Drug Delivery
Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2018)
-
Poly(amino carbonate urethane)-based biodegradable, temperature and pH-sensitive injectable hydrogels for sustained human growth hormone delivery
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Development of dextran nanoparticles for stabilizing delicate proteins
Nanoscale Research Letters (2013)
-
IL-1Ra and its Delivery Strategies: Inserting the Association in Perspective
Pharmaceutical Research (2013)