Abstract
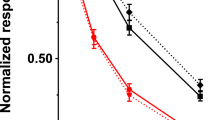
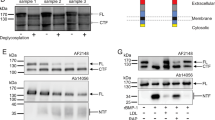
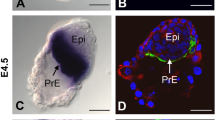
Cubilin is the intestinal receptor for the endocytosis of intrinsic factor–vitamin B12. However, several lines of evidence, including a high expression in kidney and yolk sac, indicate it may have additional functions. We isolated apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I), the main protein of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), using cubilin affinity chromatography. Surface plasmon resonance analysis demonstrated a high-affinity binding of apoA-I and HDL to cubilin, and cubilin-expressing yolk sac cells showed efficient 125I-HDL endocytosis that could be inhibited by IgG antibodies against apoA-I and cubilin. The physiological relevance of the cubilin–apoA-I interaction was further emphasized by urinary apoA-I loss in some known cases of functional cubilin deficiency. Therefore, cubilin is a receptor in epithelial apoA-I/HDL metabolism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birn, H. et al. Characterization of an epithelial approximately 460-kDa protein that facilitates endocytosis of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 and binds receptor-associated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26497– 26504 (1997).
Moestrup, S.K. et al. The intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor and target of teratogenic antibodies is a megalin-binding peripheral membrane protein with homology to developmental proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5235–5242 (1998).
Kozyraki, R. et al. The human intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin: molecular characterization and chromosomal mapping of the gene to 10p within the autosomal recessive megaloblastic anemia (MGA1) region. Blood 91, 3593–3600 ( 1998).
Aminoff, M. et al. Mutations in the CUBN gene encoding the intrinsic factor vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin cause hereditary megaloblastic anemia 1 (MGA-1) Nature Genet. 21, 309–313 (1999).
Fyfe, J.C., Ramanujam, K.S., Ramaswamy, K., Patterson, D.F., & Seetharam, B. Defective brush-border expression of intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor in canine inherited intestinal malabsorption. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 4489– 94 (1991).
Sahali, D. et al. Characterization of a 280-kD protein restricted to the coated pits of the renal brush border and the epithelial cells of the yolk sac. Teratogenic effect of the specific monoclonal antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 167, 213–218 ( 1988).
Seetharam, B., Christensen, E.I., Moestrup, S.K., Hammond, T.G. & Verroust, P.J. Identification of rat yolk sac target protein of teratogenic antibodies, gp280, as intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 2317– 2322 (1997).
Imerslund O. Idiopathic chronic megaloblastic anemia in children. Acta Paed. Scand. 49, 1–115 ( 1960).
Gräsbeck R, Gordin R, Kantero I & Kuhlback B : Selective vitamin B12 malabsorption and proteinuria in young people. Acta Med. Scand. 167, 289–296 (1960).
Brown, M.S. & Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232, 34–47 (1986).
Acton, S. et al.. Identification of scavenger receptor SR-BI as a high density lipoprotein receptor. Science 271, 518– 520 (1996).
Le Panse, .S. et al. Immunofunctional properties of a yolk sac epithelial cell line expressing two proteins gp280 and gp330 of the intermicrovillar area of proximal tubule cells: inhibition of endocytosis by the specific antibodies. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 67, 120– 129 (1995).
Wyne, K.L. & Woollett, L.A. Transport of maternal LDL and HDL to the fetal membranes and placenta of the Golden Syrian hamster is mediated by receptor-dependent and receptor-independent processes. J. Lipid. Res. 39, 518–530 ( 1998).
Moestrup, S.K. et al. β2-Glycoprotein-I (apolipoprotein-H) and β 2-Glycoprotein-I-phospholipid complex harbor a recognition site for the endocytic receptor megalin. J. Clin. Invest. 102 , 902–909 (1998).
Stefansson, S., Chappell, D.A., Argraves, K.M., Strickland, D.K. & Argraves, W.S. Glycoprotein 330/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-2 mediates endocytosis of low density lipoproteins via interaction with apolipoprotein B100. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 19417–19421(1995).
Glass, C., Pittman, R.C., Civen, M. & Steinberg, D. Uptake of high-density lipoprotein-associated apolipoprotein A-I and cholesterol esters by 16 tissues of the rat in vivo and by adrenal cells and hepatocytes in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 744–750 (1985).
Willnow, T.E., Goldstein, J.L., Orth, K., Brown, M.S. & Herz, J. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and gp330 bind similar ligands, including plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes and lactoferrin, an inhibitor of chylomicron remnant clearance. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 26172– 26180 (1992).
Kounnas, M.Z. et al. Identification of glycoprotein 330 as an endocytic receptor for apolipoprotein J/clusterin. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13070–13075 (1995).
Kozarksky, K.F. et al. Overexpression of the HDL receptor SR-BI alters plasma HDL and bile cholesterol levels. Nature 387, 414–417 (1997).
Saku K., Reddy, G.S., Hynd, B.A. & Kashyap. M. Renal handling of high-density lipoprotein by isolated perfused kidneys. Metabolism 33, 432–438 ( 1984).
Farese, R.V., Jr. & Herz, J. Cholesterol metabolism and embryogenesis. Trends Genet. 14, 115–120 (1998).
Kolf-Clauw, M. et al. Inhibition of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase by the teratogen AY9944: a rat model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Teratology 54, 115–125 ( 1996).
Cooper, M.K., Porter, J.A, Young. K.E., Beachy, P.A. Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling. Science 280 , 1603–1607. (1998).
Farese, R.V. Jr. et al. A novel function for apolipoprotein B: lipoprotein synthesis in the yolk sac is critical for maternal-fetal lipid transport in mice. J. Lipid Res. 37, 347–360 (1996).
Farese, R.V. Jr., Ruland, S.L., Flynn, L.M., Stokowski, R.P. & Young, S.G. Knockout of the mouse apolipoprotein B gene results in embryonic lethality in homozygotes and protection against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in heterozygotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 1774–1778 (1995).
Homanics, G.E. et al. Exencephaly and hydrocephaly in mice with targeted modification of the apolipoprotein B (Apob) gene. Teratology 51, 1–10 (1995).
Willnow, T.E. et al. Defective forebrain development in mice lacking gp330/megalin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8460– 8464 (1996).
Sahali, D. et al. Comparative immunochemistry and ontogeny of two closely related coated pit proteins. The 280-kd target of teratogenic antibodies and the 330-kd target of nephritogenic antibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 142, 1654–1667 (1993).
Plump, A.S. et al. ApoA-I knockout mice:characterization of HDL metabolism in homozygotes and identification of a post-RNA mechanism of apoA-I upregulation in heterozygotes. J. Lipid. Res. 36, 1933 –1047 (1997).
Rigotti, A. et al. Scavenger receptor BI—a cell surface receptor for high density lipoprotein. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 8, 181–188 (1997).
Hatzopoulos, A.K., Rigotti, A., Rosenberg, R.D & Krieger, M. Temporal and spatial pattern of expression of the HDL receptor SR-BI during murine embryogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 39, 495–508 (1998).
Hatch, F.T. & Lees, R.S. . Practical methods for plasma lipoprotein analysis. Adv. Lipid. Res. 6, 1– 68 (1968).
Moestrup, S.K. et al.. Megalin-mediated endocytosis of transcobalamin-vitamin-B12 complexes suggests a role of the receptor in vitamin-B12 homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8612– 8617 (1996).
Acknowledgements
The technical assistance of K. Lassen is acknowledged. The patients are thanked for their cooperation and S. Lindh, for sample collection. U. Gerdes and J. Møller are thanked for the cholesterol and creatinin measurements. J. Gliemann is thanked for comments on the manuscript. The work was financially supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Danish Medical Research Council, the Danish Biomembrane Center, Aarhus University Research Foundation, the Velux Foundation, a contract from ARC (9914, le Ministére des Affaires Etrangéres, France, NIH grant DK45341 (J.C.F.) and National Cancer Institute grant P30 CA16058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozyraki, R., Fyfe, J., Kristiansen, M. et al. The intrinsic factor–vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin, is a high-affinity apolipoprotein A-I receptor facilitating endocytosis of high-density lipoprotein. Nat Med 5, 656–661 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/9504
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/9504
This article is cited by
-
Identification and characterization of intact glycopeptides in human urine
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Deficiency of vitamin B12 and its relation with neurological disorders: a critical review
The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology (2020)
-
Loss of Cubilin, the intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor, impairs visceral endoderm endocytosis and endodermal patterning in the mouse
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Structural assembly of the megadalton-sized receptor for intestinal vitamin B12 uptake and kidney protein reabsorption
Nature Communications (2018)
-
The association between high-density lipoproteins and estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients without severe kidney disease
International Urology and Nephrology (2018)