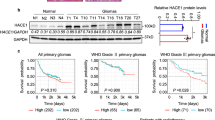
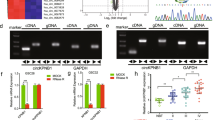
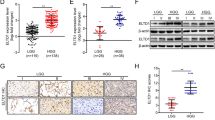
Abstract
The transfer of apoptosis genes to tumors is one of the most promising strategies for cancer gene therapy. We have shown that massive apoptosis occurs when wild-type p53 expression is induced in glioma cells carrying a p53 gene mutation. However, adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer is ineffective in causing apoptosis in glioma cells that retain a wild-type p53 genotype. We evaluated the effect of E2F-1 overexpression on the growth of gliomas in vitro and in vivo. In the in vitro study, the adenovirus-mediated transfer of exogenous E2F-1 protein precipitated generalized apoptosis in gliomas. The treatment with AdSCMV-f 2F-1 of nude mice carrying subcutaneous gliomas arrested tumor growth. Our results indicate that E2F-T has anti-glioma activity in vitro and in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherr, C.J. Cancer cell cycles. Science 274, 1672–1677 (1996).
Gomez-Manzano, C., Fueyo, J., Kyritsis, A.P. & Yung, W.K.A. in: Gene Transfer and Therapy for Neurological Disorders (eds. Chiocca, A.E. & Breakefield, X.) 201–225 (Human Press-Inc, Totowa, N.J., 1998).
Qin, X.Q. et al. The transcription factor E2F-1 is a downstream target of RB action. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 742–755 (1995).
Kovesdi, I., Reichel, R., & Nevins, J.R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in El A trans-activation. Cell 45, 219–228 (1986).
Helin, K. et al. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell 70, 337–350 (1992).
Kaelin, W.C. et al. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell 70, 351–364 (1992).
Shan, B. et al. Molecular cloning of cellular genes encoding retinoblastoma-associated proteins: identification of a gene with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 5620–5631 (1992).
Johnson, D.C., Schwarz, J.K., Cress, W.D. & Nevins, J.R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature 365, 349–352 (1993).
Singh, P., Wong, S.H. & Hong, W. Overexpression of E2F-1 in rat embryo fibrob-lasts leads to neoplastic transformation. EMBO J. 13, 3329–3338 (1994).
Qin, X.Q., Livingston, D.M., Kaelin, W.G. & Adams, P.D. Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 10918–10922 (1994).
Wu, X. & Levine, A.J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 3602–3606 (1994).
Field, S.J. et al. E2F-1 functions in mice to promote apoptosis and suppress proliferation. Cell 85, 549–561 (1996).
Yamasaki, L. et al. Tumor induction and tissue atrophy in mice lacking E2F-1. Cell 85, 537–548 (1996).
Gomez-Manzano, C. et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of the p53 gene produces rapid and generalized death of human glioma cells via apoptosis. Cancer Res. 56, 694–699 (1996).
Kyritsis, A.P., Xu, R., Bondy, M.L., Levin, V.A. & Bruner, J.M. Correlation of p53 immunoreactivity and sequencing in patients with glioma. Mol. Carcinog. 15, 1–4 (1996).
Jung, J.-M. et al. Increased levels of p21WAF1/Cipl in human brain tumors. Oncogene 11, 2021–2028 (1995).
Gomez-Manzano, C. et al. Characterization of p53 and p21 functional interactions in glioma cells en route to apoptosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 14, 1036–1044 (1997).
Hunt, K.K. et al. Adenovirus-mediated expression of the transcription factor E2F-1 induces apoptosis in human breast and ovarian carcinoma cell lines and does not require p53. Cancer Res 57, 4722–4726 (1997).
Masuda, H. Miller, C., Koeffler, H.P., Battifora, H. & Cline, M.J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 84, 7716‐7719 (1987).
Hirvonen, H.E. et al. Differential expression of myc, max and RBI genes in human gliomas and glioma cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 69, 16–25 (1994).
Huang, J.-J.S. et al. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science 242, 1563–1566 (1988).
Arap, W., Nishikawa, R., Furnari, F.B., Cavanee, W.K. & Huang, H.-J.S. Replacement of the p16/CDKN2 gene suppresses human glioma cell growth. Cancer Res. 55, 1351–1354 (1995).
Li, Y., Nichols, M.A., Shay, J.W. & Xiong, Y. Transcriptional repression of the D-type cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor pi 6 by the retinobiastoma susceptibility gene product pRB. Cancer Res. 54, 6078–6082 (1994).
Lukas, J., Petersen, B.O., Holm, K., Bartek, J. & Helin, K. Deregulated expression of E2F family members induces S-phase entry and overcomes p16INK4-mediated growth suppression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 1047–1057 (1996).
Hsieh, J.-K., Fredersdorf, S., Kouzarides, T., Martin, K. & Lu, X. E2F-1 -induced apoptosis requires DNA binding by not transactivation and is inhibited by the retinobiastoma protein through direct interaction. Genes Dev. 11, 1840–1852 (1997).
Kyritsis, A.P. In Practice Guidelines for Neurologic Therapy (eds Lechtenberg, R. & Schutta, H.S.) 473–496 (Marcel Dekker, New–York, 1997).
Fueyo, J. et al. Adenovirus-mediated p16/CDKN2 gene transfer induces growth arrest and modifies the transformed phenotype of glioma cells. Oncogene 12, 103–110 (1996).
Fueyo, J. et al. Suppression of human glioma growth by adenovirus mediated Rb gene transfer. Neurology (in the press).
Poluha, W. et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 (WAF1) is required for survival of differentiating neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 1335–1341 (1996).
Polyak, K., Waldman, T., He, T.-C., Kinzler, K.W. & Vogelstein, B. Genetic determinants of p53-induced apoptosis and growth arrest. Genes Dev. 10, 1945–1952 (1996).
Kuida, K. et al. Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature 384, 368–372 (1996).
Enari, M., Talanian, R.V., Wong, W.W. & Nagata, S. Sequential activation of ICE-like and CPP-32-like proteases during Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature 380, 723–726 (1996)
Phillips, A.C., Bates, S., Ryan, K.M., Helin, K. & Vousden, K.H. Induction of DNA synthesis and apoptosis are separable functions of E2F-1. Genes Dev. 11, 1853–1863 (1997).
Parr, M.J. et al. Tumor-selective transgene expression in vivo mediated by an E2F-responsive adenoviral vector. Nature Med. 3, 1145–1149 (1997).
Steck, P.A. et al. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor and associated glycoprotein on cultured human brain tumor cells. J. Cell Biochem. 32, 1–10 (1986).
Eastham, J.A. et al. In vivo gene therapy with p53 or p21 adenovirus for prostate cancer. CancerRes. 55, 5151–5155 (1995).
Alemany, R. et al. Growth inhibitory effect of anti-K-ras adenovirus on lung cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 3, 296–301 (1996).
Alemany, R. et al. Complementation of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors: size effects and titer fluctuations. J. Virol. Methods 68, 147–159 (1997).
Attia, M.A. & Weiss, D.W. Immunology of spontaneous mammary carcinomas in mice. V: acquired tumor resistance and enhancement in strain of mice infected with mammary tumor virus. Cancer Res. 26, 1787–1800 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fueyo, J., Gomez-Manzano, C., Yung, W. et al. Overexpression of E2F‐1 in glioma triggers apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Nat Med 4, 685–690 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0698-685
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0698-685
This article is cited by
-
Receptor-Interacting Protein 140 Enhanced Temozolomide-Induced Cellular Apoptosis Through Regulation of E2F1 in Human Glioma Cell Lines
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2022)
-
MiRNA-329 targeting E2F1 inhibits cell proliferation in glioma cells
Journal of Translational Medicine (2013)
-
Viruses, gene therapy and stem cells for the treatment of human glioma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2009)
-
Delta-24-RGD in Combination With RAD001 Induces Enhanced Anti-glioma Effect via Autophagic Cell Death
Molecular Therapy (2008)
-
Tetrazolium violet induces G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis in brain tumor cells
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2006)