Abstract
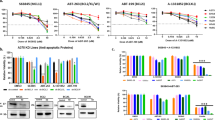
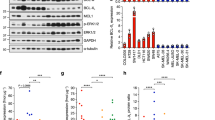
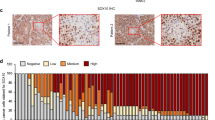
Malignant melanoma is a prime example of cancers that respond poorly to various treatment modalities including chemotherapy1. A number of chemotherapeutic agents have been shown recently to act by inducing apoptosis, a type of cell death antagonized by the bcl-2 gene2. Human melanoma expresses Bcl-2 in up to 90% of all cases3–7. In the present study we demonstrate that bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide treatment improves the chemo-sensitivity of human melanoma grown in severe combined im-munodeficient (SCID) mice. Our findings suggest that reduction of Bcl-2 in melanoma, and possibly also in a variety of other tumors, may be a novel and rational approach to improve chemosensitivity and treatment outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boring, C.C., Squires, T.S., Tong, T. & Montgomery, S. Cancer statistics 1994. CA: Cancer J. Clinic 44, 7–26 (1994).
Hickman, J.A. Apoptosis and chemotherapy resistance. Eur. J. Cancer 32A, 921–926 (1996).
Cerroni, L., Soyer, H.P. & Kerl, H. bcl-2 protein expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma and benign melanocytic nevi. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 17, 7–11 (1995).
Morales-Ducret, C.R.J., van deRijn, M., LeBrun, D.P. & Smoller, B.R. bcl-2 expression in primary malignancies of the skin. Arch. Dermatol. 131, 909–918 (1995).
Plettenberg, A. et al. Human melanocytes and melanoma cells constitutively express the Bcl-2 proto-oncogene in situ and in cell culture. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 651–659 (1995).
Tron, V.A. et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2 protein regulation in cutaneous melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 146, 643–650 (1995).
Grover, R. & Wilson, C.D. Bcl-2 expression in malignant melanoma and its prognostic significance. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 22, 347–349 (1996).
Stein, C.A. & Cheng, Y.-C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents–Is the bullet really magical? Science 261, 1004–1012 (1993).
Stein, C.A. Does antisense exist? Nature Med. 1, 1119–1121 (1995).
Christoffersen, R.E. Translating genomics information into therapeutics: A key role for oligonucleotides. Nature Biotechnol. 15, 483–484 (1997).
Monia, B.P., Johnston, J.F., Geiger, T., Muller, M. & Fabbro, D. Antitumor activity of a phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeted against C-raf kinase. Nature Med. 2, 668–675 (1996).
Comis, R.L. DTIC (NSC-45388) in malignant melanoma: A perspective. Cancer Treat Rep. 60, 165–176 (1976).
Henry, S.P., Monteith, D. & Levin, A.A. Antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. 2. Toxicological properties of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Anti-Cancer Drug Des. 12, 395–408 (1997).
Krieg, A.M. et al. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature 374, 546–549 (1995).
Wooldridge, J.E., Ballas, Z., Krieg, A.M. & Weiner, G.J. Immunostimulatory oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs enhance the efficacy of monoclonal antibody therapy of lymphoma. Blood, 89, 2994–2998 (1997).
Webb, A. et al. BCL-2 antisense therapy in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet 349, 1137–1141 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jansen, B., Schlagbauer-Wadl, H., Brown, B. et al. bcl-2 antisense therapy chemosensitizes human melanoma in SCID mice. Nat Med 4, 232–234 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0298-232
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0298-232
This article is cited by
-
Weight control interventions improve therapeutic efficacy of dacarbazine in melanoma by reversing obesity-induced drug resistance
Cancer & Metabolism (2016)
-
U1 Adaptor Oligonucleotides Targeting BCL2 and GRM1 Suppress Growth of Human Melanoma Xenografts In Vivo
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2013)
-
Oblimersen in combination with temozolomide and albumin-bound paclitaxel in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase I trial
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2013)
-
Electroporation increases antitumoral efficacy of the bcl-2 antisense G3139 and chemotherapy in a human melanoma xenograft
Journal of Translational Medicine (2011)
-
Functional and prognostic relevance of the homeobox protein MSX2 in malignant melanoma
British Journal of Cancer (2011)