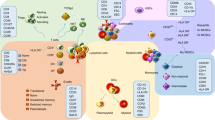
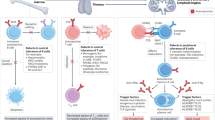
Abstract
Recent advances in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) across autoimmune and immune-mediated diseases have augmented our understanding of pathogenic mechanisms underlying these diseases. This has further highlighted their heterogeneous nature, both within and between diseases. Furthermore, varying responses to therapy have also served to underline the importance of this heterogeneity in the manner in which these diseases are diagnosed and treated. Here we discuss our current understanding of the shared pathways of autoimmunity, including the tumor necrosis factor (TNF), major histocompatibility complex (MHC), interleukin 23 receptor (IL23R) and protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22) pathways. In addition, we summarize effective specific therapies tested across major autoimmune diseases, highlighting the insight they have provided into disease mechanisms and their implications for potential future improvements.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Debbie Maizels/Nature Publishing Group

Debbie Maizels/Nature Publishing Group
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hradetzky, S. et al. The human skin-associated autoantigen alpha-NAC activates monocytes and dendritic cells via TLR-2 and primes an IL-12-dependent Th1 response. J. Invest. Dermatol. 133, 2289–2292 (2013).
Harlow, L., Fernandez, I., Soejima, M., Ridgway, W.M. & Ascherman, D.P. Characterization of TLR4-mediated auto-antibody production in a mouse model of histidyl-tRNA synthetase-induced myositis. Innate Immun. 18, 876–885 (2012).
Kopp, P. The TSH receptor and its role in thyroid disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1301–1322 (2001).
Ross, G.L., Barland, P. & Grayzel, A.I. The immunoglobulin class of anti-DNA antibodies: detection by a fluorometric immunoassay: clinical and pathological correlations in SLE. J. Rheumatol. 5, 373–383 (1978).
Klareskog, L., Catrina, A.I. & Paget, S. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373, 659–672 (2009).
Salvetti, M., Ristori, G., Bomprezzi, R., Pozzilli, P. & Leslie, R.D. Twins: mirrors of the immune system. Immunol. Today 21, 342–347 (2000).
Bogdanos, D.P. et al. Twin studies in autoimmune disease: genetics, gender and environment. J. Autoimmun. 38, J156–J169 (2012).
Fraga, M.F. et al. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10604–10609 (2005).
Stein, E.A. et al. Effect of a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9 on LDL cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1108–1118 (2012).
Sabatine, M.S. et al. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 1500–1509 (2015).
Robinson, J.G. et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 1489–1499 (2015).
Blom, D.J. et al. A 52-week placebo-controlled trial of evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 370, 1809–1819 (2014).
McDonagh, J. Statin-related cognitive impairment in the real world: you'll live longer, but you might not like it. JAMA Intern. Med. 174, 1889 (2014).
Dick, H.M. HLA and disease. Introductory review. Br. Med. Bull. 34, 271–274 (1978).
Cho, J.H. & Gregersen, P.K. Genomics and the multifactorial nature of human autoimmune disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 1612–1623 (2011).
Parkes, M., Cortes, A., van Heel, D.A. & Brown, M.A. Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 661–673 (2013).
Feldmann, M., Brennan, F.M. & Maini, R.N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 397–440 (1996).
Brennan, F.M., Chantry, D., Jackson, A., Maini, R. & Feldmann, M. Inhibitory effect of TNF-α antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2, 244–247 (1989).
Gregory, A.P. et al. TNF receptor 1 genetic risk mirrors outcome of anti-TNF therapy in multiple sclerosis. Nature 488, 508–511 (2012).
Maini, R. et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 354, 1932–1939 (1999).
Present, D.H. et al. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 1398–1405 (1999).
Targan, S.R. et al. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor α for Crohn's disease. Crohn's Disease cA2 Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 337, 1029–1035 (1997).
Rutgeerts, P. et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 2462–2476 (2005).
Chaudhari, U. et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab monotherapy for plaque-type psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet 357, 1842–1847 (2001).
Mease, P.J. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in psoriatic arthritis: pathophysiology and treatment with TNF inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 61, 298–304 (2002).
Gorman, J.D., Sack, K.E. & Davis, J.C. Jr. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor α. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1349–1356 (2002).
Sfikakis, P.P. Behcet's disease: a new target for anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 61 Suppl 2, ii51–ii53 (2002).
Kontoyiannis, D., Pasparakis, M., Pizarro, T.T., Cominelli, F. & Kollias, G. Impaired on/off regulation of TNF biosynthesis in mice lacking TNF AU-rich elements: implications for joint and gut-associated immunopathologies. Immunity 10, 387–398 (1999).
Kuchroo, V.K. et al. T cell response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): role of self and cross-reactive antigens in shaping, tuning, and regulating the autopathogenic T cell repertoire. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 101–123 (2002).
Ferber, I.A. et al. Mice with a disrupted IFN-γ gene are susceptible to the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J. Immunol. 156, 5–7 (1996).
Lemmel, E.M., Obert, H.J. & Hofschneider, P.H. Low-dose γ-interferon in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1, 598 (1988).
Williams, R.O., Williams, D.G., Feldmann, M. & Maini, R.N. Increased limb involvement in murine collagen-induced arthritis following treatment with anti-interferon-γ. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 92, 323–327 (1993).
Cua, D.J. et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 421, 744–748 (2003).
Ahern, P.P. et al. Interleukin-23 drives intestinal inflammation through direct activity on T cells. Immunity 33, 279–288 (2010).
Cho, J.H. The genetics and immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 458–466 (2008).
Zhou, L., Chong, M.M. & Littman, D.R. Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation. Immunity 30, 646–655 (2009).
Duerr, R.H. et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 314, 1461–1463 (2006).
Nair, R.P. et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat. Genet. 41, 199–204 (2009).
Cargill, M. et al. A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 273–290 (2007).
Reveille, J.D. et al. Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 42, 123–127 (2010).
Bowes, J. et al. Dense genotyping of immune-related susceptibility loci reveals new insights into the genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat. Commun. 6, 6046 (2015).
Sarin, R., Wu, X. & Abraham, C. Inflammatory disease protective R381Q IL23 receptor polymorphism results in decreased primary CD4+ and CD8+ human T-cell functional responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 9560–9565 (2011).
Di Meglio, P. et al. The IL23R R381Q gene variant protects against immune-mediated diseases by impairing IL-23-induced Th17 effector response in humans. PLoS ONE 6, e17160 (2011).
Pidasheva, S. et al. Functional studies on the IBD susceptibility gene IL23R implicate reduced receptor function in the protective genetic variant R381Q. PLoS ONE 6, e25038 (2011).
Griffiths, C.E. et al. Comparison of ustekinumab and etanercept for moderate-to-severe psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 118–128 (2010).
Gottlieb, A. & Narang, K. Ustekinumab in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: latest findings and clinical potential. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 5, 277–285 (2013).
Sandborn, W.J. et al. Ustekinumab induction and maintenance therapy in refractory Crohn's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 1519–1528 (2012).
OP025. A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled phase 2a induction study of MEDI2070 (anti-p19 antibody) in patients with active Crohn's disease who have failed anti-TNF antibody therapy. J. Crohns Colitis 9 Suppl 1, S15–S16 (2015).
Krueger, J.G. et al. Anti-IL-23A mAb BI 655066 for treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis: Safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and biomarker results of a single-rising-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. (2015).
Criswell, L.A. et al. Analysis of families in the Multiple Autoimmune Disease Genetics Consortium (MADGC) Collection: the PTPN22 620W allele associates with multiple autoimmune phenotypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76, 561–571 (2005).
Jostins, L. et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 491, 119–124 (2012).
Stanford, S.M. & Bottini, N. PTPN22: the archetypal non-HLA autoimmunity gene. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 10, 602–611 (2014).
Hasegawa, K. et al. PEST domain-enriched tyrosine phosphatase (PEP) regulation of effector/memory T cells. Science 303, 685–689 (2004).
Arechiga, A.F. et al. Cutting edge: the PTPN22 allelic variant associated with autoimmunity impairs B cell signaling. J. Immunol. 182, 3343–3347 (2009).
Vang, T. et al. Autoimmune-associated lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is a gain-of-function variant. Nat. Genet. 37, 1317–1319 (2005).
Zhang, J. et al. The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness. Nat. Genet. 43, 902–907 (2011).
Zikherman, J. et al. PTPN22 deficiency cooperates with the CD45 E613R allele to break tolerance on a non-autoimmune background. J. Immunol. 182, 4093–4106 (2009).
Cui, J. et al. Genome-wide association study and gene expression analysis identifies CD84 as a predictor of response to etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003394 (2013).
Breedveld, F. The value of early intervention in RA–a window of opportunity. Clin. Rheumatol. 30 Suppl 1, S33–S39 (2011).
Goekoop-Ruiterman, Y.P. et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 3381–3390 (2005).
Leonardi, C.L. et al. Etanercept as monotherapy in patients with psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 2014–2022 (2003).
Krueger, G.G. et al. A human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 580–592 (2007).
Langley, R.G. et al. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis–results of two phase 3 trials. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 326–338 (2014).
Gottlieb, A.B. et al. TNF inhibition rapidly down-regulates multiple proinflammatory pathways in psoriasis plaques. J. Immunol. 175, 2721–2729 (2005).
Nestle, F.O., Kaplan, D.H. & Barker, J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 496–509 (2009).
Mease, P.J. et al. Brodalumab, an anti-IL17RA monoclonal antibody, in psoriatic arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 370, 2295–2306 (2014).
Littman, D.R. & Rudensky, A.Y. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell 140, 845–858 (2010).
Krueger, J.G. Hiding under the skin: a welcome surprise in psoriasis. Nat. Med. 18, 1750–1751 (2012).
Hueber, W. et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn's disease: unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 61, 1693–1700 (2012).
O'Connor, W. Jr. et al. A protective function for interleukin 17A in T cell–mediated intestinal inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 10, 603–609 (2009).
Kühn, R., Lohler, J., Rennick, D., Rajewsky, K. & Muller, W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75, 263–274 (1993).
Li, M.O. & Flavell, R.A. TGF-β: a master of all T cell trades. Cell 134, 392–404 (2008).
Li, M.O., Wan, Y.Y. & Flavell, R.A. T cell-produced transforming growth factor-beta1 controls T cell tolerance and regulates Th1- and Th17-cell differentiation. Immunity 26, 579–591 (2007).
Hooper, L.V., Littman, D.R. & Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 336, 1268–1273 (2012).
Fung, T.C., Artis, D. & Sonnenberg, G.F. Anatomical localization of commensal bacteria in immune cell homeostasis and disease. Immunol. Rev. 260, 35–49 (2014).
Sonnenberg, G.F. et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote anatomical containment of lymphoid-resident commensal bacteria. Science 336, 1321–1325 (2012).
Glocker, E.O. et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and mutations affecting the interleukin-10 receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2033–2045 (2009).
Zielinski, C.E. et al. Pathogen-induced human TH17 cells produce IFN-γ or IL-10 and are regulated by IL-1β. Nature 484, 514–518 (2012).
Poddubnyy, D., Hermann, K.G., Callhoff, J., Listing, J. & Sieper, J. Ustekinumab for the treatment of patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a 28-week, prospective, open-label, proof-of-concept study (TOPAS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 817–823 (2014).
McInnes, I.B. et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis: 1-year results of the phase 3, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled PSUMMIT 1 trial. Lancet 382, 780–789 (2013).
McInnes, I.B. et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab, a fully human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriatic arthritis: a 24-week, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II proof-of-concept trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 349–356 (2014).
Baeten, D. et al. Anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab in treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 382, 1705–1713 (2013).
Schett, G., Elewaut, D., McInnes, I.B., Dayer, J.M. & Neurath, M.F. How cytokine networks fuel inflammation: Toward a cytokine-based disease taxonomy. Nat. Med. 19, 822–824 (2013).
Belasco, J. et al. Comparative genomic profiling of psoriatic arthritis synovium versus skin lesions. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67, 934–944 (2015).
Okada, Y. et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 506, 376–381 (2014).
Eyre, S. et al. High-density genetic mapping identifies new susceptibility loci for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 44, 1336–1340 (2012).
Onengut-Gumuscu, S. et al. Fine mapping of type 1 diabetes susceptibility loci and evidence for colocalization of causal variants with lymphoid gene enhancers. Nat. Genet. 47, 381–386 (2015).
Cooper, J.D. et al. Seven newly identified loci for autoimmune thyroid disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 5202–5208 (2012).
Trynka, G. et al. Dense genotyping identifies and localizes multiple common and rare variant association signals in celiac disease. Nat. Genet. 43, 1193–1201 (2011).
Kuehn, H.S. et al. Immune dysregulation in human subjects with heterozygous germline mutations in CTLA4. Science 345, 1623–1627 (2014).
Zeissig, S. et al. Early-onset Crohn's disease and autoimmunity associated with a variant in CTLA-4. Gut (2014).
Genovese, M.C. et al. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 1114–1123 (2005).
Sandborn, W.J. et al. Abatacept for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 143, 62–69 (2012).
Kaser, A. Not all monoclonals are created equal—lessons from failed drug trials in Crohn's disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 28, 437–449 (2014).
Hu, X. et al. Integrating autoimmune risk loci with gene-expression data identifies specific pathogenic immune cell subsets. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 89, 496–506 (2011).
Farh, K.K. et al. Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature 518, 337–343 (2015).
Edwards, J.C. et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2572–2581 (2004).
Hauser, S.L. et al. B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 676–688 (2008).
Wendling, D. et al. Rituximab treatment for spondyloarthritis. A nationwide series: data from the AIR registry of the French Society of Rheumatology. J. Rheumatol. 39, 2327–2331 (2012).
Song, I.H. et al. Different response to rituximab in tumor necrosis factor blocker-naive patients with active ankylosing spondylitis and in patients in whom tumor necrosis factor blockers have failed: a twenty-four-week clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 1290–1297 (2010).
Leiper, K. et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of rituximab (anti-CD20) in active ulcerative colitis. Gut 60, 1520–1526 (2011).
Kandala, N.B. et al. Belimumab: a technological advance for systemic lupus erythematosus patients? Report of a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open (2013).
Fattah, Z. & Isenberg, D.A. Recent developments in the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: focusing on biologic therapies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 14, 311–326 (2014).
Collins, F.S. Reengineering translational science: the time is right. Sci. Transl. Med. 3, 90cm17 (2011).
Collins, F.S. & Varmus, H. A new initiative on precision medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 793–795 (2015).
Baert, F. et al. Influence of immunogenicity on the long-term efficacy of infliximab in Crohn's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 601–608 (2003).
Shankar, G., Shores, E., Wagner, C. & Mire-Sluis, A. Scientific and regulatory considerations on the immunogenicity of biologics. Trends Biotechnol. 24, 274–280 (2006).
Weinblatt, M. et al. Selective co-stimulation modulation using abatacept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis while receiving etanercept: a randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 228–234 (2007).
Genovese, M.C. et al. Combination therapy with etanercept and anakinra in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have been treated unsuccessfully with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 1412–1419 (2004).
MacArthur, D.G. et al. Guidelines for investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Nature 508, 469–476 (2014).
Nicolae, D.L. et al. Trait-associated SNPs are more likely to be eQTLs: annotation to enhance discovery from GWAS. PLoS Genet. 6, e1000888 (2010).
Fairfax, B.P. et al. Innate immune activity conditions the effect of regulatory variants upon monocyte gene expression. Science 343, 1246949 (2014).
Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 518, 317–330 (2015).
Lavin, Y. et al. Tissue-resident macrophage enhancer landscapes are shaped by the local microenvironment. Cell 159, 1312–1326 (2014).
Bach, J.F. The effect of infections on susceptibility to autoimmune and allergic diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 911–920 (2002).
Pritchard, J.K. & Di Rienzo, A. Adaptation—not by sweeps alone. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 665–667 (2010).
Yatsunenko, T. et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486, 222–227 (2012).
Kau, A.L., Ahern, P.P., Griffin, N.W., Goodman, A.L. & Gordon, J.I. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature 474, 327–336 (2011).
Scher, J.U. et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. eLife 2, e01202 (2013).
Wen, L. et al. Innate immunity and intestinal microbiota in the development of Type 1 diabetes. Nature 455, 1109–1113 (2008).
Jacobs, J. The Jewish Encyclopedia: A Guide to its Contents, an Aid to its Use (Funk & Wagnalls, 1906).
Quintana-Murci, L. & Clark, A.G. Population genetic tools for dissecting innate immunity in humans. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 280–293 (2013).
Aaltonen, K.J. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of existing TNF blocking agents in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 7, e30275 (2012).
Lichtenstein, G.R. et al. Serious infection and mortality in patients with Crohn's disease: more than 5 years of follow-up in the TREAT registry. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 107, 1409–1422 (2012).
Keane, J. et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor α-neutralizing agent. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 1098–1104 (2001).
Acknowledgements
J.H.C. is supported by US National Institutes of Health grants U01 DK62429, U01 DK062422, R01 DK092235, SUCCESS, by he Helmsley Charitable Trust and by the Sanford J. Grossman Charitable Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The Kennedy Institute and M.F. receive royalties on patents using combination therapies of methotrexate plus anti-TNF.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J., Feldman, M. Heterogeneity of autoimmune diseases: pathophysiologic insights from genetics and implications for new therapies. Nat Med 21, 730–738 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3897
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3897
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic approaches targeting CD95L/CD95 signaling in cancer and autoimmune diseases
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Multi-omics approach to precision medicine for immune-mediated diseases
Inflammation and Regeneration (2021)
-
Kinase inhibition in autoimmunity and inflammation
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2021)
-
Prevalence of co-existing autoimmune disease in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a cross-sectional study
Pediatric Rheumatology (2020)
-
A systematic review of the applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in autoimmune diseases
npj Digital Medicine (2020)