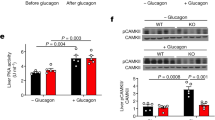
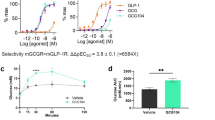
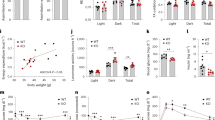
Abstract
Glucagon activates hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) to increase glucose production1,2, but the gluco-stimulatory effect is transient even in the presence of continuous intravenous glucagon infusion3,4,5. Continuous intravenous infusion of insulin, however, inhibits glucose production through its sustained actions in both the liver6 and the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH)7,8. In a pancreatic clamp setting, MBH infusion with glucagon activated MBH PKA and inhibited hepatic glucose production (HGP) in rats, as did central glucagon infusion in mice. Inhibition of glucagon receptor–PKA signaling in the MBH and hepatic vagotomy each negated the effect of MBH glucagon in rats, whereas the central effect of glucagon was diminished in glucagon receptor knockout mice. A sustained rise in plasma glucagon concentrations transiently increased HGP, and this transiency was abolished in rats with negated MBH glucagon action. In a nonclamp setting, MBH glucagon infusion improved glucose tolerance, and inhibition of glucagon receptor–PKA signaling in the MBH enhanced the ability of intravenous glucagon injection to increase plasma glucose concentrations. We also detected a similar enhancement of glucose concentrations that was associated with a disruption in MBH glucagon signaling in rats fed a high-fat diet. We show that hypothalamic glucagon signaling inhibits HGP and suggest that hypothalamic glucagon resistance contributes to hyperglycemia in diabetes and obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beale, E., Andreone, T., Koch, S., Granner, M. & Granner, D. Insulin and glucagon regulate cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) mRNA in rat liver. Diabetes 33, 328–332 (1984).
Lok, S. et al. The human glucagon receptor encoding gene: structure, cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization. Gene 140, 203–209 (1994).
Bomboy, J.D. Jr., Lewis, S.B., Lacy, W.W., Sinclair-Smith, B.C. & Liljenquist, J.E. Transient stimulatory effect of sustained hyperglucagonemia on splanchnic glucose production in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes 26, 177–184 (1977).
Eigler, N., Sacca, L. & Sherwin, R.S. Synergistic interactions of physiologic increments of glucagon, epinephrine, and cortisol in the dog: a model for stress-induced hyperglycemia. J. Clin. Invest. 63, 114–123 (1979).
Felig, P., Wahren, J. & Hendler, R. Influence of physiologic hyperglucagonemia on basal and insulin-inhibited splanchnic glucose output in normal man. J. Clin. Invest. 58, 761–765 (1976).
Cherrington, A.D. Banting lecture 1997. Control of glucose uptake and release by the liver in vivo. Diabetes 48, 1198–1214 (1999).
Könner, A.C. et al. Insulin action in AgRP-expressing neurons is required for suppression of hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 5, 438–449 (2007).
Pocai, A. et al. Hypothalamic K(ATP) channels control hepatic glucose production. Nature 434, 1026–1031 (2005).
Sherwin, R.S., Fisher, M., Hendler, R. & Felig, P. Hyperglucagonemia and blood glucose regulation in normal, obese and diabetic subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 294, 455–461 (1976).
Ferrannini, E., DeFronzo, R.A. & Sherwin, R.S. Transient hepatic response to glucagon in man: role of insulin and hyperglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. 242, E73–E81 (1982).
Cherrington, A.D., Lacy, W.W. & Chiasson, J.L. Effect of glucagon on glucose production during insulin deficiency in the dog. J. Clin. Invest. 62, 664–677 (1978).
Liljenquist, J.E. et al. Evidence for an important role of glucagon in the regulation of hepatic glucose production in normal man. J. Clin. Invest. 59, 369–374 (1977).
Unger, R.H. & Cherrington, A.D. Glucagonocentric restructuring of diabetes: a pathophysiologic and therapeutic makeover. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 4–12 (2012).
Inokuchi, A., Oomura, Y., Shimizu, N. & Yamamoto, T. Central action of glucagon in rat hypothalamus. Am. J. Physiol. 250, R120–R126 (1986).
Hoosein, N.M. & Gurd, R.S. Identification of glucagon receptors in rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 4368–4372 (1984).
Wetsel, W.C., Eraly, S.A., Whyte, D.B. & Mellon, P.L. Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone by protein kinase-A and -C in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 132, 2360–2370 (1993).
Langhans, W., Duss, M. & Scharrer, E. Decreased feeding and supraphysiological plasma levels of glucagon after glucagon injection in rats. Physiol. Behav. 41, 31–35 (1987).
Banks, W.A. & Kastin, A.J. Peptides and the blood-brain barrier: lipophilicity as a predictor of permeability. Brain Res. Bull. 15, 287–292 (1985).
Reaven, G.M., Chen, Y.D., Golay, A., Swislocki, A.L. & Jaspan, J.B. Documentation of hyperglucagonemia throughout the day in nonobese and obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 64, 106–110 (1987).
Brand, C.L. et al. Immunoneutralization of endogenous glucagon with monoclonal glucagon antibody normalizes hyperglycaemia in moderately streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 37, 985–993 (1994).
Johnson, D.G., Goebel, C.U., Hruby, V.J., Bregman, M.D. & Trivedi, D. Hyperglycemia of diabetic rats decreased by a glucagon receptor antagonist. Science 215, 1115–1116 (1982).
Coll, A.P., Farooqi, I.S. & O'Rahilly, S. The hormonal control of food intake. Cell 129, 251–262 (2007).
Flier, J.S. Obesity wars: molecular progress confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell 116, 337–350 (2004).
Lam, T.K. Neuronal regulation of homeostasis by nutrient sensing. Nat. Med. 16, 392–395 (2010).
Yue, J.T. & Lam, T.K. Lipid sensing and insulin resistance in the brain. Cell Metab. 15, 646–655 (2012).
Zhang, X. et al. Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-κB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 135, 61–73 (2008).
Breen, D.M. et al. Jejunal nutrient sensing is required for duodenal-jejunal bypass surgery to rapidly lower glucose concentrations in uncontrolled diabetes. Nat. Med. 18, 950–955 (2012).
Muse, E.D., Lam, T.K., Scherer, P.E. & Rossetti, L. Hypothalamic resistin induces hepatic insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1670–1678 (2007).
Singhal, N.S., Lazar, M.A. & Ahima, R.S. Central resistin induces hepatic insulin resistance via neuropeptide Y. J. Neurosci. 27, 12924–12932 (2007).
Honda, K. et al. The mechanism underlying the central glucagon-induced hyperglycemia and anorexia in chicks. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 163, 260–264 (2012).
Gelling, R.W. et al. Lower blood glucose, hyperglucagonemia, and pancreatic alpha cell hyperplasia in glucagon receptor knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 1438–1443 (2003).
Parker, J.C., Andrews, K.M., Allen, M.R., Stock, J.L. & McNeish, J.D. Glycemic control in mice with targeted disruption of the glucagon receptor gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290, 839–843 (2002).
Geary, N. & Smith, G.P. Pancreatic glucagon and postprandial satiety in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 28, 313–322 (1982).
Inokuchi, A., Oomura, Y. & Nishimura, H. Effect of intracerebroventricularly infused glucagon on feeding behavior. Physiol. Behav. 33, 397–400 (1984).
Sheriff, S. et al. Hypothalamic administration of cAMP agonist/PKA activator inhibits both schedule feeding and NPY-induced feeding in rats. Peptides 24, 245–254 (2003).
Morton, G.J., Cummings, D.E., Baskin, D.G., Barsh, G.S. & Schwartz, M.W. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443, 289–295 (2006).
Day, J.W. et al. A new glucagon and GLP-1 co-agonist eliminates obesity in rodents. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5, 749–757 (2009).
Pocai, A. et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon receptor dual agonism reverses obesity in mice. Diabetes 58, 2258–2266 (2009).
Béguin, P., Nagashima, K., Nishimura, M., Gonoi, T. & Seino, S. PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the human K(ATP) channel: separate roles of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunit phosphorylation. EMBO J. 18, 4722–4732 (1999).
Neelands, P.J. & Clandinin, M.T. Diet fat influences liver plasma-membrane lipid composition and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. Biochem. J. 212, 573–583 (1983).
Chari, M., Lam, C.K., Wang, P.Y. & Lam, T.K. Activation of central lactate metabolism lowers glucose production in uncontrolled diabetes and diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 57, 836–840 (2008).
Yang, C.S. et al. Hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase regulates glucose production. Diabetes 59, 2435–2443 (2010).
Inokuchi, A., Oomura, Y. & Nishimura, H. Effect of intracerebroventricularly infused glucagon on feeding behavior. Physiol. Behav. 33, 397–400 (1984).
Brand, C.L. et al. Immunoneutralization of endogenous glucagon with monoclonal glucagon antibody normalizes hyperglycaemia in moderately streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 37, 985–993 (1994).
Unson, C.G., Gurzenda, E.M. & Merrifield, R.B. Biological activities of des-His1[Glu9]glucagon amide, a glucagon antagonist. Peptides 10, 1171–1177 (1989).
van den Hoek, A.M. et al. Intracerebroventricular neuropeptide Y infusion precludes inhibition of glucose and VLDL production by insulin. Diabetes 53, 2529–2534 (2004).
Filippi, B.M., Yang, C.S., Tang, C. & Lam, T.K. Insulin activates Erk1/2 signaling in the dorsal vagal complex to inhibit glucose production. Cell Metab. 16, 500–510 (2012).
Wang, P.Y. et al. Upper intestinal lipids trigger a gut-brain-liver axis to regulate glucose production. Nature 452, 1012–1016 (2008).
Young, A.A., Cooper, G.J., Carlo, P., Rink, T.J. & Wang, M.W. Response to intravenous injections of amylin and glucagon in fasted, fed, and hypoglycemic rats. Am. J. Physiol. 264, E943–E950 (1993).
Chari, M. et al. Glucose transporter-1 in the hypothalamic glial cells mediates glucose sensing to regulate glucose production in vivo. Diabetes 60, 1901–1906 (2011).
Jaskolski, F., Mulle, C. & Manzoni, O.J. An automated method to quantify and visualize colocalized fluorescent signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 146, 42–49 (2005).
Livak, K.J. & Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔC(T) method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank P.Y.T. Wang for technical assistance and D.J. Drucker from the Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute for providing the Gcgr−/− and Gcgr+/+ mice. This work was supported by a research grant from the Canadian Diabetes Association. P.I.M. was supported by an Ontario Graduate Scholarship and a scholarship from the University of Toronto Banting and Best Diabetes Centre (BBDC). J.T.Y.Y. is supported by a BBDC and University Health Network postdoctoral fellowship. M.A.A. is supported by a BBDC scholarship. M.C. was supported by an Ontario Graduate scholarship and a BBDC scholarship. C.K.L.L. and C.S.Y. were supported by graduate scholarships from the Canadian Institute of Health Research and the BBDC. T.K.T.L. holds the John Kitson McIvor (1915–1942) Endowed Chair in Diabetes Research and the Canada Research Chair in Obesity at the Toronto General Research Institute and the University of Toronto.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.I.M. and J.T.Y.Y. conducted and designed experiments, performed data analyses and wrote the manuscript. B.M.F. assisted in experiments involving molecular biology techniques. M.A.A., M.C., C.K.L.L., C.S.Y. and N.R.C. assisted in in vivo experiments. M.J.C. generated and provided the Gcgr−/− mice. T.K.T.L. supervised the project, designed experiments and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Tables 1–3 (PDF 1271 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mighiu, P., Yue, J., Filippi, B. et al. Hypothalamic glucagon signaling inhibits hepatic glucose production. Nat Med 19, 766–772 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3115
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3115
This article is cited by
-
Metabolic Messengers: glucagon
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
100 years of glucagon and 100 more
Diabetologia (2023)
-
A hindbrain inhibitory microcircuit mediates vagally-coordinated glucose regulation
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Hypothalamic dopamine signalling regulates brown fat thermogenesis
Nature Metabolism (2019)
-
Neuronal control of peripheral insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism
Nature Communications (2017)