Abstract
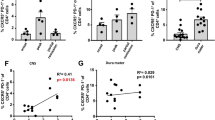
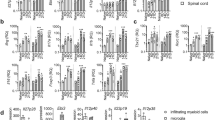
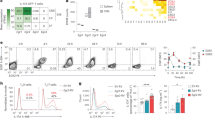
Interleukin-7 receptor (IL-7R) is genetically associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Here we describe that IL-7 is essential for survival and expansion of pathogenic T helper type 17 (TH17) cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). IL-7 directly expanded effector TH17 cells in EAE and human TH17 cells from subjects with multiple sclerosis, whereas it was not required for TH17 differentiation. IL-7R antagonism rendered differentiated TH17 cells susceptible to apoptosis through the inhibition of Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 (JAK-STAT5) pathway and altered expression of the prosurvival protein Bcl-2 and the proapoptotic protein Bax, leading to decreased severity of EAE. In contrast, TH1 and regulatory T (Treg) cells were less susceptible to or not affected by IL-7R antagonism in vivo. The selectivity was attributable to minimal expression of IL-7Rα in Treg cells and correlated with a high level of Socs1 (encoding suppressor of cytokine signaling-1) expression in TH1 cells. The study reveals a unique, previously undescribed role of IL-7–IL-7R in TH17 cell survival and expansion and has implications in the treatment of autoimmune disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
05 December 2013
The above manuscript was authored by scientists from the GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Research and Development Center in Shanghai, China, and a researcher from Baylor Medical College who later became a GSK employee. Following anonymous reports of inaccuracies in this study, GSK conducted an investigation into these allegations.
References
McFarland, H.F. & Martin, R. Multiple sclerosis: a complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 8, 913–919 (2007).
Sospedra, M. & Martin, R. Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23, 683–747 (2005).
Issazadeh, S. et al. Interferon γ, interleukin 4 and transforming growth factor β in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats: dynamics of cellular mRNA expression in the central nervous system and lymphoid cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 40, 579–590 (1995).
Steinman, L. A brief history of TH17, the first major revision in the TH1/TH2 hypothesis of T cell–mediated tissue damage. Nat. Med. 13, 139–145 (2007).
Korn, T., Bettelli, E., Oukka, M. & Kuchroo, V.K. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 485–517 (2009).
Park, H. et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1133–1141 (2005).
Bettelli, E. et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441, 235–238 (2006).
Matusevicius, D. et al. Interleukin-17 mRNA expression in blood and CSF mononuclear cells is augmented in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 5, 101–104 (1999).
Tzartos, J.S. et al. Interleukin-17 production in central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 172, 146–155 (2008).
Komiyama, Y. et al. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 177, 566–573 (2006).
Miossec, P., Korn, T. & Kuchroo, V.K. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 888–898 (2009).
Weaver, C.T., Hatton, R.D., Mangan, P.R. & Harrington, L.E. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 821–852 (2007).
Weiner, H.L. A shift from adaptive to innate immunity: a potential mechanism of disease progression in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 255 Suppl 1, 3–11 (2008).
Veldhoen, M., Hocking, R.J., Atkins, C.J., Locksley, R.M. & Stockinger, B. TGFβ in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24, 179–189 (2006).
Serada, S. et al. IL-6 blockade inhibits the induction of myelin antigen–specific TH17 cells and Th1 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 9041–9046 (2008).
Korn, T. et al. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory TH17 cells. Nature 448, 484–487 (2007).
Langrish, C.L. et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 201, 233–240 (2005).
Sutton, C.E. et al. Interleukin-1 and IL-23 induce innate IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells, amplifying TH17 responses and autoimmunity. Immunity 31, 331–341 (2009).
Cua, D.J. et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 421, 744–748 (2003).
Stritesky, G.L., Yeh, N. & Kaplan, M.H. IL-23 promotes maintenance but not commitment to the TH17 lineage. J. Immunol. 181, 5948–5955 (2008).
McGeachy, M.J. et al. The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17–producing effector T helper cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 10, 314–324 (2009).
Lock, C. et al. Gene-microarray analysis of multiple sclerosis lesions yields new targets validated in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Med. 8, 500–508 (2002).
Gregory, S.G. et al. Interleukin 7 receptor α chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 39, 1083–1091 (2007).
Hafler, D.A. et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 851–862 (2007).
Lundmark, F. et al. Variation in interleukin 7 receptor α chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 39, 1108–1113 (2007).
Palmer, M.J. et al. Interleukin-7 receptor signaling network: an integrated systems perspective. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 5, 79–89 (2008).
Jiang, Q. et al. Cell biology of IL-7, a key lymphotrophin. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16, 513–533 (2005).
Peschon, J.J. et al. Early lymphocyte expansion is severely impaired in interleukin 7 receptor–deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1955–1960 (1994).
von Freeden-Jeffry, U. et al. Lymphopenia in interleukin (IL)-7 gene-deleted mice identifies IL-7 as a nonredundant cytokine. J. Exp. Med. 181, 1519–1526 (1995).
Fry, T.J. & Mackall, C.L. The many faces of IL-7: from lymphopoiesis to peripheral T cell maintenance. J. Immunol. 174, 6571–6576 (2005).
Seddon, B., Tomlinson, P. & Zamoyska, R. Interleukin 7 and T cell receptor signals regulate homeostasis of CD4 memory cells. Nat. Immunol. 4, 680–686 (2003).
Bielekova, B. et al. Preferential expansion of autoreactive T lymphocytes from the memory T-cell pool by IL-7. J. Neuroimmunol. 100, 115–123 (1999).
Tan, J.T. et al. IL-7 is critical for homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8732–8737 (2001).
Akirav, E.M., Bergman, C.M., Hill, M. & Ruddle, N.H. Depletion of CD4+CD25+ T cells exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by mouse, but not rat, antigens. J. Neurosci. Res. 87, 3511–3519 (2009).
McGeachy, M.J., Stephens, L.A. & Anderton, S.M. Natural recovery and protection from autoimmune encephalomyelitis: contribution of CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells within the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 175, 3025–3032 (2005).
Yang, L. et al. IL-21 and TGF-β are required for differentiation of human TH17 cells. Nature 454, 350–352 (2008).
Rochman, Y., Spolski, R. & Leonard, W.J. New insights into the regulation of T cells by γc family cytokines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 480–490 (2009).
Elder, J.T. IL-15 and psoriasis: another genetic link to TH17? J. Invest. Dermatol. 127, 2495–2497 (2007).
Lu, N., Wang, Y.H., Arima, K., Hanabuchi, S. & Liu, Y.J. TSLP and IL-7 use two different mechanisms to regulate human CD4+ T cell homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2111–2119 (2009).
Isaksen, D.E. et al. Uncoupling of proliferation and Stat5 activation in thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated signal transduction. J. Immunol. 168, 3288–3294 (2002).
Bettelli, E. Building different mouse models for human MS. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1103, 11–18 (2007).
Chen, Y. et al. Anti–IL-23 therapy inhibits multiple inflammatory pathways and ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1317–1326 (2006).
O'Shea, J.J., Gadina, M. & Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 109 Suppl, S121–S131 (2002).
Liu, X., Lee, Y.S., Yu, C.R. & Egwuagu, C.E. Loss of STAT3 in CD4+ T cells prevents development of experimental autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 180, 6070–6076 (2008).
Egwuagu, C.E. STAT3 in CD4+ T helper cell differentiation and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 47, 149–156 (2009).
Laurence, A. et al. Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell generation. Immunity 26, 371–381 (2007).
Veldhoen, M., Hirota, K., Christensen, J., O'Garra, A. & Stockinger, B. Natural agonists for aryl hydrocarbon receptor in culture medium are essential for optimal differentiation of TH17 T cells. J. Exp. Med. 206, 43–49 (2009).
Amadi-Obi, A. et al. TH17 cells contribute to uveitis and scleritis and are expanded by IL-2 and inhibited by IL-27/STAT1. Nat. Med. 13, 711–718 (2007).
Cho, M.L. et al. STAT3 and NF-κB signal pathway is required for IL-23–mediated IL-17 production in spontaneous arthritis animal model IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 176, 5652–5661 (2006).
Seddiki, N. et al. Expression of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 receptors discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1693–1700 (2006).
Liu, W. et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1701–1711 (2006).
Kumar, M. et al. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T lymphocytes fail to suppress myelin basic protein-induced proliferation in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 180, 178–184 (2006).
Sakaguchi, S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 531–562 (2004).
Viglietta, V., Baecher-Allan, C., Weiner, H.L. & Hafler, D.A. Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 199, 971–979 (2004).
Seki, Y. et al. IL-7/STAT5 cytokine signaling pathway is essential but insufficient for maintenance of naive CD4 T cell survival in peripheral lymphoid organs. J. Immunol. 178, 262–270 (2007).
Wang, Z. et al. Role of IFN-γ in induction of Foxp3 and conversion of CD4+ CD25− T cells to CD4+ Tregs. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 2434–2441 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Dong for critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.L., S.L. and J.Z.Z. designed and discussed the study; X.L., C.W. and Z.T. performed the majority of the T cell experiments; J.W. performed viral gene expression experiments; Y.Z. performed EAE mouse experiments; B.W., X.Q. and L.L. performed the adoptive transfer experiments; R.L. and H.P. performed immunoblotting experiments; M.S. and A.L. performed histopathology analyses; J.H. performed human in vitro experiments; X.L., S.L., T.B.G., L.F., H.L. and J.Z.Z. contributed to the writing of the paper; J.Z.Z. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
GlaxoSmithKline Research and Development Center is a division of GlaxoSmithKline. All authors except J.H. were employed by GlaxoSmithKline at the time of these studies.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 534 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Leung, S., Wang, C. et al. Crucial role of interleukin-7 in T helper type 17 survival and expansion in autoimmune disease. Nat Med 16, 191–197 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2077
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2077
This article is cited by
-
Mouse CD163 deficiency strongly enhances experimental collagen-induced arthritis
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
IL-33 drives the antitumor effects of dendritic cells via the induction of Tc9 cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2019)
-
Levels of hepatic Th17 cells and regulatory T cells upregulated by hepatic stellate cells in advanced HBV-related liver fibrosis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2017)
-
Evaluation of Selected MicroRNAs Expression in Remission Phase of Multiple Sclerosis and Their Potential Link to Cognition, Depression, and Disability
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2017)
-
IL7R gene expression network associates with human healthy ageing
Immunity & Ageing (2015)