Abstract
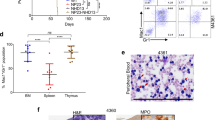
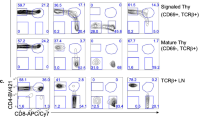
Using a human CD25 reporter transgene controlled by regulatory sequences from the gene encoding pre-T cell receptor α, we identified a common lymphocyte precursor (CLP-2) population that, in contrast to the previously identified CLP-1 population, was c-Kit−B220+. In short-term culture, the CLP-2 could be derived from the CLP-1 subset, and contained cells that in clonogenic assays were assessed to be bipotent precursors of T and B cells. Intravenous injection of bone marrow cells yielded a selective accumulation of CLP-2 thymic immigrants that in thymic organ culture generated mature αβ T cells. Although the CLP-2 subset may represent the most differentiated population with T cell potential before commitment to the B cell lineage, other subsets of thymic immigrants capable of generating T cells may exist.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissman, I.L., Anderson, D.J. & Gage, F. Stem and progenitor cells: origins, phenotypes, lineage commitments, and transdifferentiations. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 387–403 (2001).
Adolfsson, J. et al. Upregulation of Flt3 expression within the bone marrow Lin−Sca1+c-kit+ stem cell compartment is accompanied by loss of self-renewal capacity. Immunity 15, 659–669 (2001).
Christensen, J.L. & Weissman, I.L. Flk-2 is a marker in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation: a simple method to isolate long-term stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14541–14546 (2001).
Spangrude, G.J., Heimfeld, S. & Weissman, I.L. Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Science 241, 58–62 (1988).
Kondo, M., Weissman, I.L. & Akashi, K. Identification of clonogenic common lymphoid progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Cell 91, 661–672 (1997).
Jaleco, A.C. et al. Differential effects of Notch ligands Delta-1 and Jagged-1 in human lymphoid differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 194, 991–1002 (2001).
Yan, X.Q. et al. A novel Notch ligand, Dll4, induces T-cell leukemia/lymphoma when overexpressed in mice by retroviral-mediated gene transfer. Blood 98, 3793–3799 (2001).
Dorsch, M. et al. Ectopic expression of Delta-4 impairs hematopoietic development and leads to lymphoproliferative disease. Blood 100, 2046–2055 (2002).
Schmitt, T.M. & Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Induction of T cell development from hematopoietic progenitor cells by delta-like-1 in vitro. Immunity 17, 749–756 (2002).
Radtke, F. et al. Deficient T cell fate specification in mice with an induced inactivation of Notch1. Immunity 10, 547–558 (1999).
Wilson, A., MacDonald, H.R. & Radtke, F. Notch 1-deficient common lymphoid precursors adopt a B cell fate in the thymus. J. Exp. Med. 194, 1003–1012 (2001).
Koch, U. et al. Subversion of the T/B lineage decision in the thymus by lunatic fringe-mediated inhibition of Notch-1. Immunity 15, 225–236 (2001).
Izon, D.J. et al. Deltex1 redirects lymphoid progenitors to the B cell lineage by antagonizing Notch1. Immunity 16, 231–243 (2002).
Pui, J.C. et al. Notch1 expression in early lymphopoiesis influences B versus T lineage determination. Immunity 11, 299–308 (1999).
Shortman, K. & Wu, L. Early T lymphocyte progenitors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 29–47 (1996).
Allman, D. et al. Thymopoiesis independent of common lymphoid progenitors. Nat. Immunol. 4, 168–174 (2003).
Hardy, R.R., Carmack, C.E., Shinton, S.A., Kemp, J.D. & Hayakawa, K. Resolution and characterization of pro-B and pre-pro-B cell stages in normal mouse bone marrow. J. Exp. Med. 173, 1213–1225 (1991).
Osmond, D.G., Rolink, A. & Melchers, F. Murine B lymphopoiesis: towards a unified model. Immunol. Today 19, 65–68 (1998).
Li, Y.S., Wasserman, R., Hayakawa, K. & Hardy, R.R. Identification of the earliest B lineage stage in mouse bone marrow. Immunity 5, 527–535 (1996).
Tudor, K.S., Payne, K.J., Yamashita, Y. & Kincade, P.W. Functional assessment of precursors from murine bone marrow suggests a sequence of early B lineage differentiation events. Immunity 12, 335–345 (2000).
Allman, D., Li, J. & Hardy, R.R. Commitment to the B lymphoid lineage occurs before DH-JH recombination. J. Exp. Med. 189, 735–740 (1999).
Schlueter, A.J. et al. Distribution of Ly-6C on lymphocyte subsets: I. Influence of allotype on T lymphocyte expression. J. Immunol. 158, 4211–4222 (1997).
Hardy, R.R. & Hayakawa, K. B cell development pathways. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 595–621 (2001).
Reizis, B. & Leder, P. Expression of the mouse pre-T cell receptor a gene is controlled by an upstream region containing a transcriptional enhancer. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1669–1678 (1999).
Gounari, F. et al. Tracing lymphopoiesis with the aid of a pTa-controlled reporter gene. Nat. Immunol. 3, 489–496 (2002).
Igarashi, H., Gregory, S.C., Yokota, T., Sakaguchi, N. & Kincade, P.W. Transcription from the RAG1 locus marks the earliest lymphocyte progenitors in bone marrow. Immunity 17, 117–130 (2002).
Miyamoto, T. et al. Myeloid or lymphoid promiscuity as a critical step in hematopoietic lineage commitment. Dev. Cell. 3, 137–147 (2002).
Georgopoulos, K. Haematopoietic cell-fate decisions, chromatin regulation and ikaros. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 162–174 (2002).
Wu, L., Antica, M., Johnson, G.R., Scollay, R. & Shortman, K. Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult mouse thymus. J. Exp. Med. 174, 1617–1627 (1991).
Mori, S., Shortman, K. & Wu, L. Characterization of thymus-seeding precursor cells from mouse bone marrow. Blood 98, 696–704 (2001).
Asensi, V., Kimeno, K., Kawamura, I., Sakumoto, M. & Nomoto, K. Treatment of autoimmune MRL/lpr mice with anti-B220 monoclonal antibody reduces the level of anti-DNA antibodies and lymphadenopathies. Immunology 68, 204–208 (1989).
Domiati-Saad, R., Ogle, E.W. & Justement, L.B. Administration of anti-CD45 mAb specific for a B cell-restricted epitope abrogates the B cell response to a T-dependent antigen in vivo. J. Immunol. 151, 5936–59347 (1993).
Okada, T. et al. Murine thymic plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 33, 1012–1019 (2003).
Nishi, M., Ishida, Y. & Honjo, T. Expression of functional interleukin-2 receptors in human light chain/Tac transgenic mice. Nature 331, 267–269 (1988).
Dejbakhsh-Jones, S., Jerabek, L., Weissman, I.L. & Strober, S. Extrathymic maturation of ab T cells from hemopoietic stem cells. J. Immunol. 155, 3338–3344 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Hoeflinger for technical assistance, and M. Handley and H. Levine for cell sorting. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants (R01A147281 and R01A145846 to H.v.B.); the Claudia Adams Barr program (to F.G.); a Eugenia Spanopoulou Irvington Institute Award (to I.A.); the Division of Medical Sciences of Harvard Medical School (C.M.); and the Cancer Research Institute (B.R.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, C., Aifantis, I., Scimone, M. et al. Efficient thymic immigration of B220+ lymphoid-restricted bone marrow cells with T precursor potential. Nat Immunol 4, 866–873 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni965
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni965
This article is cited by
-
Thymus Colonization: Who, How, How Many?
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2018)
-
Molecular Insights Into Pathogenesis of Peripheral T Cell Lymphoma: a Review
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2018)
-
MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic
Nature Reviews Immunology (2016)
-
The development and function of thymic B cells
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Two waves of distinct hematopoietic progenitor cells colonize the fetal thymus
Nature Immunology (2014)