Abstract
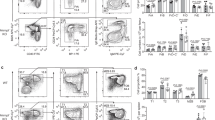
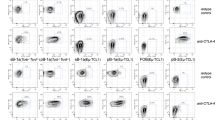
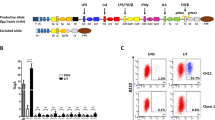
Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin E (IgE) in normal circumstances are kept much lower than those of other Ig isotypes to avoid allergic reactions. B cells lacking Id2 have increased E2A activity, which leads to specific enhancement of germline transcription of the immunoglobulin ε locus. As a consequence, Id2-deficient B cells undergo class switch recombination (CSR) to IgE at a much higher frequency than wild-type B cells. In contrast, Id2 is induced in wild-type B cells by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and suppresses IgE CSR. Our results provide evidence for the inhibitory and selective role of Id2 in IgE CSR in response to TGF-β1. Id2 might act as molecular safeguard to suppress IgE CSR to prevent serious complications such as allergic hypersensitivity during the normal course of immune responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corry, D.B. & Kheradmand, F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature 402, 18–23 (1999).
Muramatsu, M. et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102, 553–563 (2000).
Lundgren, M. et al. Activation of the Ig germ-line γ1 promoter. Involvement of C/enhancer-binding protein transcription factors and their possible interaction with an NF-IL-4 site. J. Immunol. 153, 2983–2995 (1994).
Delphin, S. & Stavnezer, J. Characterization of an interleukin 4 (IL-4) responsive region in the immunoglobulin heavy chain germline ε promoter: regulation by NF-IL-4, a C/EBP family member and NF-κB/p50. J. Exp. Med. 181, 181–192 (1995).
Honjo, T., Kinoshita, K. & Muramatsu, M. Molecular mechanism of class switch recombination: Linkage with somatic hypermutation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 165–196 (2002).
Lee, C.G. et al. Quantitative regulation of class switch recombination by switch region transcription. J. Exp. Med. 194, 365–374 (2001).
Lutzker, S., Rothman, P., Pollock, R., Coffman, R. & Alt, F.W. Mitogen- and IL-4-regulated expression of germ-line Ig 2b transcripts: evidence for directed heavy chain class switching. Cell 53, 177–184 (1988).
Zhang, J., Alt, F.W. & Honjo, T. Regulation of class switch recombination of the immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. in Immunoglobulin Genes (eds. Honjo, T. & Alt, F. W.) 235–265 (Academic Press, London, 1995).
Kuhn, R., Rajewsky, K. & Muller, W. Generation and analysis of interleukin-4 deficient mice. Science 254, 707–710 (1991).
Kopf, M. et al. Disruption of the murine IL-4 gene blocks Th2 cytokine responses. Nature 362, 245–248 (1993).
Takeda, K. et al. Essential role of STAT6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature 380, 627–630 (1996).
Shimoda, K. et al. Lack of IL-4-induced Th2 response and IgE class switching in mice with disrupted STAT6 gene. Nature 380, 630–633 (1996).
Snapper, C.M., Finkelman, F.D. & Paul, W.E. Differential regulation of IgG1 and IgE synthesis by interleukin 4. J. Exp. Med. 167, 183–196 (1988).
Jung, S., Siebenkotten, G. & Radbruch, A. Frequency of immunoglobulin E class switching is autonomously determined and independent of prior switching to other classes. J. Exp. Med. 179, 2023–2026 (1994).
Purkerson, J.M. & Isakson, P.C. Independent regulation of DNA recombination and immunoglobulin (Ig) secretion during isotype switching to IgG1 and IgE. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1877–1883 (1994).
Bottaro, A. et al. S region transcription per se promotes basal IgE class switch recombination but additional factors regulate the efficiency of the process. EMBO J. 13, 665–674 (1994).
Norton, J.D., Deed, R.W., Craggs, G. & Sablitzky, F. Id helix-loop-helix proteins in cell growth and differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 8, 58–65 (1998).
Yokota, Y. & Mori, S. Role of Id family proteins in growth control. J. Cell. Physiol. 190, 21–28 (2002).
Yokota, Y. et al. Development of peripheral lymphoid organs and natural killer cells depends on the helix-loop-helix inhibitor Id2. Nature 397, 702–706 (1999).
Kusunoki, T. et al. Th2 dominance and defective CD8+ dendritic cell subset in Id2-deficient mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunnol. (in the press, 2003).
Chu, C.C., Paul, W.E. & Max, E.E. Quantitation of immunoglobulin μ-γ 1 heavy chain switch region recombination by a digestion-circularization polymerase chain reaction method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6978–6982 (1992).
Qiu, G. & Stavnezer, J. Overexpression of BSAP/Pax-5 inhibits switching to IgA and enhances switching to IgE in the 1.29 μ B cell line. J. Immunol. 161, 2906–2918 (1998).
Harris, M.B. et al. Transcriptional repression of STAT6-dependent interleukin-4-induced genes by BCL-6: specific regulation of iε transcription and immunoglobulin E switching. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 7264–7275 (1999).
Kamogawa, Y. et al. A conditionally active form of STAT6 can mimic certain effects of IL-4. J. Immunol. 161, 1074–1077 (1998).
Nosaka, T. et al. STAT5 as a molecular regulator of proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 18, 4754–4765 (1999).
Ye, S.K. et al. Induction of germline transcription in the TCRγ locus by Stat5: implications for accessibility control by the IL-7 receptor. Immunity 11, 213–223 (1999).
Quong, M.W., Harris, D.P., Swain, S.L. & Murre, C. E2A activity is induced during B-cell activation to promote immunoglobulin class switch recombination. EMBO J. 18, 6307–6318 (1999).
Gauchat, J.F., Aversa, G., Gascan, H. & de Vries, J.E. Modulation of IL-4 induced germline ε RNA synthesis in human B cells by tumor necrosis factor-α, anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies or transforming growth factor-β correlates with levels of IgE production. Int. Immunol. 4, 397–406 (1992).
Shockett, P. & Stavnezer, J. Effect of cytokines on switching to IgA and α germline transcripts in the B lymphoma 1.29 μ. Transforming growth factor-β activates transcription of the unrearranged C α gene. J. Immunol. 147, 4374–4383 (1991).
van Ginkel, F.W. et al. Partial IgA-deficiency with increased Th2-type cytokines in TGF-β1 knockout mice. J. Immunol. 163, 1951–1957 (1999).
Kee, B.L., Rivera, R.R. & Murre, C. Id3 inhibits B lymphocyte progenitor growth and survival in response to TGF-β. Nature Immunol. 2, 242–247 (2001).
Roberts, E.C., Deed, R.W., Inoue, T., Norton, J.D. & Sharrocks, A.D. Id helix-loop-helix proteins antagonize pax transcription factor activity by inhibiting DNA binding. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 524–533 (2001).
Urbanek, P., Wang, Z.Q., Fetka, I., Wagner, E.F. & Busslinger, M. Complete block of early B cell differentiation and altered patterning of the posterior midbrain in mice lacking Pax5/BSAP. Cell 79, 901–912 (1994).
Wahl, S.M. Transforming growth factor β: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1587–1590 (1994).
Shull, M.M. et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-β1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 359, 693–699 (1992).
Sugai, M., Kondo, S., Shimizu, A. & Honjo, T. Isolation of differentially expressed genes upon immunoglobulin class switching by a subtractive hybridization method using uracil DNA glycosylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 911–918 (1998).
Kinsella, T.M. & Nolan, G.P. Episomal vectors rapidly and stably produce high-titer recombinant retrovirus. Hum. Gene Ther. 7, 1405–1413 (1996).
Matsuda, E. et al. Targeting of Krüppel-associated box-containing zinc finger proteins to centromeric heterochromatin. Implication for the gene silencing mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 14222–14229 (2001).
Hara, E., Hall, M. & Peters, G. Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation of Id2 modulates activity of E2A-related transcription factors. EMBO J. 16, 332–342 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to K. Ikuta for discussions, H. Karasuyama for X63mIL3, A. Kudo for mPax5 expression plasmid, T. Kitamura for pMX-IRESGFP plasmid and G. P. Nolan for Phoenix Eco cells. We thank T. Ofuji for technical assistance. Supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research including ones on Priority Areas 'Genome Biology' (13206035, 14014220) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugai, M., Gonda, H., Kusunoki, T. et al. Essential role of Id2 in negative regulation of IgE class switching. Nat Immunol 4, 25–30 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni874
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni874
This article is cited by
-
Essential role of the initial activation signal in isotype selection upon deletion of a transcriptionally committed promoter
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The Id-protein family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways
Cell Communication and Signaling (2017)
-
Safety and efficiency of active immunization with detoxified antigen against scorpion venom: side effect evaluation
Inflammation Research (2017)
-
Regulation of IgE Responses by γδ T Cells
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2015)
-
Bach2 represses plasma cell gene regulatory network in B cells to promote antibody class switch
The EMBO Journal (2010)