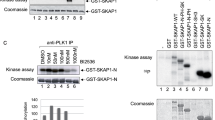
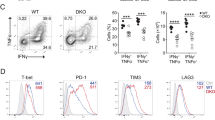
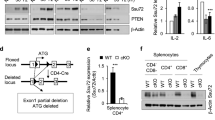
Abstract
HPK1 is a Ste20-related serine-threonine kinase that inducibly associates with the adaptors SLP-76 and Gads after T cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Here, HPK1 deficiency resulted in enhanced TCR-induced phosphorylation of SLP-76, phospholipase C-γ1 and the kinase Erk, more-persistent calcium flux, and increased production of cytokines and antigen-specific antibodies. Furthermore, HPK1-deficient mice were more susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Although the interaction between SLP-76 and Gads was unaffected, the inducible association of SLP-76 with 14-3-3τ (a phosphorylated serine–binding protein and negative regulator of TCR signaling) was reduced in HPK1-deficient T cells after TCR stimulation. HPK1 phosphorylated SLP-76 and induced the interaction of SLP-76 with 14-3-3τ. Our results indicate that HPK1 negatively regulates TCR signaling and T cell–mediated immune responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, M.C., Qiu, W.R., Wang, X., Meyer, C.F. & Tan, T.-H. Human HPK1, a novel human hematopoietic progenitor kinase that activates the JNK/SAPK kinase cascade. Genes Dev. 10, 2251–2264 (1996).
Boomer, J.S. & Tan, T-H. Functional interactions of HPK1 with adaptor proteins. J. Cell. Biochem. 95, 34–44 (2005).
Kiefer, F. et al. HPK1, a hematopoietic protein kinase activating the SAPK/JNK pathway. EMBO J. 15, 7013–7025 (1996).
Chen, Y-R., Meyer, C.F., Ahmed, B., Yao, Z. & Tan, T-H. Caspase-mediated cleavage and functional changes of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1). Oncogene 18, 7370–7377 (1999).
Arnold, R., Liou, J., Drexler, H.C., Weiss, A. & Kiefer, F. Caspase-mediated cleavage of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) converts an activator of NFκB into an inhibitor of NFκB. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 14675–14684 (2001).
Liou, J. et al. HPK1 is activated by lymphocyte antigen receptors and negatively regulates AP-1. Immunity 12, 399–408 (2000).
Ling, P. et al. Involvement of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 in T cell receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 18908–18914 (2001).
Liu, S.K., Smith, C.A., Arnold, R., Kiefer, F. & McGlade, C.J. The adaptor protein Gads (Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc) is implicated in coupling hemopoietic progenitor kinase-1 to the activated TCR. J. Immunol. 165, 1417–1426 (2000).
Sauer, K. et al. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 associates physically and functionally with the adaptor proteins B cell linker protein and SLP-76 in lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 45207–45216 (2001).
Yu, J. et al. Synergistic regulation of immunoreceptor signaling by SLP-76-related adaptor Clnk and serine/threonine protein kinase HPK1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 6102–6112 (2001).
Han, J. et al. HIP-55 is important for T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and immune responses. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 6869–6878 (2005).
Ensenat, D. et al. A novel src homology 3 domain-containing adaptor protein, HIP-55, that interacts with hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33945–33950 (1999).
Trub, T., Frantz, J.D., Miyazaki, M., Band, H. & Shoelson, S.E. The role of a lymphoid-restricted, Grb2-like SH3–SH2-SH3 protein in T cell receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 894–902 (1997).
Sawasdikosol, S., Russo, K.M. & Burakoff, S.J. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) negatively regulates prostaglandin E2-induced fos gene transcription. Blood 101, 3687–3689 (2003).
Nagata, Y., Kiefer, F., Watanabe, T. & Todokoro, K. Activation of hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 by erythropoietin. Blood 93, 3347–3354 (1999).
Hu, M.C. et al. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) stress response signaling pathway activates IκB kinases (IKK-α/β) and IKK-β is a developmentally regulated protein kinase. Oncogene 18, 5514–5524 (1999).
Ling, P. et al. Interaction of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 with adapter proteins Crk and CrkL leads to synergistic activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 1359–1368 (1999).
Ma, W. et al. Leukocyte-specific adaptor protein Grap2 interacts with hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) to activate JNK signaling pathway in T cells. Oncogene 20, 1703–1714 (2001).
Meller, N. et al. Direct interaction between protein kinase Cθ (PKCθ) and 14–3-3τ in T cells: 14–3-3 overexpression results in inhibition of PKCθ translocation and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 5782–5791 (1996).
Bonnefoy-Berard, N. et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity by association with 14–3-3 proteins in T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 10142–10146 (1995).
Muslin, A.J., Tanner, J.W., Allen, P.M. & Shaw, A.S. Interaction of 14–3-3 with signaling proteins is mediated by the recognition of phosphoserine. Cell 84, 889–897 (1996).
Yaffe, M.B. et al. The structural basis for 14–3-3:phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91, 961–971 (1997).
Sabapathy, K. et al. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK)1 and JNK2 have similar and stage-dependent roles in regulating T cell apoptosis and proliferation. J. Exp. Med. 193, 317–328 (2001).
Dong, C. et al. ICOS co-stimulatory receptor is essential for T-cell activation and function. Nature 409, 97–101 (2001).
Hehner, S.P., Hofmann, T.G., Dienz, O., Droge, W. & Schmitz, M.L. Tyrosine-phosphorylated Vav1 as a point of integration for T-cell receptor- and CD28-mediated activation of JNK, p38, and interleukin-2 transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 18160–18171 (2000).
Zhang, W., Irvin, B.J., Trible, R.P., Abraham, R.T. & Samelson, L.E. Functional analysis of LAT in TCR-mediated signaling pathways using a LAT-deficient Jurkat cell line. Int. Immunol. 11, 943–950 (1999).
Yablonski, D., Kuhne, M.R., Kadlecek, T. & Weiss, A. Uncoupling of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases from PLCγ1 in an SLP-76-deficient T cell. Science 281, 413–416 (1998).
Ebinu, J.O. et al. RasGRP links T-cell receptor signaling to Ras. Blood 95, 3199–3203 (2000).
Reynolds, L.F. et al. Vav1 transduces T cell receptor signals to the activation of phospholipase C-γ1 via phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Exp. Med. 195, 1103–1114 (2002).
Reynolds, L.F. et al. Vav1 transduces T cell receptor signals to the activation of the Ras/ERK pathway via LAT, Sos, and RasGRP1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 18239–18246 (2004).
Rao, N. et al. The linker phosphorylation site Tyr292 mediates the negative regulatory effect of Cbl on ZAP-70 in T cells. J. Immunol. 164, 4616–4626 (2000).
Erdreich-Epstein, A. et al. Cbl functions downstream of Src kinases in FcγRI signaling in primary human macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 65, 523–534 (1999).
Le Bras, S. et al. Recruitment of the actin-binding protein HIP-55 to the immunological synapse regulates T cell receptor signaling and endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 15550–15560 (2004).
Yao, Z. et al. A novel human STE20-related protein kinase, HGK, that specifically activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 2118–2125 (1999).
Diener, K. et al. Activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway by a novel protein kinase related to human germinal center kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9687–9692 (1997).
Tung, R.M. & Blenis, J. A novel human SPS1/STE20 homologue, KHS, activates Jun N-terminal kinase. Oncogene 14, 653–659 (1997).
Pombo, C.M. et al. Activation of the SAPK pathway by the human STE20 homologue germinal centre kinase. Nature 377, 750–754 (1995).
Jeffrey, K.L. et al. Positive regulation of immune cell function and inflammatory responses by phosphatase PAC-1. Nat. Immunol. 7, 274–283 (2006).
Jaeschke, A. et al. JNK2 is a positive regulator of the cJun transcription factor. Mol. Cell 23, 899–911 (2006).
Brill, L.M. et al. Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 76, 2763–2772 (2004).
Liu, Y.C., Elly, C., Yoshida, H., Bonnefoy-Berard, N. & Altman, A. Activation-modulated association of 14–3-3 proteins with Cbl in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 14591–14595 (1996).
Okuda, Y., Okuda, M. & Bernard, C.C. Regulatory role of p53 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 135, 29–37 (2003).
Zhou, G. et al. Protein phosphatase 4 is involved in tumor necrosis factor-α-induced activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6391–6398 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Belmont for assistance with embryonic stem cell culture; F.J. DeMayo (Baylor College of Medicine Transgenic Core Facility) for embryonic stem cell microinjection; K.M. Stehling for technical assistance; and D.A. Guzman and R. Cuthbert for secretarial assistance. Mouse 129/Sv/Ev embryonic stem cells (clone AB2.2) were provided by A. Bradley (The Sanger Institute); GST–14-3-3τ plasmid was provided by W.C. Lin (University of Alabama at Birmingham); and Flag–SLP-76 plasmid was provided by G. Koretzky (University of Pennsylvania). Supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01-AI42532, R01-AI066895 and R01-CA87076 to T.-H.T; and T32-AI07495 to J.-W.S., J.S.B. and G.A.D) and the American Heart Association Texas Affiliate (0465456Y to G.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.-W.S. designed and did experiments and prepared the manuscript; J.S.B. designed and did experiments and edited the manuscript; J.H., J.X. and G.A.D. did experiments; G.Z. assisted in experiments; and T.-H.T. established the initial scientific questions, designed and supervised experiments and composed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1
Generation of Mapk41−/− mice. (PDF 173 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
A schematic model of SLP-76 regulation by HPK1 during T cell signaling. (PDF 89 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shui, JW., Boomer, J., Han, J. et al. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 negatively regulates T cell receptor signaling and T cell–mediated immune responses. Nat Immunol 8, 84–91 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1416
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1416
This article is cited by
-
The phosphatase DUSP22 inhibits UBR2-mediated K63-ubiquitination and activation of Lck downstream of TCR signalling
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A knowledge-guided pre-training framework for improving molecular representation learning
Nature Communications (2023)
-
An HPK1 inhibitor enhanced the tumour response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2023)
-
The expanding role for small molecules in immuno-oncology
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2022)
-
Novel classes of immunotherapy for breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2022)