Abstract
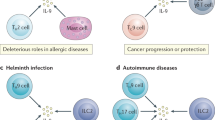
Overproduction of immunoglobulin E (IgE) and T helper cell type 2 (T H2) cytokines, including interleukin 4 (IL-4), IL-5 and IL-13, can result in allergic disorders. Although it is known that IL-4 is critical to the polarization of naïve CD4+ T cells to a TH2 phenotype, both in vitro and in many in vivo systems, other factors that regulate in vivo IL-4 production and TH2 commitment are poorly understood. IL-18, an IL-1–like cytokine that requires cleavage with caspase-1 to become active, was found to increase IgE production in a CD4+ T cells−, IL-4– and STAT6–dependent fashion. IL-18 and T cell receptor–mediated stimulation could induce naïve CD4+ T cells to develop into IL-4–producing cells in vitro. Thus, caspase-1 and IL-18 may be critical in regulation of IgE production in vivo, providing a potential therapeutic target for allergic disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coffman, R.L. et al. The role of helper T cell products in mouse B cell differentiation and isotype regulation. Immunol. Rev. 102, 5–28 (1988).
Finkelman, F.D. et al. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8, 303– 333 (1990).
Punnonen, J. et al. Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3730–3734 (1993).
Zurawski, G. & de Vries, J.E.J. Interleukin 13, an interleukin 4-like cytokine that acts on monocytes and B cells, but not on T cells. Immunol. Today. 15, 19–26 (1994).
Wills, K.M. et al. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 282, 2258–2261 ( 1998).
Grunig, G. et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma . Science 282, 2261–2263 (1998).
Hilton, D.J. et al. Cloning and characterization of a binding subunit of the interleukin 13 receptor that is also a component of the interleukin 4 receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 497– 501 (1996).
Okamura, H. et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-γ production by T cells. Nature 378, 88– 91 (1995).
Gu, Y. et al. Activation of interferon-γ inducing factor mediated by interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 275, 206– 209 (1997).
Okamura, H., Tsutsui, H., Kashiwamura, S., Yoshimoto, T. & Nakanishi, K. Interleukin-18: A novel cytokine that augments both innate and acquired immunity. Adv. Immunol. 70, 281–312 ( 1998).
Dinarello, C.A. et al. Overview of interleukin-18: more than an interferon-γ inducing factor. J. Leukoc.Biol. 63, 658 –664 (1998).
Kohno, K. et al. IFN-γ–inducing factor (IGIF) is a costimulatory factor on the activation of Th1 but not Th2 cells and exerts its effect independently of IL-12. J. Immunol. 158, 1541– 1550 (1997).
Robinson, D. et al. IGIF does not drive Th1 development but synergizes with IL-12 for interferon-γ production and activates IRAK and NFκB. Immunity 7, 571–581 ( 1997).
Yoshimoto, T. et al. IL-12 up-regulates IL-18 receptor expression on T cells, Th1 cells, and B cells: synergism with IL-18 for IFN-γ production. J. Immunol. 161, 3400–3407 (1998).
Xu, D. et al. Selective expression and functions of interleukin 18 receptor on T helper (Th) type 1 but not Th2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1485–1492 (1998).
Tsutsui, H. et al. IL-18 accounts for both TNF—- and FasL-mediated hepatotoxic pathways in endotoxin-induced liver injury. J. Immunol. 159, 3961–3967 (1997).
Yoshimoto, T., Okamura, H., Tagawa, Y.I., Iwakura, Y. & Nakanishi, K. Interleukin 18 together with interleukin 12 inhibits IgE production by induction of interferon-γ production from activated B cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 3948–3953 (1997).
Yoshimoto, T. et al. IL-18, although antiallergic when administered with IL-12, stimulates IL-4 and histamine release by basophils. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13962–13966 (1999).
Kumano, K. et al. Interleukin-18 enhances antigen-induced eosinophil recruitment into the mouse airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 160, 873–878 (1999).
Hoshino, T., Wiltrout, R.H. & Young, H.A. IL-18 is a potent coinducer of IL-13 in NK and T cells: A new potential role for IL-18 in modulating the immune response. J. Immunol. 162, 5070–5077 (1999).
Yamanaka, K. et al. Skin-specific caspase-1 transgenic mice show cutaneous apoptosis and pre-endotoxin shock condition with a high serum level of IL-18. J. Immunol. (2000) (in the press).
Noben-Trauth, N. et al. An interleukin 4 (IL-4)-independent pathway for CD4+ T cell IL-4 production is revealed in IL-4 receptor-deficient mice . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10838– 10843 (1997).
Noben-Trauth, N., Kohler, G., Burki, K. & Ledermann, B. Efficient targeting of the IL-4 gene in a BALB/c embryonic stem cell line. Transgenic Res. 5, 487–491 (1996).
Urban, J.J. et al. IL-13, IL-4Rα, and Stat6 are required for the expulsion of the gastrointestinal nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis . Immunity 8, 255–264 (1998).
Takeda, K. et al. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature 380, 627–630 ( 1996).
Takeda, K. et al. Defective NK cell activity and Th1 response in IL-18–deficient mice. Immunity 8, 583–590 (1998).
Murphy, K.M., Heimberger, A.B. & Loh, D.Y. Induction by antigen of intrathymic apoptosis of CD4+CD8+TCRlo thymocytes in vivo. Science 250, 1720–1723 ( 1990).
Salgame, P. et al. Differing lymphokine profiles of functional subsets of human CD4 and CD8 T cell clones. Science 254, 279–282 (1991).
Stoll, S. et al. Production of IL-18 (IFN-γ–inducing factor) messenger RNA and functional protein by murine keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 159, 298–302 ( 1997).
Ghayur, T. et al. Caspase-1 processes IFN-γ–inducing factor and regulates LPS-induced IFN-γ production. Nature 386, 619–623 (1997).
Paul, W.E., Seder, R.A. & Plaut, M. Lymphokine and cytokine production by Fcɛ RI+ cells. Adv. Immunol. 53, 1– 29 (1993).
Cameron, L.A. et al. Airway epithelium expresses interleukin-18. Eur. Respir. J. 14, 553–559 ( 1999).
Ohara, J. & Paul, W.E. Production of monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature 315, 333–336 ( 1985).
LeGros, G.G., Ben-Sasson, S.S., Seder, R.A., Finkelman, F.D. & Paul, W.E. Generation of interleukin 4 (IL-4)–producing cells in vivo and in vitro: IL-2 and IL-4 are required for in vitro generation of IL-4–producing cells. J. Exp. Med. 172, 921–929 ( 1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank Hayashibara Biochemical Laboratories Inc. for providing recombinant murine IL-18, S. Akira and K. Takeda at Osaka University for STAT6−/− and IL-18−/− mice, M. Kobayashi and the Research Support Team at Genetic Institute for murine sIL-13Pα—Fc and H. Fukui for excellent technical assistance. Supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research and Hitech Research Center grant from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshimoto, T., Mizutani, H., Tsutsui, H. et al. IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4+ T cells, IL-4 and STAT6. Nat Immunol 1, 132–137 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/77811
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/77811
This article is cited by
-
The effects of Leishmania RNA virus 2 (LRV2) on the virulence factors of L. major and pro-inflammatory biomarkers: an in vitro study on human monocyte cell line (THP-1)
BMC Microbiology (2023)
-
The role of pyroptosis and gasdermin family in tumor progression and immune microenvironment
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Allergen-induced CD11c + dendritic cell pyroptosis aggravates allergic rhinitis
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Co-exposure to lipopolysaccharide and desert dust causes exacerbation of ovalbumin-induced allergic lung inflammation in mice via TLR4/MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2019)
-
Allergen‐induced interleukin‐18 promotes experimental eosinophilic oesophagitis in mice
Immunology & Cell Biology (2015)