Abstract
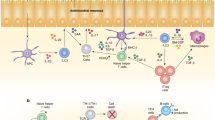
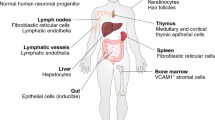
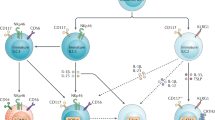
Although the cytokine interleukin 9 (IL-9) was discovered decades ago, it remains one of the most enigmatic cytokines identified so far, in particular because its functional activities remain far from clear. Breakthroughs made through the use of IL-9 reporter mice have allowed the identification of cell types that produce IL-9 in vivo and, contrary to expectations based on previous results obtained in vitro, it is not T cells but instead a previously unknown type of innate lymphoid cell, called the 'ILC2 cell', that is the main cell type that expresses IL-9 in vivo. In this perspective, we put forward a hypothesis about the potential biological functions of IL-9 in the immune system and beyond.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uyttenhove, C., Simpson, R.J. & Van Snick, J. Functional and structural characterization of P40, a mouse glycoprotein with T-cell growth factor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 6934–6938 (1988).
Schmitt, E., Van Brandwijk, R., Van Snick, J., Siebold, B. & Rude, E. TCGF III/P40 is produced by naive murine CD4+ T cells but is not a general T cell growth factor. Eur. J. Immunol. 19, 2167–2170 (1989).
Hültner, L. et al. Mast cell growth-enhancing activity (MEA) is structurally related and functionally identical to the novel mouse T cell growth factor P40/TCGFIII (interleukin 9). Eur. J. Immunol. 20, 1413–1416 (1990).
Van Snick, J. et al. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA for a new mouse T cell growth factor (P40). J. Exp. Med. 169, 363–368 (1989).
Yang, Y.C. et al. Expression cloning of cDNA encoding a novel human hematopoietic growth factor: human homologue of murine T-cell growth factor P40. Blood 74, 1880–1884 (1989).
Modi, W.S. et al. Regional localization of the human glutaminase (GLS) and interleukin-9 (IL9) genes by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 57, 114–116 (1991).
Mock, B.A. et al. IL9 maps to mouse chromosome 13 and human chromosome 5. Immunogenetics 31, 265–270 (1990).
Renauld, J.C. et al. Expression cloning of the murine and human interleukin 9 receptor cDNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5690–5694 (1992).
Eklund, K.K., Ghildyal, N., Austen, K.F. & Stevens, R.L. Induction by IL-9 and suppression by IL-3 and IL-4 of the levels of chromosome 14-derived transcripts that encode late-expressed mouse mast cell proteases. J. Immunol. 151, 4266–4273 (1993).
Dugas, B. et al. Interleukin-9 potentiates the interleukin-4-induced immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM and IgE) production by normal human B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 23, 1687–1692 (1993).
Vink, A., Warnier, G., Brombacher, F. & Renauld, J.C. Interleukin 9-induced in vivo expansion of the B-1 lymphocyte population. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1413–1423 (1999).
Fontaine, R.H. et al. IL-9/IL-9 receptor signaling selectively protects cortical neurons against developmental apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 15, 1542–1552 (2008).
Dong, Q. et al. IL-9 induces chemokine expression in lung epithelial cells and baseline airway eosinophilia in transgenic mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 2130–2139 (1999).
Gounni, A.S. et al. IL-9-mediated induction of eotaxin1/CCL11 in human airway smooth muscle cells. J. Immunol. 173, 2771–2779 (2004).
Knoops, L. & Renauld, J.C. IL-9 and its receptor: from signal transduction to tumorigenesis. Growth Factors 22, 207–215 (2004).
Faulkner, H., Humphreys, N., Renauld, J.C., Van Snick, J. & Grencis, R. Interleukin-9 is involved in host protective immunity to intestinal nematode infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 2536–2540 (1997).
Faulkner, H., Renauld, J.C., Van Snick, J. & Grencis, R.K. Interleukin-9 enhances resistance to the intestinal nematode Trichuris muris. Infect. Immun. 66, 3832–3840 (1998).
Temann, U.A., Geba, G.P., Rankin, J.A. & Flavell, R.A. Expression of interleukin 9 in the lungs of transgenic mice causes airway inflammation, mast cell hyperplasia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1307–1320 (1998).
Temann, U.A., Ray, P. & Flavell, R.A. Pulmonary overexpression of IL-9 induces Th2 cytokine expression, leading to immune pathology. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 29–39 (2002).
McMillan, S.J., Bishop, B., Townsend, M.J., McKenzie, A.N. & Lloyd, C.M. The absence of interleukin 9 does not affect the development of allergen-induced pulmonary inflammation nor airway hyperreactivity. J. Exp. Med. 195, 51–57 (2002).
Townsend, J.M. et al. IL-9-deficient mice establish fundamental roles for IL-9 in pulmonary mastocytosis and goblet cell hyperplasia but not T cell development. Immunity 13, 573–583 (2000).
Cheng, G. et al. Anti-interleukin-9 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mouse asthma model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 166, 409–416 (2002).
Kearley, J. et al. IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell numbers in the lung and chronic remodeling of the airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183, 865–875 (2011).
Khan, W.I. et al. Modulation of intestinal muscle contraction by interleukin-9 (IL-9) or IL-9 neutralization: correlation with worm expulsion in murine nematode infections. Infect. Immun. 71, 2430–2438 (2003).
Nowak, E.C. et al. IL-9 as a mediator of Th17-driven inflammatory disease. J. Exp. Med. 206, 1653–1660 (2009).
Elyaman, W. et al. IL-9 induces differentiation of TH17 cells and enhances function of FoxP3+ natural regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 12885–12890 (2009).
Faulkner, H., Renauld, J.C., Van Snick, J. & Grencis, R.K. Interleukin-9 enhances resistance to the intestinal nematode Trichuris muris. Infect. Immun. 66, 3832–3840 (1998).
Antoniu, S.A. MEDI-528, an anti-IL-9 humanized antibody for the treatment of asthma. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 12, 233–239 (2010).
Lu, L.F. et al. Mast cells are essential intermediaries in regulatory T-cell tolerance. Nature 442, 997–1002 (2006).
Eller, K. et al. IL-9 production by regulatory T cells recruits mast cells that are essential for regulatory T cell-induced immune suppression. J. Immunol. 186, 83–91 (2011).
Veldhoen, M. et al. Transforming growth factor-beta ′reprograms′ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1341–1346 (2008).
Dardalhon, V. et al. IL-4 inhibits TGF-β-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-β, generates IL-9+ IL-10+Foxp3− effector T cells. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1347–1355 (2008).
Chang, H.C. et al. The transcription factor PU.1 is required for the development of IL-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 11, 527–534 (2010).
Staudt, V. et al. Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity 33, 192–202 (2010).
Tan, C. et al. Antigen-specific Th9 cells exhibit uniqueness in their kinetics of cytokine production and short retention at the inflammatory site. J. Immunol. 185, 6795–6801 (2010).
Wilhelm, C. et al. An IL-9 fate reporter demonstrates the induction of an innate IL-9 response in lung inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 12, 1071–1077 (2011).
Spits, H. & Di Santo, J.P. The expanding family of innate lymphoid cells: regulators and effectors of immunity and tissue remodeling. Nat. Immunol. 12, 21–27 (2011).
Houssiau, F.A. et al. A cascade of cytokines is responsible for IL-9 expression in human T cells. Involvement of IL-2, IL-4, and IL-10. J. Immunol. 154, 2624–2630 (1995).
Houssiau, F.A., Renauld, J.C., Fibbe, W.E. & Van Snick, J. IL-2 dependence of IL-9 expression in human T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 148, 3147–3151 (1992).
Kajiyama, Y. et al. IL-2-induced IL-9 production by allergen-specific human helper T-cell clones. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 143, 71–75 (2007).
Uyttenhove, C., Brombacher, F. & Van Snick, J. TGF-β interactions with IL-1 family members trigger IL-4-independent IL-9 production by mouse CD4+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 40, 2230–2235 (2010).
Schmitt, E. et al. IL-9 production of naive CD4+ T cells depends on IL-2, is synergistically enhanced by a combination of TGF-β and IL-4, and is inhibited by IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 153, 3989–3996 (1994).
Fallon, P.G. et al. Expression of interleukin-9 leads to Th2 cytokine-dominated responses and fatal enteropathy in mice with chronic Schistosoma mansoni infections. Infect. Immun. 68, 6005–6011 (2000).
Temann, U.A., Laouar, Y., Eynon, E.E., Homer, R. & Flavell, R.A. IL9 leads to airway inflammation by inducing IL13 expression in airway epithelial cells. Int. Immunol. 19, 1–10 (2007).
Steenwinckel, V. et al. IL-13 mediates in vivo IL-9 activities on lung epithelial cells but not on hematopoietic cells. J. Immunol. 178, 3244–3251 (2007).
Steenwinckel, V. et al. IL-9 promotes IL-13-dependent paneth cell hyperplasia and up-regulation of innate immunity mediators in intestinal mucosa. J. Immunol. 182, 4737–4743 (2009).
Gounni, A.S. et al. Interleukin-9 enhances interleukin-5 receptor expression, differentiation, and survival of human eosinophils. Blood 96, 2163–2171 (2000).
Singhera, G.K., MacRedmond, R. & Dorscheid, D.R. Interleukin-9 and -13 inhibit spontaneous and corticosteroid induced apoptosis of normal airway epithelial cells. Exp. Lung Res. 34, 579–598 (2008).
Demoulin, J.B., Van Roost, E., Stevens, M., Groner, B. & Renauld, J.C. Distinct roles for STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 in differentiation gene induction and apoptosis inhibition by inte rleukin-9. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25855–25861 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilhelm, C., Turner, JE., Van Snick, J. et al. The many lives of IL-9: a question of survival?. Nat Immunol 13, 637–641 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2303
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2303
This article is cited by
-
Interleukin-9 production by type 2 innate lymphoid cells induces Paneth cell metaplasia and small intestinal remodeling
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Amyloid-β Pathology-Specific Cytokine Secretion Suppresses Neuronal Mitochondrial Metabolism
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2023)
-
Opposing functions of circadian protein DBP and atypical E2F family E2F8 in anti-tumor Th9 cell differentiation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Function of innate lymphoid cells in the immune-related disorders
Human Cell (2019)
-
Interleukin-9 promotes early mast cell-mediated expulsion of Strongyloides ratti but is dispensable for generation of protective memory
Scientific Reports (2018)