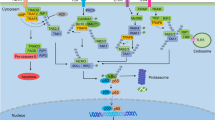
Abstract
Activation of NF-κB transcription factors by receptors of the innate or adaptive immune system is essential for host defense. However, after danger is eliminated, NF-κB signaling needs to be tightly downregulated for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. This review highlights key negative regulatory principles that affect the amount, localization or conformational properties of NF-κB-activating proteins to attenuate the NF-κB response. These mechanisms are needed to prevent inflammation, autoimmune disease and oncogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grivennikov, S.I. & Karin, M. Inflammation and oncogenesis: a vicious connection. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 20, 65–71 (2010).
Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-κB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, a001651 (2009).
Staudt, L.M. Oncogenic activation of NF-κB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a000109 (2010).
Hayden, M.S. & Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell 132, 344–362 (2008).
Vallabhapurapu, S. & Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 693–733 (2009).
Whiteside, S.T., Epinat, J.C., Rice, N.R. & Israel, A. IκB epsilon, a novel member of the IκB family, controls RelA and cRel NF-κB activity. EMBO J. 16, 1413–1426 (1997).
Hoffmann, A., Levchenko, A., Scott, M.L. & Baltimore, D. The IκB-NF-κB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 298, 1241–1245 (2002).
Sun, S.C., Ganchi, P.A., Ballard, D.W. & Greene, W.C. NF-κB controls expression of inhibitor IκBα: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 259, 1912–1915 (1993).
Le Bail, O., Schmidt-Ullrich, R. & Israel, A. Promoter analysis of the gene encoding the IκB-α/MAD3 inhibitor of NF-κB: positive regulation by members of the rel/NF-κB family. EMBO J. 12, 5043–5049 (1993).
Kearns, J.D., Basak, S., Werner, S.L., Huang, C.S. & Hoffmann, A. IκBɛ provides negative feedback to control NF-κB oscillations, signaling dynamics, and inflammatory gene expression. J. Cell Biol. 173, 659–664 (2006).
Arenzana-Seisdedos, F. et al. Inducible nuclear expression of newly synthesized IκBα negatively regulates DNA-binding and transcriptional activities of NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2689–2696 (1995).
Rao, P. et al. IκBβ acts to inhibit and activate gene expression during the inflammatory response. Nature 466, 1115–1119 (2010).
Scheibel, M. et al. IκBβ is an essential co-activator for LPS-induced IL-1β transcription in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 207, 2621–2630 (2010).
Tam, W.F. & Sen, R. IκB family members function by different mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 7701–7704 (2001).
Chen, L., Fischle, W., Verdin, E. & Greene, W.C. Duration of nuclear NF-κB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 293, 1653–1657 (2001).
Mahoney, D.J. et al. Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 regulate TNFα-mediated NF-κB activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 11778–11783 (2008).
Ea, C.K., Deng, L., Xia, Z.P., Pineda, G. & Chen, Z.J. Activation of IKK by TNFα requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol. Cell 22, 245–257 (2006).
Wu, C.J., Conze, D.B., Li, T., Srinivasula, S.M. & Ashwell, J.D. Sensing of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitination by NEMO is a key event in NF-κB activation. Nat. Cell Biol. [corrected] 8, 398–406 (2006).
Rahighi, S. et al. Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by NEMO is important for NF-κB activation. Cell 136, 1098–1109 (2009).
Kawai, T. & Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 (2010).
Rawlings, D.J., Sommer, K. & Moreno-Garcia, M.E. The CARMA1 signalosome links the signalling machinery of adaptive and innate immunity in lymphocytes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 799–812 (2006).
Wertz, I.E. & Dixit, V.M. Signaling to NF-κB: regulation by ubiquitination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a003350 (2010).
Lee, E.G. et al. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-κB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289, 2350–2354 (2000).
Wertz, I.E. et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-κB signalling. Nature 430, 694–699 (2004).
Hymowitz, S.G. & Wertz, I.E. A20: from ubiquitin editing to tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 332–341 (2010).
Boone, D.L. et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1052–1060 (2004).
Mauro, C. et al. ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKγ and co-operates with A20 in inhibiting NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 18482–18488 (2006).
Hitotsumatsu, O. et al. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 restricts nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2-triggered signals. Immunity 28, 381–390 (2008).
Duwel, M. et al. A20 negatively regulates T cell receptor signaling to NF-κB by cleaving Malt1 ubiquitin chains. J. Immunol. 182, 7718–7728 (2009).
Iha, H. et al. Inflammatory cardiac valvulitis in TAX1BP1-deficient mice through selective NF-κB activation. EMBO J. 27, 629–641 (2008).
Shembade, N. et al. The E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates inflammatory signaling pathways by controlling the function of the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20. Nat. Immunol. 9, 254–262 (2008).
Scharschmidt, E., Wegener, E., Heissmeyer, V., Rao, A. & Krappmann, D. Degradation of Bcl10 induced by T-cell activation negatively regulates NF-κB signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 3860–3873 (2004).
Wagner, S. et al. Ubiquitin binding mediates the NF-κB inhibitory potential of ABIN proteins. Oncogene 27, 3739–3745 (2008).
Enesa, K. et al. NF-κB suppression by the deubiquitinating enzyme Cezanne: a novel negative feedback loop in pro-inflammatory signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 7036–7045 (2008).
Kovalenko, A. et al. The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-κB signalling by deubiquitination. Nature 424, 801–805 (2003).
Trompouki, E. et al. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-κB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 424, 793–796 (2003).
Sun, S.C. CYLD: a tumor suppressor deubiquitinase regulating NF-κB activation and diverse biological processes. Cell Death Differ. 17, 25–34 (2010).
Massoumi, R., Chmielarska, K., Hennecke, K., Pfeifer, A. & Fassler, R. Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by blocking Bcl-3-dependent NF-κB signaling. Cell 125, 665–677 (2006).
Reiley, W., Zhang, M., Wu, X., Granger, E. & Sun, S.C. Regulation of the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD by IκB kinase γ-dependent phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 3886–3895 (2005).
Burns, K. et al. Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4. J. Exp. Med. 197, 263–268 (2003).
Janssens, S., Burns, K., Vercammen, E., Tschopp, J. & Beyaert, R. MyD88S, a splice variant of MyD88, differentially modulates NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent gene expression. FEBS Lett. 548, 103–107 (2003).
Kobayashi, K. et al. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 110, 191–202 (2002).
Escoll, P. et al. Rapid up-regulation of IRAK-M expression following a second endotoxin challenge in human monocytes and in monocytes isolated from septic patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 311, 465–472 (2003).
van 't Veer, C. et al. Induction of IRAK-M is associated with lipopolysaccharide tolerance in a human endotoxemia model. J. Immunol. 179, 7110–7120 (2007).
Carty, M. et al. The human adaptor SARM negatively regulates adaptor protein TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat. Immunol. 7, 1074–1081 (2006).
Wegener, E. et al. Essential role for IκB kinase β in remodeling Carma1-Bcl10-Malt1 complexes upon T cell activation. Mol. Cell 23, 13–23 (2006).
Lobry, C., Lopez, T., Israel, A. & Weil, R. Negative feedback loop in T cell activation through IκB kinase-induced phosphorylation and degradation of Bcl10. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 908–913 (2007).
Bidere, N. et al. Casein kinase 1α governs antigen-receptor-induced NF-κB activation and human lymphoma cell survival. Nature 458, 92–96 (2009).
Liu, B. et al. PIAS1 selectively inhibits interferon-inducible genes and is important in innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 5, 891–898 (2004).
Liu, B. et al. Negative regulation of NF-κB signaling by PIAS1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 1113–1123 (2005).
Tahk, S. et al. Control of specificity and magnitude of NF-κB and STAT1-mediated gene activation through PIASy and PIAS1 cooperation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 11643–11648 (2007).
Liu, B. et al. Proinflammatory stimuli induce IKKα-mediated phosphorylation of PIAS1 to restrict inflammation and immunity. Cell 129, 903–914 (2007).
Lawrence, T., Bebien, M., Liu, G.Y., Nizet, V. & Karin, M. IKKα limits macrophage NF-κB activation and contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature 434, 1138–1143 (2005).
Li, Q. et al. Enhanced NF-κB activation and cellular function in macrophages lacking IκB kinase 1 (IKK1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 12425–12430 (2005).
Natoli, G. & Chiocca, S. Nuclear ubiquitin ligases, NF-κB degradation, and the control of inflammation. Sci. Signal. 1, pe1 (2008).
Tanaka, T., Grusby, M.J. & Kaisho, T. PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-κB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nat. Immunol. 8, 584–591 (2007).
Maine, G.N., Mao, X., Komarck, C.M. & Burstein, E. COMMD1 promotes the ubiquitination of NF-κB subunits through a cullin-containing ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J. 26, 436–447 (2007).
Kinjyo, I. et al. SOCS1/JAB is a negative regulator of LPS-induced macrophage activation. Immunity 17, 583–591 (2002).
Yang, X.D. et al. Negative regulation of NF-κB action by Set9-mediated lysine methylation of the RelA subunit. EMBO J. 28, 1055–1066 (2009).
Senftleben, U. et al. Activation by IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κ B signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 (2001).
Xiao, G., Harhaj, E.W. & Sun, S.C. NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-κB2 p100. Mol. Cell 7, 401–409 (2001).
Basak, S. et al. A fourth IκB protein within the NF-κB signaling module. Cell 128, 369–381 (2007).
Liao, G., Zhang, M., Harhaj, E.W. & Sun, S.C. Regulation of the NF-κB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 26243–26250 (2004).
Varfolomeev, E. et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-κB activation, and TNFα-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131, 669–681 (2007).
Zarnegar, B.J. et al. Noncanonical NF-κB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1371–1378 (2008).
Yeh, W.C. et al. Early lethality, functional NF-κB activation, and increased sensitivity to TNF-induced cell death in TRAF2-deficient mice. Immunity 7, 715–725 (1997).
He, J.Q. et al. Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-κB deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2413–2418 (2006).
Vallabhapurapu, S. et al. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-κB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1364–1370 (2008).
Razani, B. et al. Negative feedback in noncanonical NF-κB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKα-mediated phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 3, ra41 (2010).
Oeckinghaus, A. & Ghosh, S. The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, a000034 (2009).
Baltimore, D., Boldin, M.P., O'Connell, R.M., Rao, D.S. & Taganov, K.D. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat. Immunol. 9, 839–845 (2008).
O'Neill, L.A., Sheedy, F.J. & McCoy, C.E. MicroRNAs: the fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 163–175 (2011).
Taganov, K.D., Boldin, M.P., Chang, K.J. & Baltimore, D. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12481–12486 (2006).
Ceppi, M. et al. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2735–2740 (2009).
Tang, B. et al. Identification of MyD88 as a novel target of miR-155, involved in negative regulation of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. FEBS Lett. 584, 1481–1486 (2010).
Jungnickel, B. et al. Clonal deleterious mutations in the IκBα gene in the malignant cells in Hodgkin's lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 191, 395–402 (2000).
Bredel, M. et al. NFKBIA deletion in glioblastomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 627–637 (2011).
Kato, M. et al. Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature 459, 712–716 (2009).
Compagno, M. et al. Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-κB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 459, 717–721 (2009).
Ferch, U. et al. Inhibition of MALT1 protease activity is selectively toxic for activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2313–2320 (2009).
Musone, S.L. et al. Multiple polymorphisms in the TNFAIP3 region are independently associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 40, 1062–1064 (2008).
Plenge, R.M. et al. Two independent alleles at 6q23 associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 39, 1477–1482 (2007).
Nair, R.P. et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat. Genet. 41, 199–204 (2009).
Balaci, L. et al. IRAK-M is involved in the pathogenesis of early-onset persistent asthma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 1103–1114 (2007).
Keats, J.J. et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-κB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 12, 131–144 (2007).
Annunziata, C.M. et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 12, 115–130 (2007).
Rosebeck, S. et al. Cleavage of NIK by the API2-MALT1 fusion oncoprotein leads to noncanonical NF-κB activation. Science 331, 468–472 (2011).
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Sonderforschungsbereich grants).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruland, J. Return to homeostasis: downregulation of NF-κB responses. Nat Immunol 12, 709–714 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2055
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2055
This article is cited by
-
Peptidase inhibitor (PI16) impairs bladder cancer metastasis by inhibiting NF-κB activation via disrupting multiple-site ubiquitination of NEMO
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2023)
-
LncRNA H19 Regulates P-glycoprotein Expression Through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Model of Status Epilepticus
Neurochemical Research (2023)
-
The NF-κB Pathway: a Focus on Inflammatory Responses in Spinal Cord Injury
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Nerve growth factor receptor (Ngfr) induces neurogenic plasticity by suppressing reactive astroglial Lcn2/Slc22a17 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease
npj Regenerative Medicine (2023)
-
Novel cytoplasmic lncRNA IKBKBAS promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by upregulating IKKβ and consequential activation of NF-κB signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2021)