Abstract
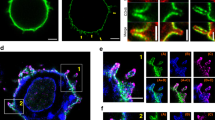
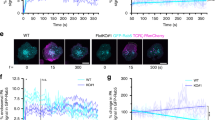
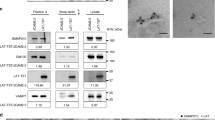
Engaged T cell antigen receptors (TCRs) initiate signaling through the adaptor protein Lat. In quiescent T cells, Lat is segregated into clusters on the cell surface, which raises the question of how TCR triggering initiates signaling. Using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, we found that pre-existing Lat domains were neither phosphorylated nor laterally transported to TCR activation sites, which suggested that these clusters do not participate in TCR signaling. Instead, TCR activation resulted in the recruitment and phosphorylation of Lat from subsynaptic vesicles. Studies of Lat mutants confirmed that recruitment preceded and was essential for phosphorylation and that both processes were independent of surface clustering of Lat. Our data suggest that TCR ligation preconditions the membrane for vesicle recruitment and bulk activation of the Lat signaling network.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Merwe, P.A. & Davis, S.J. Immunology. The immunological synapse—a multitasking system. Science 295, 1479–1480 (2002).
Varma, R., Campi, G., Yokosuka, T., Saito, T. & Dustin, M.L. T cell receptor-proximal signals are sustained in peripheral microclusters and terminated in the central supramolecular activation cluster. Immunity 25, 117–127 (2006).
Yokosuka, T. et al. Newly generated T cell receptor microclusters initiate and sustain T cell activation by recruitment of Zap70 and SLP-76. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1253–1262 (2005).
Gaus, K., Chklovskaia, E., Fazekas de St Groth, B., Jessup, W. & Harder, T. Condensation of the plasma membrane at the site of T lymphocyte activation. J. Cell Biol. 171, 121–131 (2005).
Owen, D.M. et al. High plasma membrane lipid order imaged at the immunological synapse periphery in live T cells. Mol. Membr. Biol. 27, 178–189 (2010).
Campi, G., Varma, R. & Dustin, M.L. Actin and agonist MHC-peptide complex-dependent T cell receptor microclusters as scaffolds for signaling. J. Exp. Med. 202, 1031–1036 (2005).
Kaizuka, Y., Douglass, A.D., Varma, R., Dustin, M.L. & Vale, R.D. Mechanisms for segregating T cell receptor and adhesion molecules during immunological synapse formation in Jurkat T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 20296–20301 (2007).
Monks, C.R., Freiberg, B.A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998).
Grakoui, A. et al. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 285, 221–227 (1999).
Samelson, L.E. & Klausner, R.D. Tyrosine kinases and tyrosine-based activation motifs. Current research on activation via the T cell antigen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 24913–24916 (1992).
Weiss, A. & Littman, D.R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell 76, 263–274 (1994).
Blanchard, N., Di Bartolo, V. & Hivroz, C. In the immune synapse, ZAP-70 controls T cell polarization and recruitment of signaling proteins but not formation of the synaptic pattern. Immunity 17, 389–399 (2002).
Finco, T.S., Kadlecek, T., Zhang, W., Samelson, L.E. & Weiss, A. LAT is required for TCR-mediated activation of PLCγ1 and the Ras pathway. Immunity 9, 617–626 (1998).
Zhang, W., Irvin, B.J., Trible, R.P., Abraham, R.T. & Samelson, L.E. Functional analysis of LAT in TCR-mediated signaling pathways using a LAT-deficient Jurkat cell line. Int. Immunol. 11, 943–950 (1999).
Zhang, W. et al. Essential role of LAT in T cell development. Immunity 10, 323–332 (1999).
Aguado, E., Martinez-Florensa, M. & Aparicio, P. Activation of T lymphocytes and the role of the adapter LAT. Transpl. Immunol. 17, 23–26 (2006).
Shen, S. et al. The importance of LAT in the activation, homeostasis, and regulatory function of T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 35393–35405 (2010).
Ilani, T., Vasiliver-Shamis, G., Vardhana, S., Bretscher, A. & Dustin, M.L. T cell antigen receptor signaling and immunological synapse stability require myosin IIA. Nat. Immunol. 10, 531–539 (2009).
Lee, K.H. et al. T cell receptor signaling precedes immunological synapse formation. Science 295, 1539–1542 (2002).
Lee, K.H. et al. The immunological synapse balances T cell receptor signaling and degradation. Science 302, 1218–1222 (2003).
Lillemeier, B.F. et al. TCR and Lat are expressed on separate protein islands on T cell membranes and concatenate during activation. Nat. Immunol. 11, 90–96 (2010).
Betzig, E. et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313, 1642–1645 (2006).
Hess, S.T., Girirajan, T.P. & Mason, M.D. Ultra-high resolution imaging by fluorescence photoactivation localization microscopy. Biophys. J. 91, 4258–4272 (2006).
Rust, M.J., Bates, M. & Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat. Methods 3, 793–795 (2006).
Heilemann, M. et al. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 47, 6172–6176 (2008).
Mattheyses, A.L. & Axelrod, D. Direct measurement of the evanescent field profile produced by objective-based total internal reflection fluorescence. J. Biomed. Opt. 11, 014006 (2006).
Douglass, A.D. & Vale, R.D. Single-molecule microscopy reveals plasma membrane microdomains created by protein-protein networks that exclude or trap signaling molecules in T cells. Cell 121, 937–950 (2005).
Scita, G. & Di Fiore, P.P. The endocytic matrix. Nature 463, 464–473 (2010).
Howarth, M., Takao, K., Hayashi, Y. & Ting, A.Y. Targeting quantum dots to surface proteins in living cells with biotin ligase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7583–7588 (2005).
Hartgroves, L.C. et al. Synergistic assembly of linker for activation of T cells signaling protein complexes in T cell plasma membrane domains. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 20389–20394 (2003).
Tanimura, N., Saitoh, S., Kawano, S., Kosugi, A. & Miyake, K. Palmitoylation of LAT contributes to its subcellular localization and stability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 341, 1177–1183 (2006).
Hundt, M. et al. Palmitoylation-dependent plasma membrane transport but lipid raft-independent signaling by linker for activation of T cells. J. Immunol. 183, 1685–1694 (2009).
Zhang, W., Trible, R.P. & Samelson, L.E. LAT palmitoylation: its essential role in membrane microdomain targeting and tyrosine phosphorylation during T cell activation. Immunity 9, 239–246 (1998).
Lin, J., Weiss, A. & Finco, T.S. Localization of LAT in glycolipid-enriched microdomains is required for T cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28861–28864 (1999).
Montoya, M.C. et al. Role of ICAM-3 in the initial interaction of T lymphocytes and APCs. Nat. Immunol. 3, 159–168 (2002).
Bunnell, S.C. et al. T cell receptor ligation induces the formation of dynamically regulated signaling assemblies. J. Cell Biol. 158, 1263–1275 (2002).
Purbhoo, M. et al. Dynamics of subsynaptic vesicles and surface microclusters at the immunological synapse. Sci. Signal. 3, ra36–ra36 (2010).
Bonello, G. et al. Dynamic recruitment of the adaptor protein LAT: LAT exists in two distinct intracellular pools and controls its own recruitment. J. Cell Sci. 117, 1009–1016 (2004).
Malissen, B., Aguado, E. & Malissen, M. Role of the LAT adaptor in T-cell development and Th2 differentiation. Adv. Immunol. 87, 1–25 (2005).
Tanimura, N. et al. Dynamic changes in the mobility of LAT in aggregated lipid rafts upon T cell activation. J. Cell Biol. 160, 125–135 (2003).
Zech, T. et al. Accumulation of raft lipids in T-cell plasma membrane domains engaged in TCR signalling. EMBO J. 28, 466–476 (2009).
Harder, T. & Kuhn, M. Selective accumulation of raft-associated membrane protein LAT in T cell receptor signaling assemblies. J. Cell Biol. 151, 199–208 (2000).
Rentero, C. et al. Functional implications of plasma membrane condensation for T cell activation. PLoS ONE 3, e2262 (2008).
Wilson, B.S., Pfeiffer, J.R., Surviladze, Z., Gaudet, E.A. & Oliver, J.M. High resolution mapping of mast cell membranes reveals primary and secondary domains of FcɛRI and LAT. J. Cell Biol. 154, 645–658 (2001).
Liu, H., Purbhoo, M.A., Davis, D.M. & Rudd, C.E. SH2 domain containing leukocyte phosphoprotein of 76-kDa (SLP-76) feedback regulation of ZAP-70 microclustering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 10166–10171 (2010).
Barr, V.A. et al. T-cell antigen receptor-induced signaling complexes: internalization via a cholesterol-dependent endocytic pathway. Traffic 7, 1143–1162 (2006).
Mingueneau, M. et al. Loss of the LAT adaptor converts antigen-responsive T cells into pathogenic effectors that function independently of the T cell receptor. Immunity 31, 197–208 (2009).
Liu, H., Rhodes, M., Wiest, D.L. & Vignali, D.A. On the dynamics of TCR:CD3 complex cell surface expression and downmodulation. Immunity 13, 665–675 (2000).
Chen, I., Howarth, M., Lin, W. & Ting, A.Y. Site-specific labeling of cell surface proteins with biophysical probes using biotin ligase. Nat. Methods 2, 99–104 (2005).
Owen, D.M. et al. PALM imaging and cluster analysis of protein heterogeneity at the cell surface. J Biophotonics 3, 446–454 (2010).
Acknowledgements
Supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (D.J.W., J.J.G. and K.G.), the Australian Research Council (D.M.O., J.J.G. and K.G.) and Human Frontier Science Program (K.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.J.W., molecular biology, PALM, crosslinking experiments and analysis, and manuscript preparation; D.M.O., conceptualization and PALM-STORM analysis; J.R., STORM experiments and analysis; A.M., PALM experiments and analysis of surface-patterning experiments; M.W., surface-patterning experiments; J.J.G., conceptualization of surface patterning; and K.G., conceptualization and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1612 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Lat cluster map movie. (AVI 7297 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williamson, D., Owen, D., Rossy, J. et al. Pre-existing clusters of the adaptor Lat do not participate in early T cell signaling events. Nat Immunol 12, 655–662 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2049
This article is cited by
-
A framework for evaluating the performance of SMLM cluster analysis algorithms
Nature Methods (2023)
-
CD44 promotes angiogenesis in myocardial infarction through regulating plasma exosome uptake and further enhancing FGFR2 signaling transduction
Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Correction of multiple-blinking artifacts in photoactivated localization microscopy
Nature Methods (2022)
-
Liquid–liquid phase separation as an organizing principle of intracellular space: overview of the evolution of the cell compartmentalization concept
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
CD45 pre-exclusion from the tips of T cell microvilli prior to antigen recognition
Nature Communications (2021)