Abstract
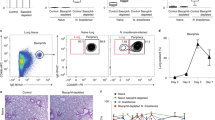
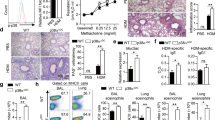
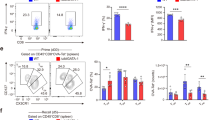
T helper type 2 (TH2)-mediated immune responses are induced after infection with multicellular parasites and can be triggered by a variety of allergens. The mechanisms of induction and the antigen-presenting cells involved in the activation of TH2 responses remain poorly defined, and the innate immune sensing pathways activated by parasites and allergens are largely unknown. Basophils are required for the in vivo induction of TH2 responses by protease allergens. Here we show that basophils also function as antigen-presenting cells. We show that although dendritic cells were dispensable for allergen-induced activation of TH2 responses in vitro and in vivo, antigen presentation by basophils was necessary and sufficient for this. Thus, basophils function as antigen-presenting cells for TH2 differentiation in response to protease allergens.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, J. & Paul, W.E. CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults. Blood 112, 1557–1569 (2008).
Janeway, C.A. Jr. & Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 197–216 (2002).
Brown, G.D. Dectin-1: a signalling non-TLR pattern-recognition receptor. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 33–43 (2006).
LeibundGut-Landmann, S. et al. Syk- and CARD9-dependent coupling of innate immunity to the induction of T helper cells that produce interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 8, 630–638 (2007).
Acosta-Rodriguez, E.V. et al. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, 639–646 (2007).
Iwasaki, A. & Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 987–995 (2004).
Schnare, M. et al. Toll-like receptors control activation of adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2, 947–950 (2001).
Joffre, O., Nolte, M.A., Sporri, R. & Reis e Sousa, C. Inflammatory signals in dendritic cell activation and the induction of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 227, 234–247 (2009).
Sporri, R. & Reis e Sousa, C. Inflammatory mediators are insufficient for full dendritic cell activation and promote expansion of CD4+ T cell populations lacking helper function. Nat. Immunol. 6, 163–170 (2005).
McKerrow, J.H., Caffrey, C., Kelly, B., Loke, P. & Sajid, M. Proteases in parasitic diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 1, 497–536 (2006).
McGuinness, D.H., Dehal, P.K. & Pleass, R.J. Pattern recognition molecules and innate immunity to parasites. Trends Parasitol. 19, 312–319 (2003).
Chambers, L. et al. Enzymatically active papain preferentially induces an allergic response in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253, 837–840 (1998).
Gough, L., Schulz, O., Sewell, H.F. & Shakib, F. The cysteine protease activity of the major dust mite allergen Der p 1 selectively enhances the immunoglobulin E antibody response. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1897–1902 (1999).
Sokol, C.L., Barton, G.M., Farr, A.G. & Medzhitov, R. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses. Nat. Immunol. 9, 310–318 (2008).
Mohrs, M., Shinkai, K., Mohrs, K. & Locksley, R.M. Analysis of type 2 immunity in vivo with a bicistronic IL-4 reporter. Immunity 15, 303–311 (2001).
Oh, K., Shen, T., Le Gros, G. & Min, B. Induction of Th2 type immunity in a mouse system reveals a novel immunoregulatory role of basophils. Blood 109, 2921–2927 (2007).
Steimle, V., Otten, L.A., Zufferey, M. & Mach, B. Complementation cloning of an MHC class II transactivator mutated in hereditary MHC class II deficiency (or bare lymphocyte syndrome). Cell 75, 135–146 (1993).
Chang, C.H. & Flavell, R.A. Class II transactivator regulates the expression of multiple genes involved in antigen presentation. J. Exp. Med. 181, 765–767 (1995).
Chang, C.H., Fontes, J.D., Peterlin, M. & Flavell, R.A. Class II transactivator (CIITA) is sufficient for the inducible expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1367–1374 (1994).
Muhlethaler-Mottet, A., Otten, L.A., Steimle, V. & Mach, B. Expression of MHC class II molecules in different cellular and functional compartments is controlled by differential usage of multiple promoters of the transactivator CIITA. EMBO J. 16, 2851–2860 (1997).
Reith, W. LeibundGut-Landmann, S. & Waldburger, J.M. Regulation of MHC class II gene expression by the class II transactivator. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 793–806 (2005).
Grakoui, A. et al. The immunological synapse: a molecular machine controlling T cell activation. Science 285, 221–227 (1999).
Monks, C.R., Freiberg, B.A., Kupfer, H., Sciaky, N. & Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 395, 82–86 (1998).
Itano, A.A. et al. Distinct dendritic cell populations sequentially present antigen to CD4 T cells and stimulate different aspects of cell-mediated immunity. Immunity 19, 47–57 (2003).
Sixt, M. et al. The conduit system transports soluble antigens from the afferent lymph to resident dendritic cells in the T cell area of the lymph node. Immunity 22, 19–29 (2005).
Jung, S. et al. In vivo depletion of CD11c+ dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8+ T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity 17, 211–220 (2002).
Zammit, D.J., Cauley, L.S., Pham, Q.M. & Lefrancois, L. Dendritic cells maximize the memory CD8 T cell response to infection. Immunity 22, 561–570 (2005).
Voehringer, D., Shinkai, K. & Locksley, R.M. Type 2 immunity reflects orchestrated recruitment of cells committed to IL-4 production. Immunity 20, 267–277 (2004).
Lemos, M.P., Fan, L., Lo, D. & Laufer, T.M. CD8α+ and CD11b+ dendritic cell-restricted MHC class II controls Th1 CD4+ T cell immunity. J. Immunol. 171, 5077–5084 (2003).
Lemos, M.P., Esquivel, F., Scott, P. & Laufer, T.M. MHC class II expression restricted to CD8α+ and CD11b+ dendritic cells is sufficient for control of Leishmania major. J. Exp. Med. 199, 725–730 (2004).
Domen, J., Gandy, K.L. & Weissman, I.L. Systemic overexpression of BCL-2 in the hematopoietic system protects transgenic mice from the consequences of lethal irradiation. Blood 91, 2272–2282 (1998).
Tsujimura, Y. et al. Basophils play a pivotal role in immunoglobulin-G-mediated but not immunoglobulin-E-mediated systemic anaphylaxis. Immunity 28, 581–589 (2008).
Min, B. et al. Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. J. Exp. Med. 200, 507–517 (2004).
Voehringer, D., Reese, T.A., Huang, X., Shinkai, K. & Locksley, R.M. Type 2 immunity is controlled by IL-4/IL-13 expression in hematopoietic non-eosinophil cells of the innate immune system. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1435–1446 (2006).
Sullivan, B.M. & Locksley, R.M. Basophils: a nonredundant contributor to host immunity. Immunity 30, 12–20 (2009).
Hida, S., Tadachi, M., Saito, T. & Taki, S. Negative control of basophil expansion by IRF-2 critical for the regulation of Th1/Th2 balance. Blood 106, 2011–2017 (2005).
Denzel, A. et al. Basophils enhance immunological memory responses. Nat. Immunol. 9, 733–742 (2008).
Karasuyama, H., Mukai, K., Tsujimura, Y. & Obata, K. Newly discovered roles for basophils: a neglected minority gains new respect. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 9–13 (2009).
Gauchat, J.F. et al. Induction of human IgE synthesis in B cells by mast cells and basophils. Nature 365, 340–343 (1993).
Yanagihara, Y. et al. Cultured basophils but not cultured mast cells induce human IgE synthesis in B cells after immunologic stimulation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 111, 136–143 (1998).
Mack, M. et al. Identification of antigen-capturing cells as basophils. J. Immunol. 174, 735–741 (2005).
Min, B. Basophils: what they 'can do' versus what they 'actually do'. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1333–1339 (2008).
Eisenbarth, S.C. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen. J. Exp. Med. 196, 1645–1651 (2002).
Piggott, D.A. et al. MyD88-dependent induction of allergic Th2 responses to intranasal antigen. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 459–467 (2005).
Trompette, A. et al. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature 457, 585–588 (2008).
Franchi, L. & Nunez, G. The Nlrp3 inflammasome is critical for aluminium hydroxide-mediated IL-1beta secretion but dispensable for adjuvant activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 2085–2089 (2008).
Hornung, V. et al. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the NALP3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat. Immunol. 9, 847–856 (2008).
Li, H., Nookala, S. & Re, F. Aluminum hydroxide adjuvants activate caspase-1 and induce IL-1β and IL-18 release. J. Immunol. 178, 5271–5276 (2007).
Li, H., Willingham, S.B., Ting, J.P. & Re, F. Cutting edge: inflammasome activation by alum and alum's adjuvant effect are mediated by NLRP3. J. Immunol. 181, 17–21 (2008).
Eisenbarth, S.C., Colegio, O.R., O'Connor, W., Sutterwala, F.S. & Flavell, R.A. Crucial role for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants. Nature 453, 1122–1126 (2008).
Reese, T.A. et al. Chitin induces accumulation in tissue of innate immune cells associated with allergy. Nature 447, 92–96 (2007).
MacDonald, A.S., Straw, A.D., Bauman, B. & Pearce, E.J. CD8− dendritic cell activation status plays an integral role in influencing Th2 response development. J. Immunol. 167, 1982–1988 (2001).
Kambayashi, T. et al. Indirect involvement of allergen-captured mast cells in antigen presentation. Blood 111, 1489–1496 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Weissman (Stanford University) for H-2k–Bcl-2 mice; K. Bottomly (Yale University) for DO11.10 × 4get transgenic mice; A. Iwasaki (Yale University) for mice and reagents; S. Holley, C. Annicelli and M. Kotas for technical assistance; and J. Kagan and D. Hargreaves for experimental input. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (Medical Scientist Training Program TG2T32GM07205 to C.L.S. and R01 AI46688 and R01 AI055502 to R.M.), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (R.M.) and the Sandler Program in Asthma Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L.S. and R.M. designed the experiments; C.L.S., N.-Q.C., S.Y. and S.A.N. did the experiments; C.L.S. and R.M. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; and T.M.L. provided CD11c-IABB mice.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 8178 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokol, C., Chu, NQ., Yu, S. et al. Basophils function as antigen-presenting cells for an allergen-induced T helper type 2 response. Nat Immunol 10, 713–720 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1738
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1738
This article is cited by
-
The association between eosinophils (CD16+ eosinophils), basophils (CD203+ basophils), and CD23 B lymphocytes in patients with atopic dermatitis on dupilumab therapy: pilot study
Dermatology and Therapy (2023)
-
Balamuthia mandrillaris trophozoites ingest human neuronal cells via a trogocytosis-independent mechanism
Parasites & Vectors (2022)
-
Estimates of genomic heritability and genome-wide association studies for blood parameters in Akkaraman sheep
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Shuang-Huang-Lian prevents basophilic granulocyte activation to suppress Th2 immunity
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2018)
-
TH2 cell development and function
Nature Reviews Immunology (2018)