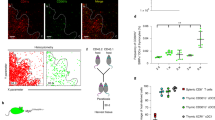
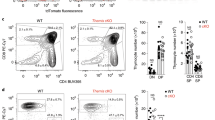
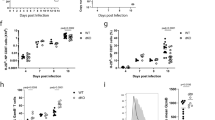
Abstract
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) and T cell antigen receptor signals have been proposed to be the main drivers of homeostatic T cell proliferation. However, it is not known why CD4+ T cells undergo less-efficient homeostatic proliferation than CD8+ T cells do. Here we show that systemic IL-7 concentrations increased during lymphopenia because of diminished use of IL-7 but that IL-7 signaling on IL-7 receptor-α–positive (IL-7Rα+) dendritic cells (DCs) in lymphopenic settings paradoxically diminished the homeostatic proliferation of CD4+ T cells. This effect was mediated at least in part by IL-7-mediated downregulation of the expression of major histocompatibility complex class II on IL-7Rα+ DCs. Our results indicate that IL-7Rα+ DCs are regulators of the peripheral CD4+ T cell niche and that IL-7 signals in DCs prevent uncontrolled CD4+ T cell population expansion in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mackall, C.L. et al. Age, thymopoiesis, and CD4+ T-lymphocyte regeneration after intensive chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 143–149 (1995).
Heitger, A. et al. Essential role of the thymus to reconstitute naive (CD45RA+) T-helper cells after human allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 90, 850–857 (1997).
Dumont-Girard, F. et al. Reconstitution of the T-cell compartment after bone marrow transplantation: restoration of the repertoire by thymic emigrants. Blood 92, 4464–4471 (1998).
Hakim, F.T. et al. Constraints on CD4 recovery postchemotherapy in adults: thymic insufficiency and apoptotic decline of expanded peripheral CD4 cells. Blood 90, 3789–3798 (1997).
Douek, D.C. et al. Evidence for increased T cell turnover and decreased thymic output in HIV infection. J. Immunol. 167, 6663–6668 (2001).
Hakim, F.T. et al. Age-dependent incidence, time course, and consequences of thymic renewal in adults. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 930–939 (2005).
Goldrath, A.W. & Bevan, M.J. Low-affinity ligands for the TCR drive proliferation of mature CD8+ T cells in lymphopenic hosts. Immunity 11, 183–190 (1999).
Surh, C.D. & Sprent, J. Homeostatic T cell proliferation: how far can T cells be activated to self-ligands? J. Exp. Med. 192, F9–F14 (2000).
Seddon, B. & Zamoyska, R. TCR signals mediated by Src family kinases are essential for the survival of naive T cells. J. Immunol. 169, 2997–3005 (2002).
Schluns, K.S., Kieper, W.C., Jameson, S.C. & Lefrancois, L. Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 1, 426–432 (2000).
Vivien, L., Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. T lymphocytes need IL-7 but not IL-4 or IL-6 to survive in vivo. Int. Immunol. 13, 763–768 (2001).
Mackall, C.L. et al. IL-7 increases both thymic-dependent and thymic-independent T-cell regeneration after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 97, 1491–1497 (2001).
Fry, T.J. et al. IL-7 therapy dramatically alters peripheral T-cell homeostasis in normal and SIV-infected nonhuman primates. Blood 101, 2294–2299 (2003).
Sportes, C. et al. Administration of rhIL-7 in humans increases in vivo TCR repertoire diversity by preferential expansion of naive T cell subsets. J. Exp. Med. (in the press) (2008).
Geiselhart, L.A. et al. IL-7 administration alters the CD4:CD8 ratio, increases T cell numbers, and increases T cell function in the absence of activation. J. Immunol. 166, 3019–3027 (2001).
Napolitano, L.A. et al. Increased production of IL-7 accompanies HIV-1-mediated T-cell depletion: implications for T-cell homeostasis. Nat. Med. 7, 73–79 (2001).
Fry, T.J. et al. A potential role for interleukin-7 in T-cell homeostasis. Blood 97, 2983–2990 (2001).
Bolotin, E., Annett, G., Parkman, R. & Weinberg, K. Serum levels of IL-7 in bone marrow transplant recipients: relationship to clinical characteristics and lymphocyte count. Bone Marrow Transplant. 23, 783–788 (1999).
Muthukumar, A. et al. Elevated interleukin-7 levels not sufficient to maintain T-cell homeostasis during simian immunodeficiency virus-induced disease progression. Blood 103, 973–979 (2004).
Park, J.H. et al. Suppression of IL7Rα transcription by IL-7 and other prosurvival cytokines: a novel mechanism for maximizing IL-7-dependent T cell survival. Immunity 21, 289–302 (2004).
Iwata, M., Graf, L., Awaya, N. & Torok-Storb, B. Functional interleukin-7 receptors (IL-7Rs) are expressed by marrow stromal cells: binding of IL-7 increases levels of IL-6 mRNA and secreted protein. Blood 100, 1318–1325 (2002).
Pillai, M., Torok-Storb, B. & Iwata, M. Expression and function of IL-7 receptors in marrow stromal cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 45, 2403–2408 (2004).
Min, B., Foucras, G., Meier-Schellersheim, M. & Paul, W.E. Spontaneous proliferation, a response of naive CD4 T cells determined by the diversity of the memory cell repertoire. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3874–3879 (2004).
Kieper, W.C. et al. Recent immune status determines the source of antigens that drive homeostatic T cell expansion. J. Immunol. 174, 3158–3163 (2005).
Kassiotis, G., Zamoyska, R. & Stockinger, B. Involvement of avidity for major histocompatibility complex in homeostasis of naive and memory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1007–1016 (2003).
Bourgeois, C., Kassiotis, G. & Stockinger, B. A major role for memory CD4 T cells in the control of lymphopenia-induced proliferation of naive CD4 T cells. J. Immunol. 174, 5316–5323 (2005).
Melchionda, F. et al. Adjuvant IL-7 or IL-15 overcomes immunodominance and improves survival of the CD8+ memory cell pool. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1177–1187 (2005).
Jung, S. et al. In vivo depletion of CD11c+ dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8+ T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity 17, 211–220 (2002).
Takeda, S., Rodewald, H.R., Arakawa, H., Bluethmann, H. & Shimizu, T. MHC class II molecules are not required for survival of newly generated CD4+ T cells, but affect their long-term life span. Immunity 5, 217–228 (1996).
Boursalian, T.E. & Bottomly, K. Survival of naive CD4 T cells: roles of restricting versus selecting MHC class II and cytokine milieu. J. Immunol. 162, 3795–3801 (1999).
Kieper, W.C., Burghardt, J.T. & Surh, C.D. A role for TCR affinity in regulating naive T cell homeostasis. J. Immunol. 172, 40–44 (2004).
Labrecque, N. et al. How much TCR does a T cell need? Immunity 15, 71–82 (2001).
Fry, T.J. et al. Flt3 ligand enhances thymic-dependent and thymic-independent immune reconstitution. Blood 104, 2794–2800 (2004).
Tan, J.T. et al. IL-7 is critical for homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8732–8737 (2001).
Moniuszko, M. et al. Recombinant interleukin-7 induces proliferation of naive macaque CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in vivo. J. Virol. 78, 9740–9749 (2004).
de Saint-Vis, B. et al. The cytokine profile expressed by human dendritic cells is dependent on cell subtype and mode of activation. J. Immunol. 160, 1666–1676 (1998).
Sorg, R.V., McLellan, A.D., Hock, B.D., Fearnley, D.B. & Hart, D.N. Human dendritic cells express functional interleukin-7. Immunobiology 198, 514–526 (1998).
Harnaha, J. et al. Interleukin-7 is a survival factor for CD4+ CD25+ T-cells and is expressed by diabetes-suppressive dendritic cells. Diabetes 55, 158–170 (2006).
Mackall, C.L. et al. Distinctions between CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell regenerative pathways result in prolonged T-cell subset imbalance after intensive chemotherapy. Blood 89, 3700–3707 (1997).
Dion, M.L. et al. Slow disease progression and robust therapy-mediated CD4+ T-cell recovery are associated with efficient thymopoiesis during HIV-1 infection. Blood 109, 2912–2920 (2007).
Yao, Y. et al. ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways negatively regulate CIITA gene expression in dendritic cells and macrophages. J. Immunol. 177, 70–76 (2006).
Crawley, J.B. et al. T cell proliferation in response to interleukins 2 and 7 requires p38MAP kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 15023–15027 (1997).
Moschella, F. et al. Transcript profiling of human dendritic cells maturation-induced under defined culture conditions: comparison of the effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha, soluble CD40 ligand trimer and interferon gamma. Br. J. Haematol. 114, 444–457 (2001).
Vasir, B. et al. Dendritic cells induce MUC1 expression and polarization on human T cells by an IL-7-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 174, 2376–2386 (2005).
Fluur, C. et al. Potential role for IL-7 in Fas-mediated T cell apoptosis during HIV infection. J. Immunol. 178, 5340–5350 (2007).
Killian, M.S., Fujimura, S.H., Hecht, F.M. & Levy, J.A. Similar changes in plasmacytoid dendritic cell and CD4 T-cell counts during primary HIV-1 infection and treatment. AIDS 20, 1247–1252 (2006).
Giraud, S. et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cell reconstitution following bone marrow transplantation: subnormal recovery and functional deficit of IFN-α/β production in response to herpes simplex virus. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 25, 135–143 (2005).
Mohty, M. et al. Impact of plasmacytoid dendritic cells on outcome after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 19, 1–6 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank V. Kapoor and N. Voong for flow cytometry expertise; M.A. Caligiuri (Ohio State University) for Flt3 ligand; S. Durum (National Cancer Institute) for Rag1−/−Il7−/− mice; and S. Durum, A. Singer and R. Gress for review of the manuscript. Supported by the Intramural Program of the National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.G. did most of the experiments, contributed to experimental design and wrote the manuscript; R.G.V., D.J.G. and R.D.M. did experiments; H.Z. did experiments and provided intellectual input; Y.C. did experiments, generated Stat5a−/−Stat5b−/− mice and provided intellectual and technical input; S.Y.K. provided technical support for immunofluorescence studies; R.N. bred and genotyped Stat5a+/−Stat5b+/− mice and provided fetal livers; L.H. provided Stat5a+/−Stat5b+/− mice and intellectual input; P.M. provided intellectual input and transgenic mice; B.E. provided intellectual input and generated and provided GFP–IL-7Rα mice; M.S.M. did experiments and provided intellectual input; and C.L.M. provided intellectual input and research support and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 127 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guimond, M., Veenstra, R., Grindler, D. et al. Interleukin 7 signaling in dendritic cells regulates the homeostatic proliferation and niche size of CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 10, 149–157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1695
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1695
This article is cited by
-
Immune subset-committed proliferating cells populate the human foetal intestine throughout the second trimester of gestation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Age-associated phenotypic imbalance in TCD4 and TCD8 cell subsets: comparison between healthy aged, smokers, COPD patients and young adults
Immunity & Ageing (2022)
-
The role of interleukin‑7 serum level as biological marker in breast cancer: a cross‑sectional, observational, and analytical study
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2022)
-
Selective dependence on IL-7 for antigen-specific CD8 T cell responses during airway influenza infection
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Temporal progression of gene regulation of peripheral white blood cells explains gender dimorphism of critically ill patients after trauma
Molecular Medicine (2019)