Abstract
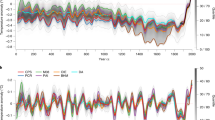
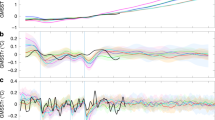
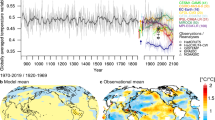
The climate of the past millennium was marked by substantial decadal and centennial scale variability in the Northern Hemisphere1. Low solar activity has been linked to cooling during the Little Ice Age (AD 1450–1850; ref. 1) and there may have been solar forcing of regional warmth during the Medieval Climate Anomaly2,3,4,5 (AD 950–1250; ref. 1). The amplitude of the associated changes is, however, poorly constrained5,6, with estimates of solar forcing spanning almost an order of magnitude7,8,9. Numerical simulations tentatively indicate that a small amplitude best agrees with available temperature reconstructions10,11,12,13. Here we compare the climatic fingerprints of high and low solar forcing derived from model simulations with an ensemble of surface air temperature reconstructions14 for the past millennium. Our methodology15 also accounts for internal climate variability and other external drivers such as volcanic eruptions, as well as uncertainties in the proxy reconstructions and model output. We find that neither a high magnitude of solar forcing nor a strong climate effect of that forcing agree with the temperature reconstructions. We instead conclude that solar forcing probably had a minor effect on Northern Hemisphere climate over the past 1,000 years, while, volcanic eruptions and changes in greenhouse gas concentrations seem to be the most important influence over this period.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 January 2014
In the version of this Letter originally published, 'seventh and early ninth century' in the second paragraph should have read 'seventeenth and early nineteenth centuries'. Additionally, there were errors in Fig. 1. These errors have now been corrected in all versions of the Letter.
References
Masson-Delmotte, V. et al. in IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis (eds Stocker, T. F. D. et al.) (Cambridge Univ. Press, in the press).
Eddy, J. A. Maunder minimum. Science 192, 1189–1202 (1976).
Swingedouw, D. et al. Natural forcing of climate during the last millennium: Fingerprint of solar variability. Clim. Dynam. 36, 1349–1364 (2011).
Van Hateren, J. H. A fractal climate response function can simulate global average temperature trends of the modern era and the past millennium. Clim. Dynam. 40, 2651–2670 (2012).
Gray, L. J. et al. Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 48, RG4001 (2010).
Schmidt, G. A. et al. Climate forcing reconstructions for use in PMIP simulations of the last millennium (v1.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 5, 185–191 (2012).
Shapiro, A. I. et al. A new approach to the long-term reconstruction of the solar irradiance leads to large historical solar forcing. Astron. Astrophys. 529, A67 (2011).
Steinhilber, F., Beer, J. & Fröhlich, C. Total solar irradiance during the Holocene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L19704 (2009).
Wang, Y-M., Lean, J. L. & Sheeley, N. R. Modeling the Sun’s magnetic field and irradiance since 1713. Astrophys. J. 625, 522–538 (2005).
Ammann, C. et al. Solar influence on climate during the past millennium: Results from transient simulations with the NCAR Climate System Model. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 3713–3718 (2007).
Jungclaus, J. H. et al. Climate and carbon-cycle variability over the last Millennium. Clim. Past Discuss. 6, 1009–1044 (2010).
Feulner, G. Are the most recent estimates for Maunder Minimum solar irradiance in agreement with temperature reconstructions? Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L16706 (2011).
Hind, A. & Moberg, A. Past millennial solar forcing magnitude. Clim. Dynam. 41, 2527–2537 (2012).
Frank, D. C. et al. Ensemble reconstruction constraints on the global carbon cycle sensitivity to climate. Nature 463, 527–530 (2010).
Allen, M. R. & Stott, P. A. Estimating signal amplitudes in optimal fingerprinting, Part I: Theory. Clim. Dynam. 21, 477–491 (2003).
Stott, P. A., Jones, G. S. & Mitchell, J. F. B. Do models underestimate the solar contribution to recent climate change? J. Clim. 16, 4079–4093 (2003).
Benestad, R. E. & Schmidt, G. A. Solar trends and global warming. J. Geophys. Res. 114 (2009).
Hegerl, G. C. et al. Detection of human influence on a new 1500 yr climate reconstruction. J. Clim. 20, 650–666 (2007).
Hegerl, G. et al. Influence of human and natural forcing on European seasonal temperatures. Nature Geosci. 4, 99–103 (2011).
Gordon, C. et al. The simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments. Clim. Dynam. 16, 147–168 (2000).
Tett, S. F. B. et al. The impact of natural and anthropogenic forcings on climate and hydrology since 1550. Clim. Dynam. 28, 3–34 (2007).
Crowley, T. J. et al. Volcanism and the little ice age. PAGES News 16, 22–23 (2008).
Pongratz, J., Reick, C., Raddatz, T. & Claussen, M. A reconstruction of global agricultural areas and land cover for the last millennium. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 22, GB3018 (2008).
Morice, C. P., Kennedy, J. J., Rayner, N. A. & Jones, P. D. Quantifying uncertainties in global and regional temperature change using an ensemble of observational estimates: The HadCRUT4 data set. J. Geophys. Res. 117, D0810 (2012).
Schurer, A. P., Hegerl, G. C., Mann, M. E., Tett, S. F. B. & Phipps, S. J. Separating forced from chaotic climate variability over the past millennium. J. Clim. 26, 6954–6973 (2013).
Timmreck, C. et al. Limited temperature response to the very large AD 1258 volcanic eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L21708 (2009).
Mann, M. E., Fuentes, J. D. & Rutherford, S. Underestimation of volcanic cooling in tree-ring-based reconstructions of hemispheric temperatures. Nature Geosci. 5, 202–205 (2012).
Anchukaitis, K. et al. Tree rings and volcanic cooling. Nature Geosci. 5, 836–837 (2012).
Woollings, T., Lockwood, M., Masato, G., Bell, C. & Gray, L. Enhanced signature of solar variability in Eurasian winter climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L20805 (2010).
Shindell, D. T., Faluvegi, G., Miller, R. L., Schmidt, G. A., Hansen, J. E. & Sun, S. Solar and anthropogenic forcing of tropical hydrology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L24706 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by NERC grant NE/G019819/1. We acknowledge CMIP5 and PMIP3 and we thank the climate modelling groups (listed in Supplementary Section 5) for producing and making available their model output, G. Jones for making a long HadCM3 control simulation available for our use, D. Frank for making his reconstructions available, for providing code to carry out the cubic spine smoothing and for several helpful comments and M. Williams, J. Pongratz and T. Crowley for advice in forcing implementation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.P.S. and S.F.B.T. set up and carried out the simulations. A.P.S. and G.C.H. carried out the fingerprinting analysis. All contributed to the writing and the design of modelling and analysis strategy.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 2713 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schurer, A., Tett, S. & Hegerl, G. Small influence of solar variability on climate over the past millennium. Nature Geosci 7, 104–108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2040
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2040
This article is cited by
-
Trends and variability in the Southern Annular Mode over the Common Era
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Climatic controls on the survival and loss of ancient types of barley on North Atlantic Islands
Climatic Change (2023)
-
Recent weakening of seasonal temperature difference in East Asia beyond the historical range of variability since the 14th century
Science China Earth Sciences (2023)
-
Quantitative attribution of Northern Hemisphere temperatures over the past 2000 years
Frontiers of Earth Science (2023)
-
Tropical volcanoes synchronize eastern Canada with Northern Hemisphere millennial temperature variability
Nature Communications (2022)