Abstract
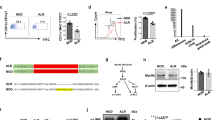
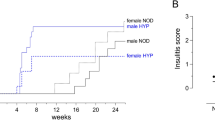
The autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, IDDM) has a multifactorial etiology. So far, the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is the only major susceptibility locus that has been identified for this disease1 and its animal models2,3. The Komeda diabetes-prone (KDP) rat is a spontaneous animal model of human type 1 diabetes4 in which the major susceptibility locus Iddm/kdp1 accounts, in combination with MHC, for most of the genetic predisposition to diabetes5. Here we report the positional cloning of Iddm/kdp1 and identify a nonsense mutation in Cblb, a member of the Cbl/Sli family of ubiquitin-protein ligases6,7. Lymphocytes of the KDP rat infiltrate into pancreatic islets and several tissues including thyroid gland and kidney, indicating autoimmunity. Similar findings in Cblb-deficient mice are caused by enhanced T-cell activation8,9. Transgenic complementation with wildtype Cblb significantly suppresses development of the KDP phenotype. Thus, Cblb functions as a negative regulator of autoimmunity and Cblb is a major susceptibility gene for type 1 diabetes in the rat. Impairment of the Cblb signaling pathway may contribute to human autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Davies, J.L. et al. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature 371, 130–136 (1994).
Wicker, L.S., Todd, J.A. & Peterson, L.B. Genetic control of autoimmune diabetes in the NOD mouse. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 179–200 (1995).
Jacob, H.J. et al. Genetic dissection of autoimmune type I diabetes in the BB rat. Nature Genet. 2, 56–60 (1992).
Komeda, K. et al. Establishment of two substrains, diabetes-prone and non-diabetic, from Long-Evans Tokushima Lean (LETL) rats. Endocr. J. 45, 737–744 (1998).
Yokoi, N. et al. A non-MHC locus essential for autoimmune type I diabetes in the Komeda diabetes-prone rat. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 2015–2021 (1997).
Keane, M.M., Rivero-Lezcano, O.M., Mitchell, J.A., Robbins, K.C. & Lipkowitz, S. Cloning and characterization of Cblb: a SH3 binding protein with homology to the c-cbl proto-oncogene. Oncogene 10, 2367–2377 (1995).
Joazeiro, C.A.P. et al. The tyrosine kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science 286, 309–312 (1999).
Bachmaier, K. et al. Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cblb. Nature 403, 211–216 (2000).
Chiang, Y.J. et al. Cblb regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 403, 216–220 (2000).
Kawano, K. et al. New inbred strain of Long-Evans Tokushima Lean rats with IDDM without lymphopenia. Diabetes 40, 1375–1381 (1991).
Bowen, M.A. et al. Cloning, mapping, and characterization of activated leukocyte-cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), a CD6 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 181, 2213–2220 (1995).
Ellerman, K.E. & Like, A.A. Susceptibility to diabetes is widely distributed in normal class IIu haplotype rats. Diabetologia 43, 890–898 (2000).
Nepom, G. & Kwok, W. Molecular basis for HLA-DQ associations with IDDM. Diabetes 47, 1177–1184 (1998).
Janeway, C.A. Jr. & Bottomly, K. Signals and signs for lymphocyte responses. Cell 76, 275–285 (1994).
Schwartz, R.H. Models of T-cell anergy: is there a common molecular mechanism? J. Exp. Med. 184, 1–8 (1996).
Krawczyk, C. et al. Cblb is a negative regulator of receptor clustering and raft aggregation in T cells. Immunity 13, 463–473 (2000).
Bustelo, X.R., Crespo, P., Lopez-Barahona, M., Gutkind, J.S. & Barbacid, M. Cblb, a member of the Sli-1/c-Cbl protein family, inhibits Vav-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. Oncogene 15, 2511–2520 (1997).
Chikuba, N. et al. Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus with coexisting autoimmune thyroid disease in Japan. Intern. Med. 31, 1076–1080 (1992).
Lorini, R., d'Annunzio, G., Vitali, L. & Scaramuzza, A. IDDM and autoimmune thyroid disease in the pediatric age group. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 9, 89–94 (1996).
Shinkura, R. et al. Alymphoplasia is caused by a point mutation in the mouse gene encoding Nf-kb-inducing kinase. Nature Genet. 22, 74–77 (1999).
Nishi, M., Ishida, Y. & Honjo, T. Expression of functional interleukin-2 receptors in human light chain/Tac transgenic mice. Nature 331, 267–269 (1988).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Miki, Z. Cui and T. Kuramoto for support and advice; M. Namae for help with animal breeding; and T. Hirata, E. Okiyama, M. Fuse, A. Hara, R. Yanobu, S. Kaji, K. Kobayashi, and R. Yagi for technical assistance. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Creative Basic Research, for Scientific Research on Priority Areas and for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, by Scientific Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, and by grants from Novo Nordisk Pharma (S.S.), and Takeda Science Foundation (N.Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoi, N., Komeda, K., Wang, HY. et al. Cblb is a major susceptibility gene for rat type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet 31, 391–394 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng927
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng927
This article is cited by
-
Current advancement in the preclinical models used for the assessment of diabetic neuropathy
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2023)
-
The RING finger protein family in health and disease
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Experimental animal models for diabetes and its related complications—a review
Laboratory Animal Research (2021)
-
Signature RNAS and related regulatory roles in type 1 diabetes mellitus based on competing endogenous RNA regulatory network analysis
BMC Medical Genomics (2021)
-
Rat models of human diseases and related phenotypes: a systematic inventory of the causative genes
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)